Assignment:
Introduction: The Moon orbits the earth about once a month.
Half of the Moon's surface is always illuminated by the sun. But the fraction of the Moon's illuminated face that is visible from Earth will change according to the Moon - Earth - Sun alignment at a given time.
Using the Styrofoam ball as the Moon, a flashlight as the Sun and your head as the Earth make observations and design experiments to simulate the phases of the Moon. Answer the following questions:
1- Is the bright side of the Moon facing toward the Sun, or away from it? Indicate in the sketch below the lit side of the Moon (shade with your pencil the dark side, leave the lit side white)
2- Sketch the Earth, Moon and Sun when the Moon is in the full phase. What is the angle Moon - Earth - Sun?
3- Sketch the Earth, Moon and Sun when the Moon is in the first quarter phase. What is the angle Moon - Earth - Sun?
4- If it is Waxing Crescent Moon in the Northern Hemisphere, which phase will it be for the Southern Hemisphere?
5- How much of the entire Moon surface is illuminated by the Sun during New Moon?
a) None of the surface.
b) Less than half of the surface is illuminated.
c) Half of he surface is illuminated.
6- How much of the Moon's illuminated surface is visible from Earth during New Moon?
a) None of the surface (visible from Earth) is illuminated.
b) Less than half of the surface (visible from Earth) is illuminated.
c) Half of the surface (visible from Earth) is illuminated.
7- You observe a full Moon rising in the east. Which image shown best represents how the Moon will appear as it is setting?

The time for the Moon to make one complete orbit is the same time as it takes to rotate on its axis, and is approximately 27.3 days. As a result, the Moon always keeps the same face toward earth. In fact, nobody knew what was on the far side (the side we never see) of the
Moon until it was photographed from spacecraft in the 1960's.
8- What is the phase of the Moon when the dark side (night) and the far side (the side we never see) of the Moon are the same? Include a sketch.
9- What is the phase of the Moon when the dark side (night) of the Moon is facing Earth? Include a sketch.
To determine how and when the various phases of the Moon occur, we will find it useful to look at the following diagram:
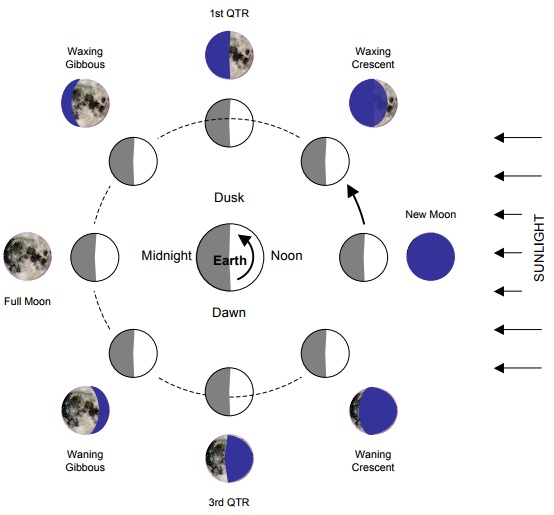
The diagram above is a view of the Moon's orbit from the NCP (North Celestial Pole) perspective. When the Moon is located in its orbit in the general direction of the sun, it cannot be seen. Not only is it located in the bright, daytime sky, but also the hemisphere facing the earth is not sunlit. This is known as new Moon. At all other positions in its orbit, the Moon is visible. The changing shape of the illuminated portion of Moon, as different amounts of the sunlit face are seen, is known as the phase cycle. Following new Moon, one sees crescent phases for several days. Crescent phase is followed by the first quarter Moon, then the gibbous phases until full Moon is reached. This waxing (increasing illumination) half of the cycle is followed by the waning (decreasing illumination) half of the cycle, returning to the new Moon again.
One can use the Moon phase diagram to determine rising and setting times. (The local time is given by the clock time directly above the observer's head. For example, a first quarter Moon sets around midnight).
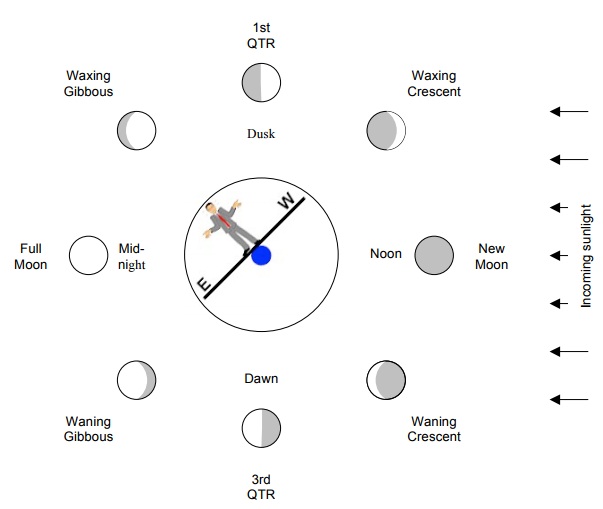
Note that the Moon orbits counterclockwise (to the east) and that the earth also rotates counterclockwise (to the east).
PROCEDURE:
The Moon phase diagram is a useful tool in determining where the Moon is at a particular time of day when the Moon is in a given phase.
Cut out the diagram on the following page and to familiarize yourself with its use, use this diagram to answer the questions below.
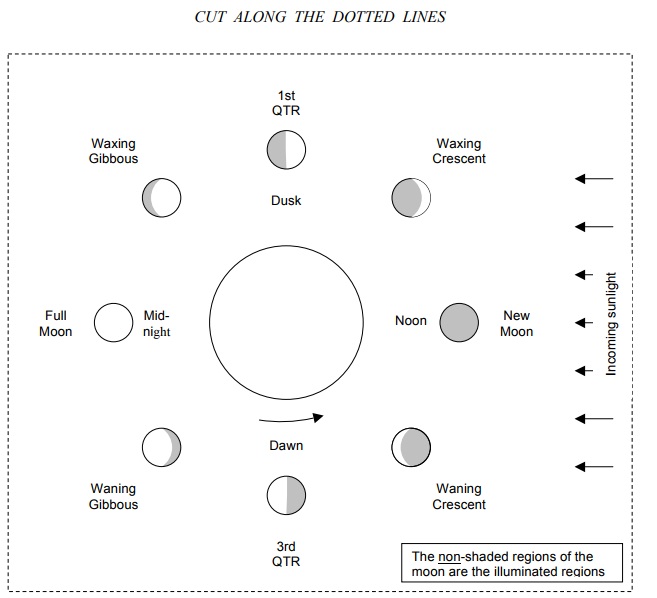
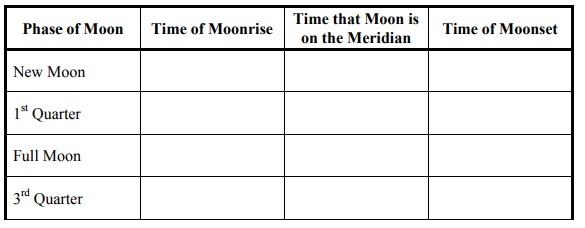
10. For the following table, use your Moon phase diagram to determine the approximate times of moonrise, moonset, and meridian crossing for each Moon phase.
11- Which of the following could never happen?
a) An observer seeing a full Moon in the middle of the day (local noon).
b) An observer seeing a new Moon in the middle of the night (local midnight).
c) Both of the above observations are impossible for any observer to see.
12- You and your friend are walking home from a party one night and your friend asks you what time it is. Neither of you are wearing a watch but you notice that the full Moon is at its highest point in the sky (crossing the meridian). Approximately what time is it?
13- For some reason you awake near dawn and notice that the Moon is halfway between the eastern horizon and zenith. What is the phase of the Moon?
14- You are looking at the Moon shortly after sunset. Which of the views shown below will you never see? Why not?

