Question 1. Which of the following statements are positive statements?
I. The government should try to actively reduce unemployment.
II. Reducing the budget deficit will help to promote economic growth.
III. Reducing unemployment will help to promote economic growth.
a. II
b. III
c. I and II
d. I and III
e. II and III
Question 2. During the recent financial crisis, many economists disagreed about whether or not the government bailout was a good idea. Economist A supports a bailout “to reduce strain on the credit markets and facilitate borrowing and lending in the economy”. However, economist B opposes the bailout because “it provides a safety-net and incentives for financial institutions to still engage in risky behavior”. Why do these economists disagree?
a. Economist A is making a normative statement, while economist B is making a positive one.
b. Economist A is making a positive statement, while economist B is making a normative one.
c. Both economists are making normative statements, but have different values about what they want economic policy to achieve.
d. Both economists are making positive statements, but are focusing on different effects of the economic policy.
e. They don’t know what they’re talking about.
Question 3. You have the following information about two economists. Economist A examines how a tax cut affects the housing market. Economist B examines how a tax cut affects the level of GDP.
a. Economist A is the macro-economist.
b. Economist B is the macro-economist.
c. They are both micro-economists.
d. They are both macro-economists.
Question 4. Data on literacy rates for all countries in 2011 is:
a. Cross-sectional data
b. Time-series data
Question 5. An economist is analyzing whether a job-training workshop for out of work individuals will help reduce unemployment. He conducts an experiment with 100 individuals who have volunteered to attend the workshop and finds that 80% of them were employed within the following year, and thus he believes that the job-training workshop is a success. However, his adviser cautions him that there might a problem with his data. This problem is most likely:
a. Measurement error in collecting data
b. A non-random sample of data
Use the following information for the next four (4) questions about the USED car market.
Consider the market for used cars in Madison. Suppose the domestic demand curve for used cars in Madison is given by Q = 10000-P and the domestic supply curve for used cars in Madison is given by Q=P-1000.
Assume that the market for used cars in Madison is a closed economy for the next two (2) questions.
Question 6. Which of the following statements is correct about the used car market in Madison given that it is a closed economy?
a. Consumer surplus is larger than producer surplus.
b. Consumer surplus is smaller than producer surplus.
c. Consumer surplus is equal to producer surplus.
d. We do not know whether consumer surplus is larger than producer surplus or not.
Question 7. Suppose the price of new cars is increasing because of an increase in the global price of steel. At the same time, the government implements an excise tax that sellers must pay when they sell a used car. Which of the following statements about the used car market in Madison is true for sure?
a. Both the trading price and trading volume will increase.
b. The trading price will increase but the trading volume is indeterminate.
c. The trading volume will increase but the trading price is indeterminate.
d. The trading price will increase while the trading volume will decrease.
Suppose now Madison opens its used car market to world trade. The world price of a used car is $4000. Use this information for the next two (2) questions. Assume that the domestic demand and domestic supply curves for used cars in Madison are the initial ones and that there is no impact on these curves from the new car market and that there is no excise tax.
Question 8. How many used cars will be imported into Madison?
a. 500 used cars
b. 1000 used cars
c. 2000 used cars
d. 3000 used cars
Question 9. Suppose the government wants to impose a tariff to reduce the amount of imported cars by 1000. Which of the following tariffs should the government choose?
a. $100 per car
b. $500 per car
c. $1000 per car
d. $1500 per car
Question 10. Anna wants to go skiing at Devils Head Resort this weekend. News from the Onion says that Devils Head will attract more skiers because of the fresh snow this Wednesday. Also, an interview with the manager of Devils Head says that the fresh snow reduces the maintenance cost. Assume the price of skiing at Devils Head is very flexible and always equates the downward sloping demand curve and upward sloping supply curve. Given this information, which of the following statements is true?
a. The price of skiing will go down and there will be more people skiing.
b. The price of skiing will go up and there will be more people skiing.
c. There will be more people skiing but the price of skiing is indeterminate.
d. The price of skiing will go up but the number of people skiing is indeterminate.
Use the following information about the Madison labor market for the next two (2) questions.
Consider the Madison labor market. The demand curve is given by Q = 50 - P and the supply curve is given by Q = 4P - 5, where P is the hourly wage measured in dollars and Q is the average work hours per week.
