1. What is the total lethality (in equivalent D250 minutes) of this thermal process? (Show work. Express answer to two places to the right of the decimal point).
Total lethality = ___________minutes
2. Is this a sufficient thermal process for this food, based on the given criteria ? Why or why not?
3. What percentage of the total lethality occurred at temperatures less than 220 F, i.e. slightly above the boiling point of water ? Record your answer to the nearest integer.
4.If the product were thermally canned beef broth (pH 6.5), would this process be sufficient? (Assume the target organism to be the same as that stipulated in Question 1). Why or why not? (Be quantitative in your answer)
5. Heat is an effective means of destroying unwanted microorganisms in foods, but has deleterious effects as well, as discussed in class. Other methods used to kill microorganisms that do not involve high temperatures are ionizing radiation and high pressure. Both can be used at room temperature, or in some cases (ionizing radiation) with frozen foods.
Figure 1 below depicts "pressure death rate" curves analogous to the "thermal death rate" curves used in Question 1 above. [ CFU stands for "colony forming unit", a measure of the number of viable organisms, and MPa is "megapascal", a unit of pressure equivalent to 145 pounds per square inch, or 10 atmospheres.] Note that as the applied pressure increases, the organism is killed at a greater rate, and the kinetics of cell death are logarithmic, as was the case with temperature. Such data are used to determine DP values analogous to the DT values in thermal processes.
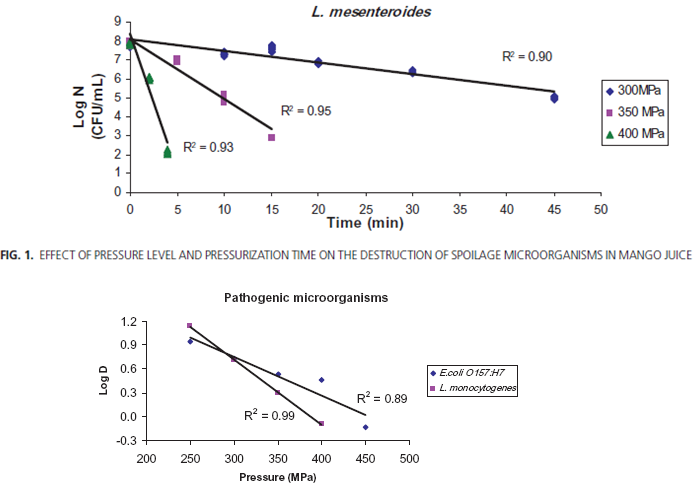
Figure 2.
Use the plots shown above to answer the following questions:
5a. Fruit juices (such as mango) are often given a 5-D treatment in order to destroy spoilage organisms such as L. mesenteroides. Using the data in Figure 1, contrast the time (to the nearest minute) required for a 5-D pressure treatment at 350 and 400 MPa:
350 MPa _________
400 MPa _________
5b. Which of the two pathogenic bacteria (E.coli O157:H7 or L. monocytogenes) is the most resistant to inactivation by high pressure, when compared at 350 MPa?
5c. Contrast the time (minutes) that would be required to accomplish a 5-D pressure process at 350 MPa, using E. coli O157:H7 or L. monocytogenes as the target organism:
(show work)
E. coli O157:H7 __________
L. monocytogenes __________