15- If a base were built on the near side of the Moon, would the residents see sunrise? Would they see ‘earthrise' and ‘earthset'?
16- If a base were built on the far side of the Moon, would the residents see sunrise? Would they see ‘earthrise' and ‘earthset'?
17- Does an observer on the near side of the Moon see the Earth on phases?
18- If an astronaut on the Moon see a full Earth, what would an observer on Earth see when observing the Moon?
19- If the Moon is a waxing crescent what would an astronaut on the Moon see when observing Earth?
20- By looking at your Moon phase diagram, determine the phase of the Moon during which a lunar and solar eclipse can occur
|
Type of Eclipse
|
Moon Phase
|
|
Lunar
|
|
|
Solar
|
|
21- Why don't eclipses occur on a monthly basis? Doesn't the Moon come between the earth and the sun every 29.5 days?
22.

The photographs above are showing:
a) Total lunar eclipse, annular solar eclipse, partial solar eclipse
b) Total solar eclipse, partial solar eclipse, Lunar eclipse
c) Total solar eclipse, annular solar eclipse, partial solar eclipse
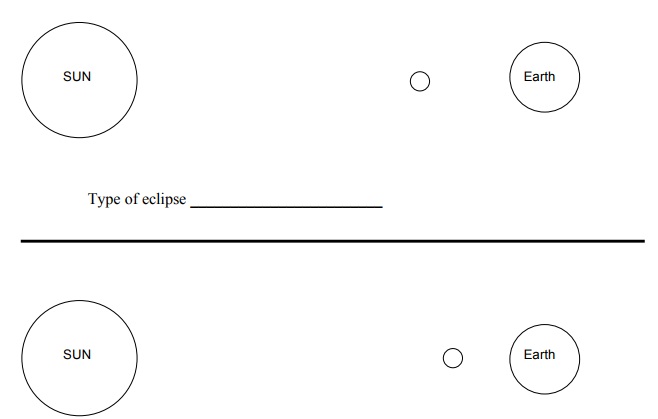
23- For the following diagrams, use a straight edge to draw the sun's rays that outline the earth's and Moon's shadows. Label the umbra and penumbra on each one. Be specific on the type of eclipse (partial or total, lunar or solar, etc.)

Attachment:- Spectroscopy Lab.rar