Binary Choice:
Question 1. What is economics?
a. The study of how people make choices under scarcity and the results of those choices for the society.
b. The study of how to run society, makingit wealthier and redistributing goods and resources from those who have a surplus to those in need.
Question 2. The statement: “An increase in the severity of punishment for cheating will result in fewerstudents cheating during the exam” is a:
a. Positive statement
b. Normative statement
Question 3. Mad City Bank makes a loan of $5,000 to a local car washing company. The loan will appear on Mad City Bank’s balance sheet (their t-account) as:
a. An asset
b. A liability
Question 4. It is known that potatoes are an inferior good for Irish peasants. Holding everything else constant, when the Irishmen expect an economic crisis and thus lower income next year, their demand curve for potatoes today shifts to the:
a. Left
b. Right
Question 5. After a report of pollution in the local tap water supply, the demand for bottled water shifts to the:
a. Left
b. Right
Question 6. The chancellor of UW-Madison has just announced a major tuition change. According to her, the general costs (tuition, room and board, and administrative fees) of attending UW-Madison will increase by 10% from year 2016 to 2017. A decomposition of the costs for this year and next yearis provided below:
2016 2017 Percentage Change
Tuition $20,000 ? 5%
Room and Board $8,000 $10,200 ?
Administrative Fees ? $1,800 -10%
Is the chancellor being honest in saying that the general costs will increase by 10%?
a. Yes
b. No
Question 7. Annie and Jack produce articles and power point presentations. Both Annie and Jack's production possibility frontiers are linear. Suppose Annie needs 4 hours to write an article, and 2 hours to create a power point presentation. Jack needs 6 hours to writean article, and 1 hour to create a power point presentation. Annie works 8 hours a day, while Jack works 3 hours a day.
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
a. Jack has absolute advantage in writing articles; Annie has absolute advantage in creating power point presentations
b. Annie has absolute advantage in writing articles; Jack has absolute advantage in creating power point presentations
Question 8. Consider the market for laptops that was in equilibrium until 2007. In 2008, there was an innovation in the production process for laptops such that computer companies could produce more laptops with the same amount of inputs. In addition, people’s incomes decreased significantly because of the global financial crisis in 2008. Iflaptops are normal goodsand these are the only two things that have happened in the laptop market, what do you predict happened to the equilibrium quantity in the market for laptops after 2008?
a. The equilibrium quantity would decrease.
b. It is not certain whether the equilibrium quantity would increase or decrease.
Question 9. Suppose last year there were 8000 students on campus who owned a MacBook. Thisyear more people are choosing to using Windows 10, so the number of students owning a MacBook has fallento 7600. What is the percentage change inthe number of students owning a MacBook from last year to this year?
a. -5%
b. -0.5%
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the next three (3)questions.
Nora and Dori are famous at providing Halloween items. They can produce sweets and decorate pumpkins. Nora can produce 20 sweets
per hour or decorate 4 pumpkins per hour, while Dori can produce 40 sweets per hour or decorate 2 pumpkins per hour. Every day they each spend 4 hours working on producing these Halloween items.
Question 10. Given the above information and holding everything else constant, Nora has a comparative advantage in __________, while Dori has an absolute advantage in __________.
a. Sweets; pumpkins
b. Sweets; sweets
c. Pumpkins; sweets
d. Pumpkins; pumpkins
Question 11. Assume that Nora and Dori decide to work together and share sweets and pumpkins. Which of the following statements is
TRUE ?
a. Every day Nora could consume60 sweets and 10 pumpkins, while Dori could consume 120 sweets and 12 pumpkins.
b. Every day each of them could consume40 sweets and 10 pumpkins.
c. Every day each of them could consume30 sweets and 11 pumpkins.
d. Every day Nora could consume140 sweets and no pumpkins, while Dori could consume 40 sweets and 16 pumpkins.
