Part 1
1. Lanni Products is a start-up computer software development firm. It currently owns computer equipment worth $30,000 and has cash on hand of $20,000 contributed by Lanni's owners. For each of the following transactions, identify the real and/or financial assets that trade hands. Are any financial assets created or destroyed in the transaction?
a. Lanni takes out a bank loan. It receives $50,000 in cash and signs a note promising to pay back the loan over 3 years.
b. Lanni uses the cash from the bank plus $20,000 of its own funds to finance the development of new financial planning software.
c. Lanni sells the software product to Microsoft, which will market it to the public under the Microsoft name. Lanni accepts payment in the form of 1,500 shares of Microsoft stock.
d. Lanni sells the shares of stock for $80 per share and uses part of the proceeds to pay off the bank loan.
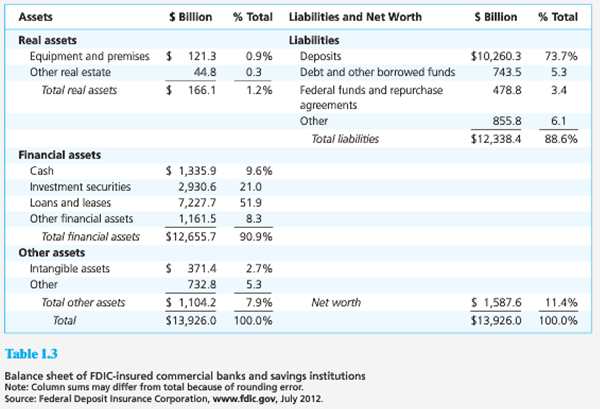
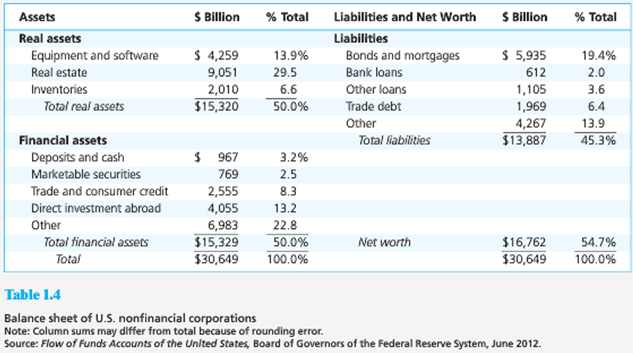
2. Examine the balance sheet of commercial banks in Table 1.3. What is the ratio of real assets to total assets? What is that ratio for nonfinancial firms (Table 1.4)? Why should this difference be expected?
Part 2
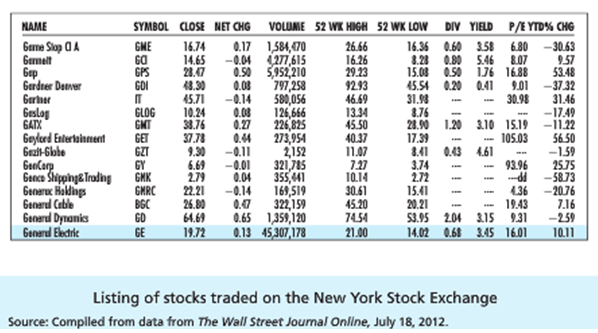
1. Turn to Figure and look at the listing for General Dynamics.
a. How many shares could you buy for $5,000?
b. What would be your annual dividend income from those shares?
c. What must be General Dynamics earnings per share?
d. What was the firm's closing price on the day before the listing?
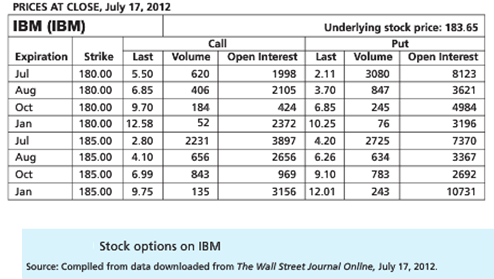
2. Turn back to Figure and look at the IBM options. Suppose you buy a January 2013 expiration call option with exercise price $180.
a. Suppose the stock price in January is $193. Will you exercise your call? What is the profit on your position?
b. What if you had bought the January call with exercise price $185?
c. What if you had bought a January put with exercise price $185?
3. Short-term municipal bonds currently offer yields of 4%, while comparable taxable bonds pay 5%. Which gives you the higher after-tax yield if your tax bracket is:
a. Zero
b. 10%
c. 20%
d. 30%
Part 3
1. You are bullish on Telecom stock. The current market price is $50 per share, and you have $5,000 of your own to invest. You borrow an additional $5,000 from your broker at an interest rate of 8% per year and invest $10,000 in the stock.
a. What will be your rate of return if the price of Telecom stock goes up by 10% during the next year? The stock currently pays no dividends.
b. How far does the price of Telecom stock have to fall for you to get a margin call if the maintenance margin is 30%? Assume the price fall happens immediately.
2. You are bearish on Telecom and decide to sell short 100 shares at the current market price of $50 per share.
a. How much in cash or securities must you put into your brokerage account if the broker's initial margin requirement is 50% of the value of the short position?
b. How high can the price of the stock go before you get a margin call if the maintenance margin is 30% of the value of the short position?
3. If you place a stop-loss order to sell 100 shares of stock at $55 when the current price is $62, how much will you receive for each share if the price drops to $50?
a. $50.
b. $55.
c. $54.87.
d. Cannot tell from the information given.
Part 4
1. An open-end fund has a net asset value of $10.70 per share. It is sold with a front-end load of 6%. What is the offering price?
2. Corporate Fund started the year with a net asset value of $12.50. By year-end, its NAV equaled $12.10. The fund paid year-end distributions of income and capital gains of $1.50. What was the (pretax) rate of return to an investor in the fund?