Assignment:
1. The decision to attend college should be made by carefully weighing the costs and benefits. Beyond the cost or tuition, fees, books, etc., likely the largest cost is the opportunity cost. For you, what is the opportunity cost of attending college, and explain how taking online courses, like this one, lowers the opportunity cost. (Hint: What I am really testing you on is your understanding of what opportunity cost is, but make sure to answer the whole question.)
2. For each of the following pairs, choose which good you would expect to have more elastic demand, and briefly (one sentence) explain why.
a. Popcorn at a movie theater OR popcorn at a grocery store
b. Multi-colored construction paper OR Toilet paper
c. Cool Ranch Doritos OR All types of chips
d. What does it mean for demand to be perfectly elastic? Describe a good or service that might have close to perfectly elastic demand for you, explain why the demand for this good or service fits this description.
3. Consider the market for basketball trading cards sold by Panini America, a large trading card company. For each of the following scenarios show how the change affects supply and/or demand basketball cards on a Demand and Supply model. Additionally, state the effect on equilibrium price and quantity of basketball cards. (This is in bold because so many students ignore this part).
Note: Though I am expecting you to draw the appropriate change on the supply and demand model, for turning in your exam you may just describe the change (e.g. the demand curve shifts to the right).
Example scenario: A strong economy means there consumers have more money to spend on trading cards.
Example answer: The consumer income leads to an increase in the demand for basketball cards shifting the curve to the right. As a result, the equilibrium price of basketball cards rises and the equilibrium quantity increases as well.
a. Technological improvements in printing technology allow Panini to produce their cards faster, cheaper, and more efficiently.
b. A major rival in the trading card market, Topps, begins raising the price of their cards.
c. Suppose over the last few years, the basketball card market has seen two major changes. First, cards are now expected to include more expensive materials causing the cost to produce cards to increase. Next, an increase in interest in the NBA has driven more potential consumers into the basketball card market.
d. Suppose in the scenario described in the above question (c.) we notice that the quantity of cards sold has decreased during this time, does this suggest there was a larger change in the supply of cards OR the demand for cards?
4. Jasmine sells Asian pears at her local farmers market. Until recently she charged $2.50 per pear and she was selling 70 pears per day. This week she tried selling them for $1.50 per pear and her sales went up to 90 pears per day. Use the midpoint formula to calculate the price elasticity of demand for Jasmine's Asian pears. Is the demand elastic or inelastic? Did her revenue increase or decrease with the price change? (20 points)
5. The figure below demonstrates a market for apartments in a major metropolitan area.
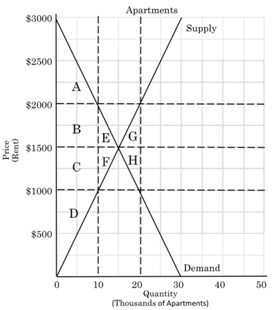
a. Suppose the government instituted a price ceiling at $1000. How many apartments would be rented in this market?
b. With the price ceiling at $1000. Would there be a shortage or a surplus in the market for apartments? How large of a shortage/surplus (I am looking for a number)?
c. With the minimum price ceiling in place, what area(s) (list the letters) represent consumer surplus in this market? What area(s) represent producer surplus? What area(s) represent dead weight loss created as a result of the minimum wage?
i. Consumer Surplus:
ii. Producer Surplus:
iii. Dead weight loss:
d. According to this model, renters (consumers of apartments in this model) are both helped (apartments are cheaper) and harmed (fewer apartments available). Again according to this model, are renters better or worse off with a the price ceiling in place? How can you tell from the model? (Hint: I have already stated how they are both helped and harmed, I am asking overall are they better or worse off using only information that can be seen above).
6. Consider the production possibilities frontier for a small country that produces two goods, tanks and butter.
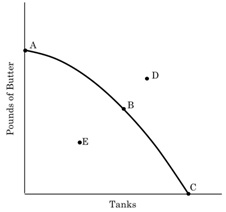
a. Does this PPF display constant opportunity cost or increasing opportunity cost between butter and tanks? How can you tell?
b. Which point or points on the PPF exhibit productive efficiency. Explain what that means.
c. Explain why we can't use the PPF model alone to make statements about allocative efficiency, what additional information is necessary?
d. What would need to happen in this economy to make a point outside the PPF, like point D attainable?
7. Elliot has $24 to spend on her two favorite things, toys and candy. Toys cost $6 and candy costs $4. The utility that she receives from both toys and candy is provided on the table below.
|
Toys
|
Total Utility
|
MU
|
MU/$6
|
Candy
|
Total Utility
|
MU
|
MU/$4
|
|
1
|
36
|
|
|
1
|
36
|
|
|
|
2
|
66
|
|
|
2
|
64
|
|
|
|
3
|
90
|
|
|
3
|
84
|
|
|
|
4
|
108
|
|
|
4
|
96
|
|
|
|
5
|
120
|
|
|
5
|
100
|
|
|
|
6
|
126
|
|
|
6
|
96
|
|
|
a. Fill out the above table completely.
b. If candy was free, how much candy would Elliot purchase?
c. With Elliot's $24 budget, what is his optimal consumption bundle? How much candy and toys does she purchase?
d. Suppose Elliot's allowance has increased so that her toy/candy budget has increased to $40. What is her new optimal consumption bundle?
e. Given your answer to part d., does are toys a normal good or inferior good for Elliot? Is candy a normal or inferior good for Elliot? Explain how you know.
f. Put the law of diminishing marginal utility in your own words. Describe a good that you purchase that demonstrates diminishing marginal utility to you. Explain why you thing that good has diminishing marginal utility.