Assignment:
Multiple Choice
Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
1. Economists normally assume that the goal of a firm is to
(i) make profit as large as possible even if it means reducing output.
(ii) make profit as large as possible even if it means incurring a higher total cost.
(iii) make revenue as large as possible.
a. (i) and (ii)
b. (i) and (iii)
c. (ii) and (iii)
d. None of the above are correct.
2. XYZ corporation produced 300 units of output but sold only 275 of the units it produced. The average cost of production for each unit of output produced was $100. Each of the 275 units sold was sold for a price of $95. Total revenue for the XYZ corporation would be
a. -$3,875.
b. $26,125.
c. $28,500.
d. $30,000.
3. A firm's opportunity costs of production amount to its
a. explicit costs only.
b. implicit costs only.
c. explicit costs + implicit costs.
d. explicit costs + implicit costs + total revenue.
The curves below reflect information about the cost structure of a firm. Use the figure to answer the following questions.
Figure 13-5.
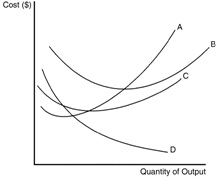
4. Refer to Figure 13-5. Which of the curves is most likely to represent average total cost?
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
5. Refer to Figure 13-5. Which of the curves is most likely to represent average fixed cost?
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
6. Refer to Figure 13-5. Which of the curves is most likely to represent average variable cost?
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
7. Refer to Figure 13-5. Which of the curves is most likely to represent marginal cost?
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
8. Refer to Figure 13-5. This particular firm is necessarily experiencing increasing marginal product when curve
a. A is falling.
b. B is falling.
c. C is falling.
d. D is falling.
9. Refer to Figure 13-5. This particular firm is necessarily experiencing diminishing marginal product when curve
(i) A is rising.
(ii) B is rising.
(iii) C is rising.
a. (i) only
b. (iii) only
c. (i) and (ii)
d. All of the above are correct.
10. Refer to Figure 13-5. Curve A is U-shaped because of
a. diminishing marginal product.
b. increasing marginal product.
c. the fact that increasing marginal product follows decreasing marginal product.
d. the fact that decreasing marginal product follows increasing marginal product.
Use the following information to answer the following questions.
Teacher's Helper is a small company that has a subcontract to produce instructional materials for disabled children in public school districts. The owner rents several small rooms in an office building in the suburbs for $600 a month and has leased computer equipment that costs $480 a month.
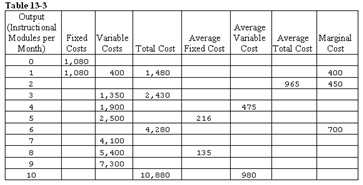
11. Refer to Table 13-3. What is the marginal cost of creating the tenth instructional module in a given month?
a. $900
b. $1,250
c. $2,500
d. $3,060
12. Refer to Table 13-3. What is the average variable cost for the month if six instructional modules are produced?
a. $180
b. $533.33
c. $700
d. $713.33
13. Refer to Table 13-3. What is the average fixed cost for the month if nine instructional modules are produced?
a. $108
b. $120
c. $150
d. $811.11
14. Refer to Table 13-3. How many instructional modules are produced when marginal cost is $1,300?
a. 4
b. 5
c. 7
d. 8
The figure below depicts average total cost functions for a firm that produces automobiles. Use the figure to answer the following questions.
Figure 13-7
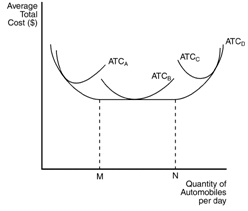
15. Refer to Figure 13-7. Which of the curves is most likely to characterize the short-run average total cost curve of the smallest factory?
a. ATCA
b. ATCB
c. ATCC
d. ATCD
16. Refer to Figure 13-7. Which curve represents the long-run average total cost?
a. ATCA
b. ATCB
c. ATCC
d. ATCD
17. Refer to Figure 13-7. In the long run, the firm can operate on which of the following average total cost curves?
a. ATCA
b. ATCB
c. ATCC
d. All of the above are correct.
