Assignment:
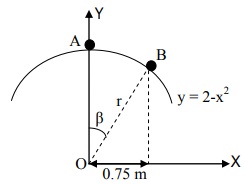
Q1) A particle when gently nudged from rest at point A begins to slide on the surface of a transparent umbrella as shown. Its motion is such that its speed increases uniformly at 0.5 m/s per second.
i) Find the time it took for the particle to reach B.
ii) Determine its velocity and acceleration at point B in en, et system
iii) Express his velocity and acceleration at B in i, j system (Hint: Recall dy/dx is the slope of a tangent at a point on the curve; |V ?|= v, the speed )
iv) Express its velocity and acceleration at B in er, eθ system (O is the origin of the er, eθ system)
v) At the instant it is at point B, find the values of r·, β·, r¨, β¨ with respect to the polar coordinate system fixed at O.
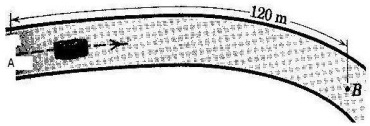
Q2) A car travels along the level curved road with a speed which is decreasing at the constant rate of 0.6 m/s each second. The speed of the car as it passes point A is 16 m/s. Calculate the magnitude of the total acceleration of the car as it passes point B which is 120 m along the road from A. The radius of curvature of the road at B is 60 m.
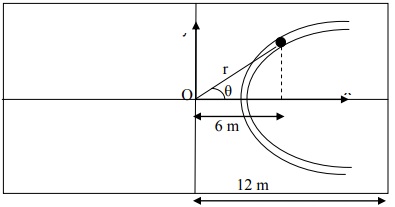
Q3) A particle is constrained to move in a parabolic slot cut in a rectangular plate [12 m x 16 m] as shown. The equation of the slot is given by y2 = x-2 [x,y in meters measured from O]. Further, as the particle moves in the slot, its y-coordinate is constrained to change uniformly at the rate of 0.25 m/s. At the instant shown (i.e. when x = 6 m),
i) Compute the radius of curvature
ii) Express its velocity and acceleration in i, j system (Hint: v→ = x·i + y·j, y· is given and x· could be found as you know the equation of the path)
iii) Express its velocity and acceleration in en, et system
iv) Find the values of r·, θ·, r¨, θ¨ recorded from O.
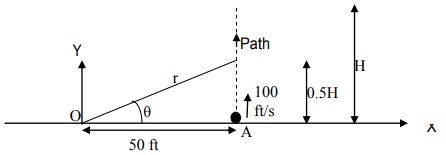
Q4) A ball is thrown vertically upward from point A with an initial speed of 100 ft/sec and its acceleration (in ft/s2 ) along its path is given by , a = - g - kv2, k = 0.002 ft-1 and v is speed in ft/sec.
i) Find the maximum height to which the ball will ascend. Denote this by H.
ii) Compute r·,θ·,r¨,θ¨(recorded relative to the stationary observer at O) when the ball reaches a height H/2 (i.e. half its maximum height)
iii) Compute the normal and tangential components of its acceleration when it reaches a height of H/2. What is the radius of curvature of its path at this instant?
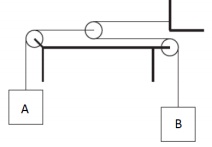
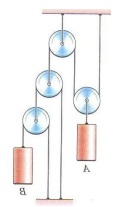
Q5) For the illustrated pulley-system, derive an equation which relates the acceleration of block B to the acceleration of block A.
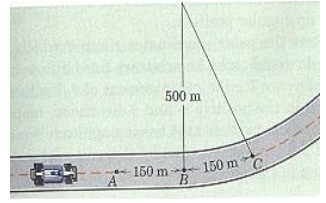
Q6) Danica traveling at a speed of 200 km/hr on a straight road applies brakes to her car at point A and reduces her speed at a uniform rate to 150 km/hr at C in a total distance of 300 meters.
a) Calculate the magnitude of the total acceleration of her car immediately after she passes point B. Assume BC to be a part of a circular path. [So, AB is a straight line while BC is a circular arc.]
b) Compute the time she took to go from A to C.
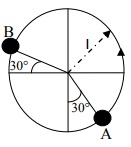
Q7) A ball tied to a thread is swung around (ccw) in a circular path as shown. It starts with a speed of 2 m/s at point A and increases its speed uniformly at the rate of 0.5 m/s2 to reach B. l = 0.5 m
a) Compute the time it took for the ball to go from A to B
b) Compute the acceleration (magnitude and direction) of the ball at B
c) Compute the average velocity of the ball for its path from A to B
d) Compute the average acceleration of the ball for its path from A to B
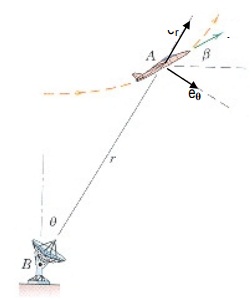
Q8) During a portion of a vertical loop, an airplane flies in an arc of radius λ = 600 m with a constant speed of 400 km/h. When the airplane is at A (as shown), its velocity vector makes an angle β = 30° with the horizontal, and radar tracking data is r = 800 m and θ = 30°. Compute the values of r·,r¨,θ·,θ¨ recorded by the radar at this instant. [unit vectors for radar coordinate system are shown]
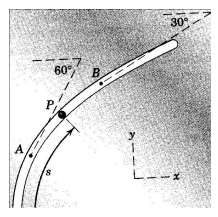
Q9) The particle P moves along the curved slot, a portion of which is shown. Its distance in meters along the slot is given by s = t2 /4, where t is in seconds. The particle is at A when t = 2 s and at B when t = 2.2 s. Determine the average acceleration of P between A and B.
Q10) Find the relationship between acceleration of block A and acceleration of block B. Thick lines represent fixed support/structure.