Question 12. Now,assume that Nora and Dori havean argument about Halloween costumes and decide to trade with each other rather than workingtogether and sharing. What is a possible trading price for a pumpkin in terms of sweets?
a. 32 sweets for a pumpkin
b. 22 sweets for a pumpkin
c. 12 sweets for a pumpkin
d. 2 sweets for a pumpkin
Question 13. The market for bikes in Smalltown is originally in equilibrium.
The following equations describe the market for bikes in Smalltown where P is the price per bike and Q is the quantity of bikes:
Market demand: Qd = 30 - P
Market supply: Qs = P + 10
A new mayor in Small town wants to encourage people to ride bikes so the major imposes a price ceiling on bikes. What will happen in the market for bikes, if the mayor imposes a price ceiling at P = $8 per bike ?
a. The equilibrium price and quantity will remain the same as it was initially: the price ceiling will have no impact on this market.
b. The quantity of bikes supplied in the market will increase by 2 bikes relative to the initial equilibrium quantity.
c. There will be a shortage of 4 bikes in this market with the imposition of this price ceiling.
d. There will be a surplus of 4 bikes in this market with the imposition of this price ceiling
Question 14. The figure below shows the self-reported life satisfaction in India, the United States, Denmark and Chile between the 2006 and 2015. The vertical axis is an index of life-satisfaction where a higher number indicates higher life satisfaction and a lower number represents lower life satisfaction. The horizontal axis measures time by specific year.
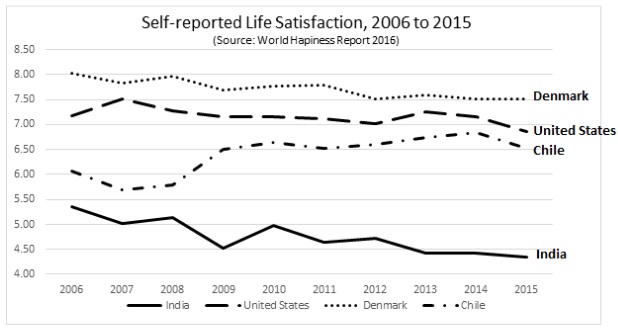
According to this figure, which country has the highest percentage change in absolute value in their self-reported life satisfaction between 2006 and 2015?
a. India
b. United States
c. Denmark
d. Chile
Question 15. A consequence of a binding (effective) price floor is:
a. An increase in consumer’s surplus relative to the consumer surplus when there is no intervention in the market.
b. An increase in the quantity demanded and a decrease in the quantity supplied relative to the market equilibrium where there is no intervention in the market.
c. Excess supplyof the good.
d. Excess demand for the good.
Use the following information to answer the next two (2) questions.
The graph below describes the market for notepads in Xerbville.
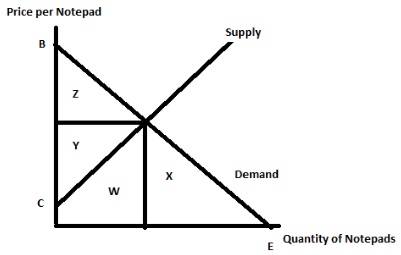
Question 16. Suppose that the government of Xerbville implements an excise tax on producers of notepads in this economy. Which of
the following statements is TRUE given the above graph and the implementation of this excise tax?
I. With the implementation of the excise tax, the government will receive a part of area Z and area Y.
II. With the implementation of the excise tax,part of area W will now be part of the deadweight loss due to the excise tax.
III. With the implementation of the excise tax, part of area Z will be part of the deadweight loss due to the excise tax.
a. Statement III is correct.
b. Statement II is correct.
c. Statements I, II and III are correct.
d. Statements I and III are correct.
Question 17. Consider the excise tax implemented in this market. Which of the following statements is TRUE given the above graph and the information you have about the excise tax?
I. The implementation of this excise tax will result in the area of consumer surplus with the excise tax and government tax revenue from the excise tax exceeding the area of producer surplus with the tax.
II. Since the tax is implemented on producers of the notepads, the producers will bear the full economic burden of this excise tax.
