Response to the following multiple choice questions:
1. What is the atomic mass/weight of an atom that has 24 protons, 26 neutrons, and 24 electrons?
(1) 24
(2) 26
(3) 48
(4) 50
(5) 74
2. What is the atomic number of an atom that has 24 protons, 26 neutrons, and 24 electrons?
(1) 26
(2) 24
(3) 48
(4) 50
(5) 74
3. Elements are defined by:
(1) the number of protons
(2) the number of neutrons
(3) the number of electrons
(4) the number of protons plus the number of neutrons
(5) the electrical charge defined by the # of positively charged protons and the # negatively charged electrons
4. Which of the following atoms is an isotope of an atom that has 8 protons and 10 neutrons)?
(1) an atom with 7 protons and 8 neutrons
(2) an atom with 6 protons and 12 neutrons
(3) an atom with 18 protons and any number of neutrons
(4) an atom with 8 protons and 8 neutrons
(5) an atom with 10 protons and 10 neutrons
5. If a mineral has a parent to daughter ration of 1:3 (one parent atom for every three daughter atoms), how many half-lives have passed since the mineral formed?
(1) 0
(2) 1
(3) 2
(4) 3
(5) 4
6. Refer to Figure 1 (below). The boundary J, between the shale G and underlying sandstone B is called a(n):
(1) angular unconformity
(2) nonconformity
(3) isotopic unconformity
(4) disconformity
(5) baked contact
7. Refer to Figure 1 (below). The boundary L, between sandstone B and underlying rocks is called a(n):
(1) angular unconformity
(2) nonconformity
(3) disconformity
(4) isotopic unconformity
(5) baked contact
8. Refer to Figure 1 (below). The boundary O, between conglomerate L and underlying metamorphic rocks (M) is called a(n):
(1) nonconformity
(2) angular unconformity
(3) disconformity
(4) isotopic unconformity
(5) baked contact
9. Refer to Figure 1 (below). Which of the following is true regarding the age of motion on fault N?
(1) it is younger than conglomerate I, but older than sandstone B
(2) it is younger than sandstone F, but older than sandstone B
(3) it is younger than dike D, but older than sandstone B
(4) it is younger than sandstone B, but older than shale G
(5) it is younger than metamorphic rocks M, but older than conglomerate I
10. Refer to Figure 1 (below). Which of the following is true regarding the age dike H?
(1) it is older than dike/sill D
(2) it is younger than sandstone B, but older than shale G
(3) it is Paleocene in age
(4) it is younger than sandstone F, but older than shale E
(5) it is younger than limestone A
11. Refer to Figure 1 (below). Which of the following is true regarding the age dike/sill D?
(1) it is younger than dike H
(2) it is younger than shale E and older than sandstone B
(3) it is younger than metamorphic rocks M, but older than sandstone F
(4) it is Paleocene in age or younger
(5) it is younger than metamorphic rocks M, but older than shale E
12. Refer to Figure 1 (below). Analysis of dike/sill D yielded 30,000 daughter atoms and 2,000 parent atoms. On the basis of this ratio, how many half-lives have passed since the mineral formed?
(1) 1
(2) 2
(3) 3
(4) 4
(5) 5
13. If the isotope from the previous question has a half-life of 25 million years, what is the age of dike/sill D?
(1) 3 million years
(2) 25 million years
(3) 50 million years
(4) 75 million years
(5) 100 million years
14. Refer to Figure 1 on the last page. Place the sequence of events in order from oldest (left) to youngest (right).
a. M - N - O - I - F - E - C - P - L - D - B - J - G - H - A - K
b. M - N - O - I - F - E - C - D - P - L - B - J - G - A - H - K
c. D - M - N - O - I - F - E - C - P - L - B - J - G - A - H - K
d. M -O - I - N - F - E - C - D - L - B - J - G - A - H - K
e. M - N - O - I - F - E - C - P - L - D - B - J - G - H - K - A
f. M - N - O - I - F - E - D - C - L - B - P - J - G - A - H - K
g. M - N - O - I - F - E - D - C - H - P - L - B - J - G - A - K
h. M - N - O - I - F - E - D - C - P - L - B - J - G - K - A - H
i. O - I - M - N - F - E - C - D - P - L - B - J - G - A - H - K
j. M - N - O - I - F - E - P - C - D - L - B - J - G - A - H - K
Figure 1
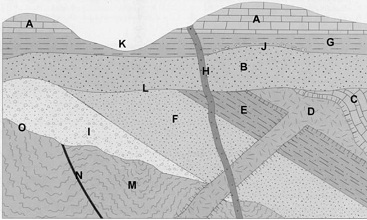
This list describes each feature, labeled with letters, in the vertical cross-section shown in Figure 1.
A. Deposition of limestone during the Oligocene
B. Deposition of sandstone during the Paleocene
C. Deposition of limestone
D. Intrusion of granite dike and sill (laccolith)
E. Deposition of shale
F. Deposition of sandstone
G. Deposition of shale during the Oligocene
H. Intrusion basalt dike
I. Deposition of conglomerate
J. ?? (boundary between units B and G)
K. Erosion to form valley
L. ?? (boundary between units B and underlying units I and F)
M. Folded & metamorphosis of rocks formed at depth
N. Fault
O. ?? (boundary between unit M and overlying units)
P. Tilting of rock layers (Note that this is not labeled in Figure 1)
Also, you will need to refer to the Geologic time scale Figure
Remember the principles of original horizontality and cross-cutting relationships
Also, recall the types of unconformities .