Assignment:
Multiple Choice Question
1. what is the electric force produced by light sensitive metal ?
a. photoelectric.
b. static electricity.
c. piezoelectric.
2. what is the definition of potential difference?
a. Quantity of electric charge transferred from high to low potential.
b. the voltage difference which exists between two bodies.
c. force that applied to electrons to remove them from their orbits.
3. What is an atom?
a. A positively charged element.
b. An element containing only electrons.
c. The smallest particle to which elements can be reduced.
4. What is the angle between each phase of a three phase alternator?
a. 45 degrees.
b. 90 degrees.
c. 120 degrees.
5. What is meant by the term coefficient of coupling between two coils?
a. Ratio between number of turns of primary and secondary coils of a transformer.
b. It is equal to the ratio of flux cutting one coil to flux originated in the other coil.
c. The amount of leakage flux among the primary and secondary windings.
6. which law to be used to determine the attraction / repulsion force between two charged bodies?
a. ohms.
b. kirchoff.
c. coulomb.
7. what is the typical unit used to state resistivity or specific resistance?
a. kilo - ohms.
b. micro - mho.
c. ohms / metre.
8. what is relationship between true power and apparent power if a circuit is capacitive?
a. they are equal.
b. true power is greater than apparent power.
c. apparent power is greater than true power.
9. what is the neutralizing agent for potassium Hyroxide spillage?
a. 1% bicarbonate of soda.
b. 2% of ammonia solution.
c. 3% solution of boric acid.
10. what happens to the resistance of a conductive material when its length changes?
a. resistance of a conductor increases as its length increases.
b. reducing the length of a conductor increases its resistance.
c. the resistance of a conductor remains constant when length changes.
11. how do you reverse the direction of rotation of a 3 phase induction motor?
a. swapping the connection of any 2 wires from 3 phase supply.
b. by shifting the shading ring to the other side of the pole face.
c. changing the supply frequency using a frequency converter.
12. what is the configuration of a band pass filter?
a. series resonant network which includes an inductor and a capacitor.
b. An inductor and a resistor connected in series which from a voltage divider.
c. A circuit with resistor inductor and capacitor connected parallel to each other.
13. what is the difference between a primary and a secondary cell?
a. A primary cell can be recharged easily.
b. secondary cell uses liquid electrolyte only.
c. chemical reaction can be reset in a secondary cell.
14. what is the standard term used in an alternating current cycle when the voltage of two sine waves reach maximum and minimum points at the same time in same direction?
a. single phase.
b. in phase.
c. unity phase.
15. what happens to the resistance of a material with a positive temperature coefficient, when the temperature increases in the vicinity?
a. decreases.
b. remains the same.
c. increases.
16. how are eddy current losses minimized in a transformer?
a. with a core made out of solid soft iron.
b. utilising thin insulated laminated.
c. using non - magnetic material as the core.
17. what factor will increase the amount of EMF induced into a coll placed in as alternating magnetic field?
a. Decrease the magnetic field strength
b. Increase the rate of change flux
c. Decrease the rate of movement of conductor.
18. What happens to two nearby bar magnets if the magnetic lines of forces of each acting in the same direction?
a. Have no effect
b. They will attract
c. Repel each other
19. What happens if two adjacent conductors are parallel and carrying current in opposite directions?
a. Their magnetic fields will cancel and have no effect
b. The conductors will be attract to each other due to magnetic induction
c. Magnetic fields are in opposite direction, so conductors will repel each other
20. What is the effective value of voltage and current of a sinusoidal wave known as?
a. Peak to peak value
b. Root-mean-square(RMS)
c. Instantaneous
21. What is the total internal of a group of cells connected in parallel?
a. It is less than the internal resistance of one cell
b. Same as internal resistance of an individual cell
c. Internal resistance of each cell will add up together
22. What will happen if a charged capacitor id connected across an alternating current (AC) sources?
a. Current will flow in the circuit
b. It will block the alternating current (AC)
c. The capacitor will slowly discharge
23. What would be the safe voltage to use in a circuit which has three 10 mf capacitor connected in parallel and their working voltage are 200V, 150V and 300V respectively?
a. 150V
b. 300V
c. 650V
24. What happens to the force of attraction, if the distance between the objects is reduced to half?
a. Reduces by 1\2 of its original value
b. The force will remain same
c. It will increase by four-fold
25. Referring to the attached image. Which letter identifies the 'commutator'?
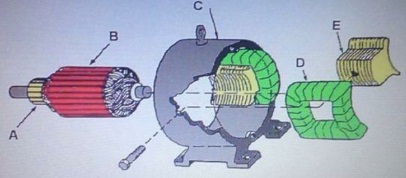
a. A
b. B
c. C
26. What is the term that describes the magnetic flux from one conductor that induces a voltage in another electrically isolated conductor?
a. Inductive reactance
b. Mutual inductive
c. Capacitive coupling
27. What type of alternator uses slip rings and brushes to provide the output?
a. Rotating armature
b. Revolving field
c. Permanent magnet
28. What is the advantage of 'star' type three phase system?
a. It is more suitable for balanced loads.