III. Since the tax is implemented on producers of the notepads, the producers will bear the full legal incidence of this excise tax.
IV. The implementation of this excise tax leaves society better off. In your answer assume that there are no negative attributes from consuming or producing notepads.
V. If the production and consumption of notepads create substantial pollution that society ignores in the marketplace, then the implementation of this excise tax could actually make this society better off.
a. Statements I and III are true.
b. Statements II and IV are true.
c. Statements I, II, III and V are true.
d. Statements I, III, and V are true.
Question 18. Suppose you have a magic factory at your home that can produce 5 tons of ice cream per hour, or 4 tons of frozen yogurt per hour. Your neighbor also has a factory, but with different production capacities. His factory can make 6 tons of ice cream per hour, or 3 tons of frozen yogurt per hour. Each factory only operates for 3 hours every night. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
a. Your opportunity cost of producing 2 tons of ice cream is 1.6 tons of frozen yogurt.
b. Your opportunity cost of producing 1 ton of ice cream is 1.25 tons of frozen yogurt.
c. Your neighbor’s opportunity cost of producing 2 tons of ice cream is 0.5 tons of frozen yogurt.
d. Your neighbor’s opportunity cost of producing 1 ton of ice cream is 2 tons of frozen yogurt.
Question 19. The following table describes the per capita production of beer and computers in three countries, as well aseach country’s population. (For example, a person can produce either 10 bottles of beers or 10 computers in country A, and the maximum amount of beer that can be produced in country A is 300 bottles)
Assume that the three countries start to jointly produce beers and computers. Given that 700 computers are produced, what is the maximum amount of beer that can be produced in the world?
Bottles of Beer Per Capita Computers Per Capita Population
Country A 10 10 30
Country B 20 60 10
Country C 20 10 20
a. 500 bottles of beer.
b. 600 bottles of beer.
c. 700 bottles of beer.
d. 800 bottles of beer.
Use the following information to answer the next two (2) questions.
The following equations describe the market for solar cars where P is the price per car and Q is the quantity of cars:
Market demand: P = 100 – Q
Market supply: P = 20 + Q
Assume that the government implements a price guarantee program that grants a subsidy to producers of $20 for each solar car produced.
Question 20. How much in total will the government spend underthisprice guarantee program? How much do consumers pay for each car they purchase with this price guarantee program?
a. $10; $45
b. $1000; $50
c. $800; $70
d. $2000; $20
Question 21. Suppose that the government abolishes the price guarantee program, but subsequently starts a price support program such that the solar car producers are indifferent between the two programs. What is the cost of the price support program to the government?
a. $1000
b. $1200
c. $1400
d. $1600
Question 22. Consider the market for toysdescribed by the following market demand and market supply curves where P is the price per toy and Q is the quantity of toys:
Market demand: P = 70 - 2Q
Market supply: P = 10 + Q
The government enacts a price floorwith the floor set at $20. Which of the following statements is true given this information and holding everything else constant?
a. The enactment of this price floor does not alter the value of consumer surplus in this market.
b. The enactment of this price floor results in a reduction in producer surplus in this market.
c. The enactment of this price floor creates a deadweight loss in this market.
d. Consumers benefit from enactment of this price floor in the toy market.
Use the following information to answer the next three (3) questions.
Coke and Pepsi are the only soft drinks available in a small rural community. The following equations describe the supply relationships for these two firms in this market where P is the price per drink and Q is the quantity of drinks:
Coke: P = Q + 3
Pepsi: P = 2Q - 1
The community consists of three residents: Ash, Misty and Brock. The graphs below depict Ash, Misty, and Brock's linear demand curves for soft drinks.
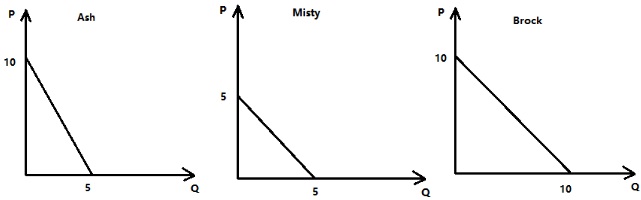
Question 23.
