Assignment
1. Why don't we include the value of intermediate goods in calculating GDP? (2)
2. The price index for year 2 is 103. Nominal GDP is $180,000,000. Find real GDP. Round to the nearest dollar. (2)
3. State whether the following will increase, decrease, or have no effect on GDP. Explain your answers.: (12)
a. Humbert decides to shovel the snow as a favor for his elderly neighbor.
b. The government increases spending without increasing taxes.
c. Marijuana sales are legalized. Cheech begins selling pot openly and reporting his income.
d. The EPA shuts down Toxic Corp. for repeated environmental violations.
e. The government reduces Social Security payments.
f. Mortimer starts bringing his own lunch to work instead of buying it.
4. A researcher finds a significant difference in GDP per capita between advanced country A and developing country B. Knowing that GDP does not count household production, is the gap in income narrower or wider than it initially appears? Explain. (3)
5. Find GDP. (2)
|
Consumption
|
1500
|
|
Gross Investment
|
800
|
|
Changes to Inventories
|
-50
|
|
New Residential Construction
|
115
|
|
Gov't Purchases of Goods and Services
|
200
|
|
Gov't Transfer Payments
|
100
|
|
Exports
|
600
|
|
Imports
|
800
|
|
GDP
|
|
6. Using the above example, find NDP if depreciation is 230. (2)
7. Explain whether each of the following would increase the rate of economic growth in the future and why or why not. (10)
a. An increase in consumption (Hint: what effect will this have on saving, ceteris paribus?)
b. Subsidies for scientific research
c. Decreased education spending.
d. A new technological breakthrough with wide ranging applications is discovered.
e. A government implements a legal system for formalizing property rights.
8. Country X wants to increase its long run rate of economic growth. In order to do this, it wants to change its tax code to encourage savings and investment. Of the following, pick one tax to lower and one tax to raise. Explain your choices. (6)
a. Sales tax
b. Tax on investment income
c. Tax on labor income
9. Based on your answer to the previous question, is there a trade-off between economic growth and economic equality? Explain. (2)
10. Firms expect a poor economy to result in lower consumer demand in the future. Based on that information: (5)
a. In the loanable funds market, which curve will shift, the supply of loanable funds or investment demand?
b. Which direction will the curve shift, left or right?
c. Will equilibrium interest rates increase or decrease?
d. Will equilibrium quantity of investment spending increase or decrease?
e. Will the future rate of economic growth increase or decrease?
11. Households increase their savings rates. Based on that information: (5)
a. In the loanable funds market, which curve will shift, the supply of loanable funds or investment demand?
b. Which direction will the curve shift, left or right?
c. Will equilibrium interest rates increase or decrease?
d. Will equilibrium quantity of investment spending increase or decrease?
e. Will the future rate of economic growth increase or decrease?
12. Which country do you expect to have faster economic growth? Explain. (3)
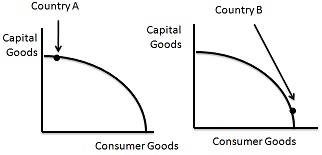
13. Real GDP increases from $125,000,000 to $137,000,000. Find the economic growth rate. (2)
14. If the population in the previous question increases from 500 to 525, find the population growth rate and the rate of per capita economic growth. (4)
15. Based on your answers to the previous questions, has this economy improved or worsened? Explain. (3)
16. Use the data below to answer the following questions: (5)
|
Interest Rate
|
Supply of Loanable Funds(Millions $)
|
Investment Demanded (Millions $)
|
|
1%
|
$3
|
$12
|
|
2%
|
$5
|
$9
|
|
3%
|
$7
|
$7
|
|
4%
|
$8
|
$6
|
|
5%
|
$9
|
$4
|
a. If the interest rate is 2%, how much will households wish to save?
b. If the interest rate is 2%, how much will firms wish to invest?
c. Will banks wish to raise or lower interest rates?
d. What will the equilibrium interest rate and quantity of loans be?
17. What do we expect to happen to interest rates as the price level rises? Why will this happen? How will this affect investment spending and real GDP as the price level increases? (5)
18. Answer the question based on the graph below: (7)
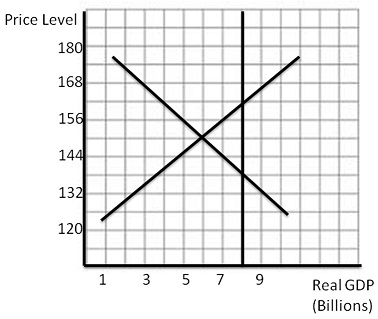
a. Find the short run equilibrium price level and equilibrium real GDP.
b. What is potential real GDP on this graph?
c. Find the long run equilibrium price level and equilibrium real GDP.
d. Find nominal GDP at the short run equilibrium.
19. A nation's exports increase. Answer the following questions: (5)
a. Which curve will shift, aggregate demand or aggregate supply?
b. Will the curve shift to the left or to the right?
c. Will this affect potential real GDP? (Will it shift the LAS?)
d. In the short run, will equilibrium real GDP increase or decrease?
e. Will the equilibrium price level increase or decrease?
20. A new technology increases a nation's productivity. Answer the following questions: (5)
a. Which curve will shift, aggregate demand or aggregate supply?
b. Will the curve shift to the left or to the right?
c. Will this affect potential real GDP? (Will it shift the LAS?)
d. In the short run, will equilibrium real GDP increase or decrease?
e. Will the equilibrium price level increase or decrease?
21. Use the numbers to answer the following questions: (10)
|
Income
|
Spending
|
|
$0
|
$12,000
|
|
$40,000
|
$36,000
|
a) What is autonomous spending?
b) What is induced spending when income = $40,000?
c) What is the mpe as income increases from $0 to $40,000?
d) What is the spending multiplier?
e) If autonomous spending increases by $50,000, what will happen to income?