Assignment:
1. A constant force of 500 N acts over a distance of 0.1 m on a 0.15 kg hockey puck that was originally at rest.
a. What is the work done by the force on the puck?
b. Assuming that there are no frictional losses, nor losses of any other kind (e.g., deformation of the puck), what is the kinetic energy of the puck at the end of the process?
c. What is the final speed of the puck?
2. With your left hand you lift a 3 N apple a distance of 0.25 m. With your right hand you lift a 0.7 N lime a distance of 1.5 m. Neither the apple nor the lime accelerate during their motion.
a. Which hand did the most work? What was the work?
b. Which hand exerted the greater force? What was the force?
c. What are the gravitational potential energies of the apple and the lime at the end of the process?
3. A spring of force constant k = 8000 N/m is compressed a distance of 0.05 m by a force. Assume there are no losses in the process.
a. What is the elastic potential energy stored in the spring as a result of the compression?
b. What was the work done by the external force?
4. Power plants use different types of stored energy to convert it into electrical energy.
a. What type of energy is used in a power plant powered by water in a dam in a river?
b. By a coal-fired plant?
c. By a natural gas plant?
5. How much more kinetic energy does a 2 kg mass have when it is moving at 10 m/s relative to the which it has when it is moving at 2 m/s?
a. Calculate the kinetic energy in both cases.
b.- Assuming there are no losses present, how much work had to be done by an external force to increase the speed of the 2kg mass from 2m/s to 10 m/s?
6. A 0.03 kg mass is dropped, starting from rest, from a window 8 m above the ground.
a. What are the initial values of the kinetic and potential energies of the mass? What is the total energy of the mass? Assume there are no frictional forces present.
b. When the mass is 4 m above the ground, what are the values of the kinetic, potential and total mechanical energy of the mass?
c.- What is the speed of the mass in part b.?
d. How does the potential and kinetic energies change during the fall? How does the total energy change during the fall?
7. A roller coaster cart starts from a maximum height of 50 m above the ground. Assume the roller coaster cart is frictionless and neglect air resistance.
The route of the roller coaster looks like this (braking starts at F).
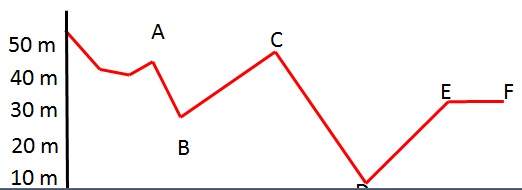
Between A and F:
a. At which point is the cart at its slowest?
b. Where is it at its fastest?
c. Over which segments is the speed increasing?
d. Over which segments is the speed decreasing?
8. Which requires greater power: lifting a mass of 10 kg a distance of 0.5 m in 20 sec, or, lifting a mass of 6 kg a distance of 1.2 m in 18 seconds?
For each case compute the work done and the power used.
9. A 50 Watt lightbulb is on for 5 minutes. How much energy does it consume?