Given the above information and holding everything else constant, what is the slope intercept form of the market supply curve for the price range between $4 and $6?
a. P = 2Q –1
b. P = (2/3)Q + 5/3
c. P = (3/2)Q –5/2
d. P = 3Q + 2
Question 24: Draw the market demand curve for soft drinks on your scratch paper. What are the coordinates of the “kink point”?
a. (Q, P) = (2.5, 5)
b. (Q, P) = (5, 2.5)
c. (Q, P) = (7.5, 5)
d. (Q, P) = (20, 0)
Question 25. Find the market equilibrium quantity(Qe) at the intersection of the market demand and marketsupply curves.
a. Qe = 33/8
b. Qe = 15/4
c. Qe = 25/4
d. Qe = 95/16
Question 26. The following equations describe the initial demand and supply for cars in Detroit where P is the price per car and Q is the quantity of cars:
Market demand: P = 1000 – Q
Market supply: P = 2Q
Suppose that due to an economic recovery, the car manufacturers are now willing to produce 100 more cars than before at every price level. The consumers, on the other hand, are willing to pay twice as much at every quantity now, then they were willing to pay initially. Given this information and holding everything else constant, the new equilibrium quantity in this market will be:
a. 633 cars.
b. 475 cars.
c. 733 cars.
d. 550 cars.
Question 27. Suppose that in town A, the average salary in 2007 was $60,000. In 2008, due to an economic crisis the average salary droppedto $57,000. Then in 2012 the average salary wasback to $60,000. Which of the following statements is TRUEgiven this information?
a. The percentage change in average salary from 2007 to 2008 is 3%.
b. The absolute value of the percentage change in average salary from 2007 to 2008 is larger than the absolute value of the percentage change in average salary from 2008 to 2012.
c. The absolute value of the percentage change inaverage salary from 2007 to 2008 is smaller thanthe absolute value of the percentage change in average salary from 2008 to 2012.
d. The percentage change inaverage salary from 2008 to 2012 is 5%.
Question 28. The following equations describe the market for hamburgers in New York City where P is the price per hamburger and Q is the quantity of hamburgers:
Market demand: P = 100 – Q
Market supply: P = 3Q
To curb obesity in New York City, Mayor Bloomberg decides to impose a $4tax on each burger consumed.
What is the dead weight loss (DWL) associated with this tax?
a. $1
b. $2
c. $3
d. $4
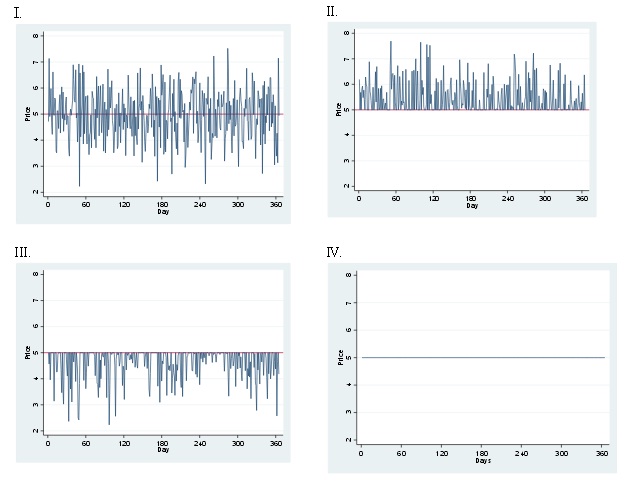
Question 29. The government decides to regulate the rental price of housing for a year by imposing a price ceiling for rent of $5000 per year. The following graphs show the daily rents for the rental housing after this price ceiling is imposed. Which of the graph (s) below
cannot possibly represent housing prices given that the regulation is strictly enforced?
In the graphs assume that price is measured in thousands of dollars.
a. II
b. II and III
c. I and II
d. II and IV