11. What’s the equilibrium price and quantity of this market?
a. P = $10, Q = 40
b. P = $11, Q = 39
c. P = $12, Q = 40
d. P = $10, Q = 35
Question 12. If the government sets the minimum wage to be $15 per hour, the average work hours per week will
a. Decrease by 4 hours per week
b. Increase by 4 hours per week
c. Decrease by 5 hours per week
d. Increase by 16 hours per week
Question 13. The opportunity cost of a choice is the
a. cost associated with making a choice.
b. value of the next best alternative which was not chosen.
c. amount paid to purchase whatever is chosen.
d. value of all the foregone alternatives not chosen.
Question 14. Which of the following would shift the production possibilities curve from curve "W" to curve "R"?
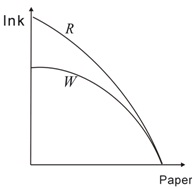
a. An improvement in widely available technology
b. An improvement in the technology for producing paper
c. An improvement in the technology for producing ink
d. People demand more ink
Use the following graph to answer the next three (3) questions.
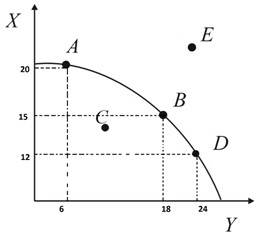
Question 15. The above figure shows the PPF for a country that produces both X and Y. Between points B and D, the opportunity cost of one Y is:
a. 3 Xs
b. 2 Xs
c. 1/2 Xs
d. 1 Xs
Question 16. Which of the following is definitely attainable for the country given ONLY the information from the above graph.
a. 13 Xs and24 Ys.
b. 16 Xs and 19 Ys.
c. 12.5 Xs and 25 Ys.
d. 19 Xs and 6 Ys.
Question 17. Which of the following is TRUE given ONLY the information from the above graph?
a. It is possible for the country to produce at point E.
b. At point A, the country is under-utilizing its resources.
c. As the country produces more and more Xs, it must give up an increasing amount of Ys.
d. It would be much better for this country to produce at point B than at point D.
Use the following information to answer the next two (2) questions.
The linear production possibility curves for 2 countries are shown in the following figure. Assume that both countries only produce butter and cloth. Use the figure to answer the following two questions.
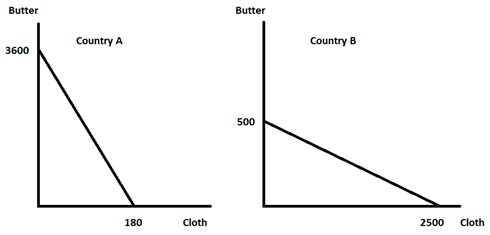
Question 18. Which country has the comparative advantage in producing Cloth?
a. Country A
b. Country B
Question 19. Which of the following trades would be beneficial to both countries?
I. Country A trades 10 butter to Country B for 1 cloth
II. Country B trades 10 butter to Country A for 1 cloth
III. Country A trades 5 butter to Country B for 1 cloth
a. I
b. II
c. III
d. I and III
e. II and III
Question 20. Given the following list of information, we can calculate GDP as __________ .
|
Consumption
|
$300,000
|
|
Financial Investment (Stocks & Bonds)
|
$200,000
|
|
Capital Investment
|
$85,000
|
|
Government Transfer Payments (Medicare & Medicaid)
|
$35,000
|
|
Taxes
|
$15,000
|
|
Imports
|
$80,000
|
|
Exports
|
$20,000
|
|
Government Expenditures
|
$165,000
|
|
Interest Payments on Government Debt
|
$25,000
|
a. $450,000
b. $460,000
c. $470,000
d. $480,000
e. $490,000
Question 21. Which of the following would not be included in United States GDP?
a. Vegetables you grow in a community garden that you eat
b. Computers produced by Dell in their factory in Japan, but that are shipped to the United States
c. A haircut at a salon in Madison
d. Answers (A) and (B) would not be included in United States GDP
e. Answers (A), (B), and (C) would not be included in United States GDP
Use the following table for the next question.
Year Real GDP
2009 $10 trillion
2010 $8 trillion
2011 $8.8 trillion
Question 22. What is the growth rate for real GDP between 2009 and 2010?
a. -20%
b. -25%
c. 20%
d. 25%
e. None of the above
Question 23. Why can GDP per capita be a poor measure of the standard of living in a country?
a. It ignores the distribution of income within a country
b. It doesn't control for the size of the population
c. GDP only measures production, it doesn't give a measure of income
d. Answers (B) and (C) are both correct answers.
Question 24. Consider a country that had modest GDP growth between 2009 and 2010. Additionally, the population for this country also grew between 2009 and 2010. Is it possible that GDP per capita could have fallen between 2009 and 2010?
a. Yes
b. No