Problem 1. Here are a couple of math review problems for you to work through.
a. Suppose you are given the two points (X, Y) = (10, 15) and (12, 20) and are told that these two points sit on a straight line. Write an equation in slope-intercept form for this line and then identify the y-intercept, the x-intercept, and the slope of this line. Also, write the equation in x-intercept form.
b. Now, suppose that you are given two new points that sit to the right of the line described in (a) and you are told that at every y-value the x-value is now 3 units higher than the initial x-value. Given the two points described in (a), what are the coordinates (X, Y) for these two new points?
c. Given the information in (a) and (b) write the equation for the second line in slope-intercept form and the equation for the second line in x-intercept form. Is one of these equations easier to find than the other? Explain your answer.
d. Now, suppose that you are given two new points on a third line that sit to the right of the line described in (a) and you are told that at every x-value the y-value is now 3 units lower than the initial y-value. Given the two points described in (a), what are the coordinates (X, Y) for these two new points?
e. Suppose you are given the following graph.
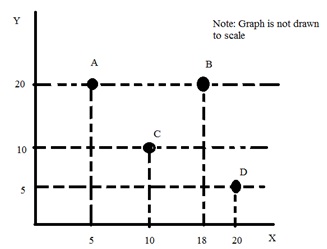
i. Is it possible that points A, C and D all sit on the same straight line? Provide an explanation to support your answer.
ii. Write an equation for a straight line that contains points A and D in y-intercept form.
iii. Write an equation for a straight line that contains points C and B in y-intercept form.
iv. What is the y-intercept of a straight line that contains points B and D? Show your work. Hint: the numbers get ugly, so just give a close approximation.
Problem 2. Suppose you are comparing prices while shopping online. You look at two websites: on both websites the list price for the product you want to buy is the same. On website A the product is offered at a 20% discount but you are told you will need to pay a $5 flat shipping fee and this shipping fee cannot be discounted. On website B the product is offered at the list price, but with free shipping.
a. At what price, are these two offers identical? Show how you found your answer.
b. Is there ever a situation where you should choose to purchase this product from website A? Explain your reasoning.
c. Is there ever a situation where you should choose to purchase this product from website B? Explain your reasoning.
Problem 3. Suppose the PPF for Smallia is given by the equation Y = 4M – (1/2)X where Y is the number of machines that are produced during the current time period, X is the number of units of consumer goods that are produced (and consumed) during the current time period, and M is the number of machines that Smallia has at the beginning of the time period. All of the X good that is produced in a given period of time is consumed in that same period of time, while all of the Y good that is produced in a given period of time is then available in subsequent periods of time and therefore the level of M in the next time period changes as the level of Y production in this time period changes. Assume that once machines are produced, that they last forever. Currently at the beginning of this time period Smallia has one machine.
a. Given the above information, construct the PPF for Smallia in this time period measuring Y, the number of machines produced this period, on the y-axis and X, the number of units of consumer goods that are produced this period, on the x-axis. To find this PPF you will want to use the provided equation and the initial amount of M.
b. Suppose that this year (the initial period of time) Smallia decides to produce and consume 6 units of consumer goods. Given this information, how many machines will Smallia be able to produce this year if they are efficient? At the end of this year how many machines will Smallia have? Show how you found your answer.
c. Given your answer in (b), draw a new graph that illustrates Smallia’s PPF for this year and for next year given that this year Smallia has decided to produce 6 units of consumer goods.
d. Suppose that instead of producing and consuming 6 units of consumer goods this year, Smallia could decide to produce and consume 5 units of consumer goods this year. Construct a graph that illustrates the initial PPF, the PPF for next year if Smallia consumes 6 units of consumer goods this year, and the PPF for next year if Smallia consumes 5 units of consumer goods this year. How does their consumption decision impact their future consumption decisions?
Problem 4. Consider two countries, East and West. Both of these countries produce cars and food and both of these countries have linear production possibility frontiers. You are told that the countries have the same level of labor resources and that labor is the only input used in producing these goods. You are also provided with the following table:
Units of Labor needed to Produce Units of Labor needed to Produce
1 Car 1 unit of Food
East 2 units of labor 1 unit of labor
West 3 units of labor 4 units of labor
a. Suppose that East and West both possess 60 units of labor. Construct their production possibility frontiers given this information. Provide a separate graph for each country and measure units of food on the x-axis and cars on the y-axis. Label your graphs carefully and completely. In your graphs provide the numeric values for each intercept.
b. What would happen to East’s PPF if the amount of labor East had increased to 90 units? Describe verbally the effect of this change on East’s PPF.
c. Suppose that East and West both have 60 units of labor available but that East has recently discovered a new technology that allows East to produce twice as many cars from its available labor. This technology does not impact East’s ability to produce food. Draw a graph illustrating East’s new PPF given this technological change.
d. Given the scenario described in (a), who has the comparative advantage in producing cars? Explain your answer.
e. Given the scenario described in (a), what is the range of trading prices measured in cars for 10 units of food?
f. Given the scenario described in (a), draw the joint PPF for East and West measuring cars on the vertical axis and units of food on the horizontal axis. Provide numeric values for all intercepts and all kink points.