18. Refer to Figure 13-7. This firm experiences diseconomies of scale at what output levels?
a. output levels above N
b. output levels between M and N
c. output levels below M
d. All of the above are correct, if the firm is operating in the long run.
19. Refer to Figure 13-7. At levels of output below M the firm experiences
a. economies of scale.
b. diseconomies of scale.
c. economic profit.
d. accounting profit.
20. In a competitive market, the actions of any single buyer or seller will
a. have a negligible impact on the market price.
b. have little effect on overall production but will ultimately change final product price.
c. cause a noticeable change in overall production and a change in final product price.
d. adversely affect the profitability of more than one firm in the market.
21. When a firm in a competitive market receives $500 in total revenue, it has a marginal revenue of $10. What is the average revenue, and how many units were sold?
a. $5 and 100
b. $10 and 50
c. $10 and 100
d. The answer cannot be determined from the information given.
22. For a competitive firm,
a. Total revenue = Average revenue.
b. Total revenue = Marginal revenue.
c. Total cost = Marginal revenue.
d. Average revenue = Marginal revenue.
23. At the profit-maximizing level of output,
a. marginal revenue = average total cost.
b. marginal revenue = average variable cost.
c. marginal revenue = marginal cost.
d. average revenue = average total cost.
Use the figures below to answer the following questions.
Figure 14-9.
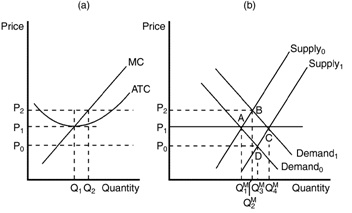
24. Refer to Figure 14-9. When the market is in long-run equilibrium at point A in panel (b), the firm represented in panel (a) will
a. have a zero economic profit.
b. have a negative accounting profit.
c. exit the market.
d. All of the above are correct.
25. Refer to Figure 14-9. An increase in market supply from Supply0 to Supply1 is most likely the result of
a. existing firms changing their cost structure.
b. existing firms in the market increasing their level of production beyond Q1.
c. the entrance of new firms in the market.
d. All of the above are correct.
26. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. A competitive firm is a price maker and a monopoly is a price taker.
b. A competitive firm is a price taker and a monopoly is a price maker.
c. Both competitive firms and monopolies are price takers.
d. Both competitive firms and monopolies are price makers.
27. When a firm's average total cost curve continually declines, the firm is a
a. government-created monopoly.
b. natural monopoly.
c. revenue monopoly.
d. All of the above are correct.
28. The market demand curve for a monopolist is typically
a. unitary elastic at the point of profit maximization.
b. downward sloping.
c. horizontal.
d. vertical.
29. For a profit-maximizing monopolist,
a. P > MR = MC.
b. P = MR = MC.
c. P > MR > MC.
d. MR < MC < P.
The figure below reflects the cost and revenue structure for a monopoly firm. Use it to answer the following questions.
Figure 15-2.
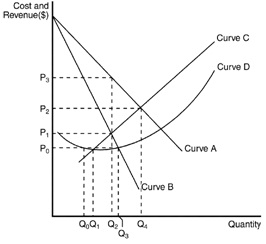
30. Refer to Figure 15-2. The demand curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve
a. A.
b. B.
c. C.
d. D.
31. Refer to Figure 15-2. The marginal revenue curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve
a. A.
b. B.
c. C.
d. D.
32. Refer to Figure 15-2. The marginal cost curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve
a. A.
b. B.
c. C.
d. D.
33. Refer to Figure 15-2. The average total cost curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve
a. A.
b. B.
c. C.
d. D.
34. What is the monopolist's profit under the following conditions? The profit-maximizing price charged for goods produced is $16. The intersection of the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves occurs where output is 10 units and marginal cost is $8. Average total cost for 10 units of output is $6.
a. $20
b. $80
c. $100
d. $160
35. Monopolistic competition is characterized by which of the following attributes?
(i) free entry
(ii) product differentiation
(iii) many sellers
a. (i) and (iii) only
b. (i) and (ii) only
c. (ii) and (iii) only
d. (i), (ii), and (iii)
36. A monopolistically competitive market has characteristics that are similar to
a. a monopoly only.
b. a competitive firm only.
c. both a monopoly and a competitive firm.
d. neither a monopoly nor a competitive firm.
