Problem 1: As you know, utility functions incorporate a decision maker's attitude towards risk. Let's consider that the subsequent utilities were assessed for Stephanie Parker.
|
x
|
u(x)
|
|
-$400
|
0
|
|
-$365
|
10
|
|
-$320
|
20
|
|
-$270
|
30
|
|
-$200
|
40
|
|
-$110
|
50
|
|
$0
|
60
|
|
$130
|
70
|
|
$300
|
80
|
|
$600
|
90
|
|
$800
|
95
|
|
$1,100
|
100
|
Use these utilities to answer the following questions.
a) What is the monetary certainty equivalent for the following gamble: gain $130 with probability 0.4, lose $320 with probability 0.6.
b) What is the risk premium in a)? Illustrate the concept of a risk premium in addition to calculating its value for a).
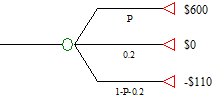
c) What probability P could make Stephanie become indifferent between getting $130 for sure or taking the following gamble?
Problem 2
a) The marketing department of a vitamin water company wishes to evaluate the maximum expected payoff from introducing a new strawberry drink. What decision, in terms of choosing the best investment level, could the marketing department make using the payoff table below? Consider that the probability that the market share is less than 1% is 0.2, that the probability that market share is between 1 and 4% is 0.5, and that the probability that market share is at least 4% is 0.3. Consider that the marketing department is risk neutral.
|
|
Market Share
|
|
Investment Level
|
< 1%
|
1%-4%
|
³ 4%
|
|
Low
|
300,000
|
400,000
|
500,000
|
|
High
|
-400,000
|
300,000
|
3,000,000
|
b) What is the maximum amount of money the company could spend to get more information about the market share?
c) The company can conduct some market research to get more information about the eventual market share. The research will result in a report with two possible results: “Predict High Market Share” and “Predict Low Market Share”. The conditional probabilities for these two types of reports depending on the three possible market shares in the past are given in the following table. How much should the company be willing to spend to conduct the market research that will result in one of the two possible reports? (10 Points)
|
|
Market Share
|
|
Report
|
Below 1%
|
Between 1% - 4%
|
Above 4%
|
|
“Predict Low Market Share”
|
0.8
|
0.6
|
0.3
|
|
“Predict High Market Share”
|
0.2
|
0.4
|
0.7
|
Problem 3
Here is a basic risky decision problem:
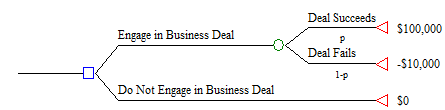
Using the template below, sketch the results of a sensitivity analysis on P(Deal Succeeds) for a risk-neutral decision maker. How high does P(Deal Succeeds) have to before before the decision maker could engage in the business deal?
Problem 4: Your department is hiring a senior manager to direct a group of strong and effective project managers who work on the company’s high-visibility, customer-facing, strategic initiatives. It’s important to find someone who can quickly ramp their knowledge of your company’s customers, business partners, and product/service offerings. In addition to content expertise, the new hire should be a very strong leader, as he/she will be managing experienced project managers as well as assuming the helm on a couple of the enterprise’s most complex and business-critical initiatives. It is also imperative that this new manager work well across multiple stakeholder functions within the company. To that end, you’ve assembled a cross-functional panel representing 8 peer departments who have each interviewed the candidates and provided thorough feedback. Finally, it is worth noting that this is an expensive role, and the candidates vary pretty widely in terms of their current salaries. If you don’t spend too much on this role, you’ll have just enough slack in your budget to hire a half-time admin, which everyone else in the department really wants you to do – all feel the pain of printing, assembling, and binding proposals when there isn’t someone whose job description encompasses that set of tasks.
A summary of the qualifications and background information about 5 candidates is shown in the following table. Please use this table and the “rating-and-weighting” approach (single-attribute value functions, swing weights) explained in class to identify the best candidate. Obviously, the answers will differ from person to person as this evaluation requires highly subjective judgments. However, I want you to demonstrate the technique of solving decision situations with multiple objectives using this example.