Problem 1: Market Structures: Perfect Competition
Suppose Julie sells Chinese teapot, sugar, and milk bowl sets in a perfectly competitive market. Her output per day and her costs are as shown in the Table.
|
Output per day
|
Total cost $
|
TR$
|
ATC$
|
MR$
|
MC$
|
Profit $
|
|
0
|
20
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1
|
32
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2
|
37
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3
|
48
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4
|
61
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5
|
75
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6
|
92
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7
|
113
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8
|
136
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) Suppose the current equilibrium price in the teapot market is $10. Complete Table-1 and answer part (b).
(b) To maximize profit, how many teapot sets will Julie produce, what price will she charge, and how much profit (or loss) will she make?
(c) Draw a graph to illustrate your answer and explain. Your graph should include Julie's demand, ATC, AVC, MC, and MR curves, the price she is charging, the quantity produced and the area representing the profit (or loss).
(d) Suppose now the current equilibrium price in the teapot set market has increased to $20, complete the relevant columns TR, MR and Profit.
(e) To maximize profit, how many teapot sets will Julie produce, what price will she charge, and how much profit (or loss) will she make?
(f) Draw a graph to illustrate your answer and explain. Your graph should include Julie's demand, ATC, AVC, MC, and MR curves, the price she is charging, the quantity produced and the area representing the profit (or loss).
Problem 2: Market Structures: Monopoly
(a) If you are the owner of the only bookstore in a small town, do you have a monopoly? Explain.
(b) Draw graph and explain the inefficiency of a monopoly firm such as public sector provision of electricity.
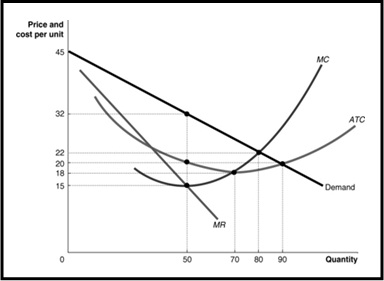
(c) Refer to monopoly Figure below and answer the following questions.
(i) What is the profit maximizing quantity and price charged by a monopoly firm?
(ii) What is the total revenue and total costs at the profit maximizing level of output?
(iii) What is the monopoly profit?
(iv) If the industry was organized as a perfectly competitive industry, what would be the profit maximizing quantity and price?
Problem 3: Market Structures Monopolistic
(a) Table below shows the demand and the cost data facing 'Velvet Touches', a monopolistically competitive producer of velvet throw pillows.
|
Quantity
|
Price $
|
TR $
|
MR$
|
TC$
|
MC $
|
Profit $
|
|
1
|
30
|
30
|
|
32
|
|
|
|
2
|
28
|
56
|
|
43
|
|
|
|
3
|
26
|
78
|
|
53
|
|
|
|
4
|
24
|
96
|
|
64
|
|
|
|
5
|
22
|
110
|
|
76
|
|
|
|
6
|
20
|
120
|
|
90
|
|
|
|
7
|
18
|
126
|
|
106
|
|
|
|
8
|
16
|
128
|
|
126
|
|
|
i) Calculate MR and MC and complete the columns.
ii) What are the profit maximizing quantity and price for 'Velvet Touches'?
iii) How much is the profit or loss of the firm? Show the working.
iv) If the firm's profit or loss is typical of all firms in the market for throw pillows, what is likely to happen in the future?
v) Will there be more firms, or will some existing firms leave the industry? Explain your answer.
vi) What will happen to a typical firm's profit or loss after all entry/exit adjustments?
Problem 4: Market Failure and Externalities:
(a) Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market. These mills, located upstream from a fishing village, discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river. The waste material affects the number of fish in the river, and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source. Study the paper market Figure and answer the following questions.
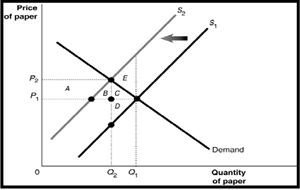
(i) What does the curve S1 and S2 represent? Explain.
(ii) What is the economically efficient output level?
(iii) What is the deadweight loss from producing at the market equilibrium? Explain why?
(b) Consider a chemical plant that discharges toxic waste into a nearby waterway. To reduce the emissions of toxic waste, the firm can install pollution abatement devices. Figure below shows the marginal benefit and the marginal cost from reduction in the toxic waste emissions.
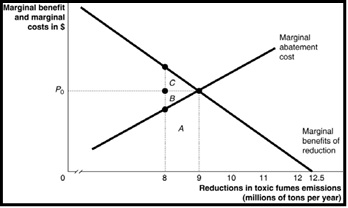
(i) What is the economically efficient level of pollution reduction?
(ii) Suppose the emissions reduction target is currently established at 8 million tons. What is the area that represents the cost of eliminating an additional 1 million tons?
(iii) Suppose the emissions reduction target is currently established at 8 million tons. Should society undertake to reduce an additional 1 million tons so that the total reduction is 9 million tons?
Principles of Economics Assignment Help service is always focused on providing the top-notch online assistance to all the students, who have been struggling to secure higher grades.
Tags: Principles of Economics Assignment Help, Principles of Economics Homework Help, Principles of Economics Coursework, Principles of Economics Solved Assignments, Market Structures: Perfect Competition Assignment Help, Market Structures: Perfect Competition Homework Help, Monopoly Assignment Help, Monopoly Homework Help, Monopoly Coursework, Market Structures Monopolistic Assignment Help, Market Structures Monopolistic Homework Help, Market Failure and Externalities Assignment Help, Market Failure and Externalities Homework Help