Assignment:
A raindrop of mass 3.01 x 10-5 kg falls vertically at constant speed under the influence of gravity and air resistance. Model the drop as a particle.
(a) As it falls 130 m, what is the work done on the raindrop by the gravitational force?
(b) What is the work done on the raindrop by air resistance?
A shopper in a supermarket pushes a cart with a force of 56.0 N directed at an angle of 25.0° below the horizontal. The force is just sufficient to balance various friction forces, so the cart moves at constant speed.
(a) Find the work done by the shopper on the cart as she moves down a 52.6-m-long aisle.
The record number of boat lifts, including the boat and its ten crew members, was achieved by Sami Heinonen and Juha-Matti Rasanen of Finland in 2000. They lifted a total mass of 653.2 kg approximately 4 in. off the ground a total of 24 times. Estimate the total work done by the two men on the boat in this record lift, ignoring the negative work done by the men when they lowered the boat back to the ground.
The force acting on a particle varies as shown in the figure below. (The x axis in the graph has its tickmarks marked in increments of 4.00 m.)
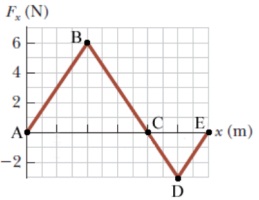
Find the work done by the force on the particle as it moves across the following distances.
(a) from x = 0 m to x = 16.00m
(b) from x = 16.00 m to x = 24.00 m 3
(c) from x = 0 m to x = 24.00 m
At an archery event, a woman draws the string of her bow back 0.374 m with a force that increases steadily from 0 to 245 N.
(a) What is the equivalent spring constant (in N/m) of the bow?
(b) How much work (in 3) does the archer do on the string in drawing the bow?
One end of a light spring with spring constant k1 = 1,250 N/m is attached to the ceiling. A second light spring is attached to the lower end, with spring constant k2 = 1,650 N/m. An object of mass 1.50 kg is attached to the lower end of the second spring.
(a) By how much does the pair of springs stretch (in m)?
(b) What is the effective spring constant (in N/m) of the spring system?
(c) What If? Two identical light springs with spring constant 850 N/m are now individually hung vertically from the ceiling and attached at each end of a symmetric object, such as a rectangular block with uniform mass density. In this case, with the springs next to each other, we describe them as being in parallel. Find the effective spring constant (in N/m) of the pair of springs as a system in this situation.
One end of a light spring with spring constant k1 is attached to the ceiling. A second light spring is attached to the lower end, with spring constant k2. An object of mass m is attached to the lower end of the second spring.
(a) By how much does the pair of springs stretch? (Use the following as necessary: k1, k2, m, and g, the gravitational acceleration.)
(b) What is the effective spring constant of the spring system? (Use the following as necessary: k1, k2, m, and g, the gravitational acceleration.)
(c) What If? Two identical light springs with spring constant k3 are now individually hung vertically from the ceiling and attached at each end of a symmetric object, such as a rectangular block with uniform mass density. In this case, with the springs next to each other, we describe them as being in parallel.
Find the effective spring constant of the pair of springs as a system in this situation in terms of k3. (Use the following as necessary: k3, M, the mass of the symmetric object, and g, the gravitational acceleration.)
A ball with a mass of 3.60 kg is moving with velocity (6.20i - 1.80j) m/s.
(a) What is the ball's kinetic energy (in J) at this velocity?
(b) Find the net work (in I) on the ball if its velocity changes to (8.00i + 4.00j) m/s.