Response to the following multiple choice questions:
Part:1
1. Recall from your reading about the nature of volcanoes to choose the best answer: A volcanic eruption is driven by __________ and __________ which forces its way upward and may ultimately break though zones of weaknesses in the Earth's crust.
heat; water pressure
heat; gas pressure
buoyancy; gas pressure
buoyancy; water pressure
2. Recall from your reading about the nature of volcanoes to choose the best answer: Which type of basaltic lava flow has a fairly smooth, unfragmented, ropy surface?
Aa
Pahoehoe
Pumice
Scoria
3. Recall from your reading about the nature of volcanoes to choose the best answer: Magma tends to rise toward Earth's surface principally because __________.
of magma cooling
mounting pressure within the reservoir
rocks become more dense when they melt
of convection in the mantle
4. Recall from your reading about the principle types of volcanoes to choose the best answer: Crater Lake, a caldera, formed from the collapse of a __________.
composite volcano.
shield volcano.
cinder volcano.
lava dome
5. Due to the nature of volcanoes the violent separation of gas from lava forms __________.
dikes
craters
cinders
pumice
6. Recall your reading of Relative Time Scale and Radiometric Time Scale and match the term with the definition.
Isotopes
Half-life
Carbon 14
Igneous rocks
Hutton
Petrology
Index fossil
Stratigraphy
A. Atoms of the same element with differing atomic weights
B. Rocks that generally do not contain fossils
C. The Scottish geologist who first proposed the fundamental principle used to classify rocks according to their relative ages
D. Forms of life which existed during limited periods of geologic time and thus are used as guides to the age of the rocks in which they are preserved
E. Studies on the origins of the various kinds of rocks
F. The time it takes for one-half of a particular radioactive isotope in a sample to decay
G. Studies of rock layering
H. Isotope found in all living plants and animals
7. Recall from your reading of Principal Types of Volcanoes, and match the description to the type of volcano.
Large, fairly steep-sided cones composed of alternating layers of lava flows and pyroclastic material.
Small basaltic cones built during one, short, eruptive episode; dominated by cinders.
Volcanoes of southwestern Alaska and the Aleutian Islands.
Big volcanoes of Hawaii
Volcano Paricutin in Mexico
Forms dikes from lava
Lava is produced after the eruption and flows from the bottom
Volcanoes with gentle slopes spreading over large areas
A. Shield volcanoes
B. Cinder cones
C. Composite/stratovolcanoes
8. Recall from your reading about the radiometric time scale to put the following isotopes in order of use, from oldest rock to youngest.
Carbon-14
Potassium-40
Samarium-147
Thorium-232
Uranium-235
Uranium-238
Rubidium-87
9. According to the figure below, give an approximate age for the Dakota Sandstone and for the Wasatch Formation. Explain what evidence you used to determine this
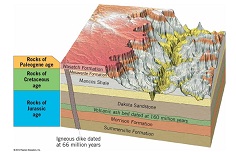
10. Recall from reading the nature of volcanoes, and in your own words, briefly discuss how the rate of cooling determines the type of rock that forms from magma/lava.
11. Recall from your reading about the nature of volcanoes, and in your own words, compare and contrast aa and pahoehoe lava in appearance and how they form.
12. In your own words, discuss volcanic hazards. Although commonly thought to be associated with most volcanic eruptions (by the general public), lava is rarely responsible for the loss of life. Which hazards would tend to be more deadly? Finally, indicate and discuss those hazards that are a direct result of a volcanic eruption as well as those hazards that are indirectly linked. (Hint: think of "indirectly associated" hazards as "side effects".).
Your response should be at least 200 words in length.
Part:2
1. When did the San Andreas Fault appear?
28 million years ago
50 million years ago
28,000 years ago
50,000 years ago
2. What unlikely feature formed along the fault scarps of Central California?
The Salton Sea
Wallace Creek
Sag ponds
Pinnacle National Park
3. In which direction does Wallace Creeks offset?
Northwest
Southwest
Southeast
Northeast
4. The Pacific Plate is comprised of:
only continental lithosphere.
only oceanic lithosphere.
mostly oceanic lithosphere with some continental lithosphere.
mostly continental lithosphere with some oceanic lithosphere.
5. What is an example of this plate movement?
The separation of California and Baja California
Rocks of Pinnacles National Park match those of Antelope Valley, nearly 200 miles away
The northward flow of rivers along the San Andreas fault
The Salton Sea
6. Why do mountains form around Big Bend?
Magma surfaces when the San Andreas Fault creeps.
The bend in the fault causes this area to be bound, squeezed, and uplifted.
The fault is raised here.
Fault creep creates pressure, causing uplift.
7. When was the last big Earthquake along the main fault?
1989
2011
1906
1871
8. The San Andreas Fault is called a:
Right lateral strike slip fault
Transform dip-slip fault
Right dip-slip fault
Transform strike slip fault
9. In your own words, what creates Earthquakes? (75 word minimum)