37. Each firm in a monopolistically competitive firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve because
a. there are many other sellers in the market.
b. there are very few other sellers in the market.
c. the firm's product is different from those offered by other firms in the market.
d. that firm faces the threat of entry into the market by new firms.
Figure 16-5
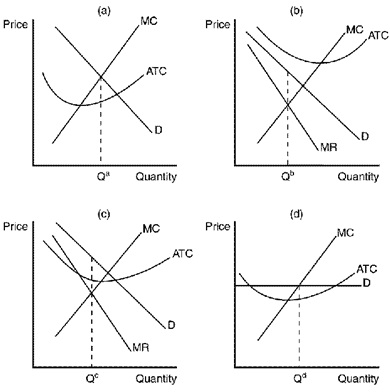
38. Refer to Figure 16-5. Which of the graphs shown would be consistent with a firm in a monopolistically competitive market that is earning a positive profit?
a. panel a
b. panel b
c. panel c
d. panel d
39. Refer to Figure 16-5. Which of the graphs depicts a monopolistically competitive firm in long-run equilibrium?
a. panel a
b. panel b
c. panel c
d. None of the above is correct.
40. Suppose a gardener produces both green beans and corn in her garden. If she must give up 14 bushels of corn to get 5 bushels of green beans, then her opportunity cost of 1 bushel of green beans is
a. 0.36 bushel of corn.
b. 2.8 bushels of corn.
c. 14 bushels of corn.
d. 70 bushels of corn.
41. Which of the following would cause price to increase?
a. an increase in supply
b. a decrease in demand
c. a surplus of the good
d. a shortage of the good
42. What would happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of coffee if the wages of coffee-bean pickers fell and the price of tea fell?
a. Price would fall, and the effect on quantity would be ambiguous.
b. Price would rise, and the effect on quantity would be ambiguous.
c. Quantity would fall, and the effect on price would be ambiguous.
d. Quantity would rise, and the effect on price would be ambiguous.
43. Inefficiency exists in an economy when a good is
a. not being consumed by buyers who value it most highly.
b. not distributed fairly among buyers.
c. not produced because buyers do not value it very highly.
d. being produced with less than all available resources.
44. Inefficiency exists in an economy when a good is
a. being produced with less than all available resources.
b. not distributed fairly among buyers.
c. not being produced by the lowest-cost producers.
d. being consumed by buyers who value it most highly.
Scenario 13-1
Calvin wants to start his own business making candles. He can purchase a candle factory that costs $400,000. Calvin currently has $500,000 in the bank earning 3 percent interest per year.
45. Refer to Scenario 13-1. If Calvin purchases the factory with his own money, what is the annual implicit opportunity cost of purchasing the factory?
a. $0
b. $3,000
c. $12,000
d. $15,000
|
Number of Workers
|
Total Output
|
Marginal Product
|
|
0
|
0
|
--
|
|
1
|
200
|
|
|
2
|
450
|
|
|
3
|
600
|
|
|
4
|
650
|
|
46. Refer to Table 13-2. What is the marginal product of the first worker?
a. 250 units
b. 200 units
c. 150 units
d. 50 units
47. Refer to Table 13-2. What is the marginal product of the second worker?
a. 250 units
b. 200 units
c. 150 units
d. 50 units
48. Refer to Table 13-2. What is the marginal product of the fourth worker?
a. 250 units
b. 200 units
c. 150 units
d. 50 units
49. Refer to Table 13-2. At which number of workers does diminishing marginal product begin?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
50. When adding another unit of labor leads to an increase in output that is smaller than the increases in output that resulted from adding previous units of labor, the firm is experiencing
a. diminishing labor.
b. diminishing output.
c. diminishing marginal product.
d. negative marginal product.