b. Line current is more than phase current
c. Two values of voltages are available
29. What happens to a transformer if applied frequency decreases beyond the rated value?
a. The output voltage and current will decrease immediately
b. It will work as normal regardless of frequency variation
c. Transformer mat be damaged as current flow increase
30. Which motor forms a rotating magnetic field in the stator when AC power is applied?
a. 3 phase induction motor
b. Split capacitor motor
c. Shaded pole motor
31. What is the reactive power in this ciruit?
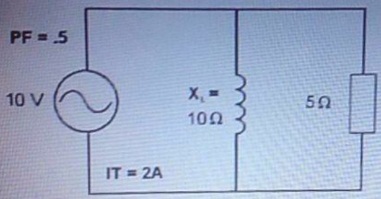
a. 5 vars
b. 10 vars
c. 20 vars
32. What is value of the resistor, if it dissipates 8W power, when the current flow is 2A?
a. 3 ohms
b. 200 ohms
c. 2000 ohms
33. What type of impurity is used to dope N-type semo-conductors?
a. Boron
b. Germanium
c. Phosphorus
34. Referring to the attached image. What is the value of total current (IT) flow in milliamperes?
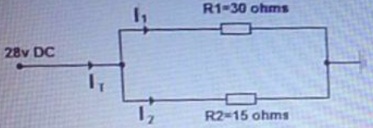
a. 2600
b. 2700
c. 2800
35. What precaution is to be taken when storing horseshoe magnets?
a. To be kept away from other magnets\magnets tools
b. Suspended in air, clear of non-magnetic materials
c. Place a soft iron keeper at the ends of the poles
36. What is an alternation with reference to sinusoidal waveform?
a. Distance from zero to the maximum value
b. Either positive or the negative half - cycle
c. Number of cycles completed in one second
37. What is SI unit of magnetic flux desity
a. Gauss
b. Weber
c. Tesla
38. Why is soft iron preferred as core material in as electromagnet?
a. Due to its low saturation point
b. Because of its high retentivity
c. As it has high permeability
39. What is the definition of energy?
a. Force required for moving an object
b. Rate at which work is being done
c. The capacity for work to be done
40. What effect does the internal resistance of a power supply have?
a. The current available for the load increase as the internal resistance as the internal resistance increase
b. When the internal resistance is zero in indicates the battery is fully discharged
c. The voltage available at the load decreases as internal resistance increase
41. Referring to the attached image Which letters identify the 'peak value' of the Triangular wave?
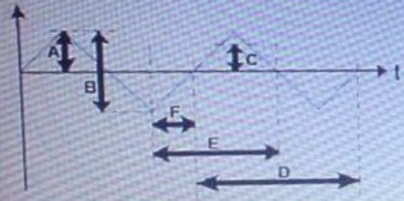
a. A
b. B
c. C
42. What is the symbol of conductance?
a. C
b. G
c. S
43. What is Kirchoffs current law?
a. The amount of current flowing in a pure resistive circuit is proportional to the applied voltage
b. Sum of current flowing into a junction equals the sum of current flowing away from junction
c. Flow of total current in a circuit is inversely proportional to the total resistance in the circuit
44. What is the true power in this circuit? R=3Q , Xc=4Q , 1A
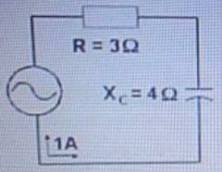
a. 3 watts
b. 4 watts
c. 5 watts
45. What is the effect on the capacity of capacitor, if the distance between the plates is halved and plate area is doubles?
a. Decreases by 50%
b. It will remain same
c. Increases by 4 times
46. What happens to the back EMF in the primary of transformer, when the secondary is connected to a load?
a. Back EMF increases as secondary flux cancels primary flux
b. Back EMF reduces and more current is drawn from the source
c. Back EMF remains unchanged because secondary flux decreases
47. What happens to the impedance value at resonant frequency on an LCR series circuit?
a. Becomes more inductive
b. Goes to minimum value
c. It will act capacitively
48. What is the purpose of a voltage dependant resistor?
a. It is used in surge protection circuits
b. Protects circuit from Over-current
c. Shields when detect high temperature
49. What distorts the main field of a DC Generator causing a reduction in the output?
a. The reactive sparking due to poor brush tension
b. Magnetic field produced by the armature current
c. Effect interpoies and compensating windings
50. What is the synchronous speed of a 3 phase induction motor?
a. Difference between field rotation speed and rotor speed
b. Speed of the rotating magnetic field formed in the stator
c. When the torque speed reaches the maximum value
51. Why, in an AC inductive circuit does the voltage cycle lead the current cycle?
a. Because an inductor needs to be fully charged first to conduct current through an inductive circuit
b. Direction of voltage cycle and the current cycle always opposite to each other in an inductive circuit
c. Voltage induced across inductors is directly proportional to the rate which the current is charged
52. What is the formula to be used to find the output power of a heater, if value of operation voltage and current consumption are given?
a. P=Vsqueer2 I
b. P=EI
c. P=1squeer2 R