Discuss the below:
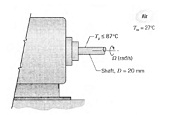
Q: The maximum surface temperature of the 20-mm. diameter shaft of a motor operating in ambient air al 27°C should not exceed 87°C. Because of power dissipation within the motor housing, it is desirable to reject as much heat as possible through the shaft to the ambient air. In this problem, we will investigate several methods for heat removal.
(a) For horizontal rotating cylinders, a suitable correlation for estimating the convection coefficient is of the form NuD = 0.133ReD2/3 Prl/3 (ReD < 4.3="" x="" 105,="" 0.7="">< pr="">< 670)="" where="" red="=" f/d2="" and="" fl="" is="" the="" rotational="" velocity="" (rad/s).="" determine="" the="" convection="" coefficient="" and="" the="" maximum="" heat="" rate="" per="" unit="" length="" as="" a="" function="" of="" rotational="" speed="" in="" the="" range="" from="" 5000="" to="" 15,000="">
(b) Estimate the free convection coefficient and the maximum heat rate per unit length for the stationary shaft. Mixed free and forced convection effects may become significant for ReD < 4.7(gr3d/pr)="" 0.137.="" are="" free="" convection="" effects="" important="" for="" the="" range="" of="" rotational="" speeds="" designated="" in="" part="">
(c) Assuming the emissivity of the shaft is 0.8 and the surroundings are at the ambient air temperature, is radiation exchange important?
(d) If ambient air is in cross flow over the shaft, what air velocities are required to remove the heat rates determined in part (a)?