I. BINARY CHOICE QUESTIONS
Question 1. The line does NOT cross
a) point (6,17)
b) point (3,8)
Question 2. "The government must keep interest rates stable," is an example of a
a) positive statement
b) normative statement
Question 3. What do we call data on the daily stock price of Samsung from 2005 to 2010?
a) Time series data
b) Cross-sectional data
Question 4. GNP is the total value of expenditures during a given year within a country's borders.
a) True
b) False
Question 5. Holding everything else constant, a decrease in Nissan car prices will cause
a) An increase in demand for Honda cars
b) A decrease in demand for Honda cars
Question 6. Holding everything else constant, if the US government decides to raise the minimum wage, this will likely result in a shortage of workers.
a) True
b) False
Question 7. Indeterminacy in prices occurs when
a) The supply and demand curves shift in the same direction
b) The supply and demand curves shift in opposite directions
Question 8. Luke studies both history and philosophy with constant opportunity costs. If he spends all week on history, he can read 200 pages. If Luke wants to read 10 more pages of philosophy, he has to give up 20 pages of history. By the end of the week, Luke reads 124 pages of history and 58 pages of philosophy. Is Luke's weekly study plan efficient?
a) Yes
b) No
Use the information below to answer the next 2 questions. The following graphs show the PPFs of the US and France. Suppose that both countries face constant opportunity costs in the production of hats and printers.
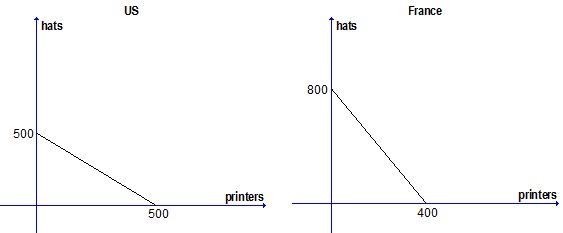
Question 9. If the US and France decide to trade with one another, which of the following is true?
a) France will specialize in printers and the US will specialize in hats.
b) The US will specialize in printers and France will specialize in hats.
Question 10. What is a possible consumption bundle for the US with international trade?
a) 180 printers, 330 hats.
b) 200 printers, 300 hats.
II. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Question 11. Which of the following equations is a correct representation of the demand curve described in the graph below?
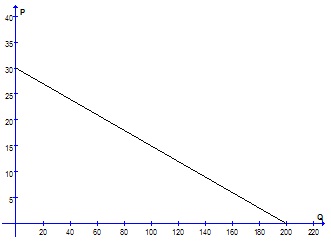
a) 30P = 200Q + 30
b) 200P + Q = 30
c) Q = -(3/20)P + 30
d) 20P + 3Q = 600
Question 12. Choose values for the missing entries A and B in the table below, assuming that the demand and supply equations are linear.
|
Quantity demanded (Units)
|
Quantity supplied (Units)
|
Price (US$)
|
|
440
|
240
|
80
|
|
A
|
280
|
160
|
|
120
|
B
|
240
|
a) A = 280 and B = 320
b) A = 240 and B = 330
c) A = 200 and B = 340
d) A = 180 and B = 350
Belgium produces only three goods: chocolate, strawberries, and waffles. Use the output information in the following table to answer the next question. Take 2010 as the base year.
|
|
2010
|
2011
|
|
|
Quantity
|
Price
|
Quantity
|
Price
|
|
Chocolate
|
20
|
$3
|
30
|
$4
|
|
Strawberries
|
75
|
$4
|
150
|
$2
|
|
Waffles
|
120
|
$5
|
110
|
$1
|
Question 13. What was Belgium's growth rate of Real GDP from 2010 to 2011?
a) 29%
b) 5%
c) 12%
d) 45%
Question 14. Suppose you are given the following information about an economy. The GDP deflator increased 20% from 2005 to 2006. Nominal GDP increased 44% from 2005 to 2006. What is the exact growth rate of real GDP between 2005 and 2006?
a) 16%
b) 20%
c) 24%
d) 28%
Question 15. Consider an economy described by the following equations:
G = 100
X - M = 50
I = 250
T = 50
C= 200 + 0.9 (Y - T)
where G is government expenditure, (X-M) is net exports, I is investment, T is the level of taxes, C is household consumption, and Y is output. What is the level of output, Y (GDP)?
a) 5550
b) 4500
c) 5050
d) 6200
Use the information provided in the table below to answer the next 3 questions. Assume that there are only three firms in the economy: Wisconsin Clothing Ltd., which produces clothing; Georgia Fabric Inc., which produces the various fabrics used in clothing production; and Texas Cotton Co., which grows the cotton needed for the production of fabric.
|
|
Wisconsin Clothing Ltd.
|
Georgia Fabric Inc.
|
Texas Cotton Co.
|
Total
factor income
|
|
Value of sales
|
$3200
|
$2000
|
$750
|
|
|
Intermediate goods
|
A
|
B
|
$0
|
|
|
Wages
|
$500
|
$1000
|
$400
|
C
|
|
Interest payments
|
$200
|
$25
|
$50
|
D
|
|
Rent
|
$400
|
$150
|
$200
|
E
|
|
Profit
|
$100
|
$75
|
$100
|
F
|
|
Total expenditures by firm
|
$3200
|
$2000
|
$750
|
|
|
Value added per firm
|
G
|
H
|
I
|
|
Question 16. What is the GDP of this economy?
a) $5200
b) $5950
c) $1900
d) $3200
Question 17. Using the "factor payments" approach to calculating GDP, which entries in the table would be added to compute GDP?
a) A and B
b) A, B, C, D, E, and F
c) C, D, E, and F
d) G, H, and I
Question 18. Provided that we use the "value added" approach to calculating GDP, which of the following missing table entries are correct?
a) A=$2000, B=$750, G=$1200, H=$1250, I=$750
b) A=$2000, B=$1250, G=$2450, H=$1250, I=$750
c) A=$2750, B=$750, G=$1200, H=$750, I=$0
d) A=$2000, B=$750, G=$750, H=$1250, I=$750
Question 19. In 2010, Tim bought 400 shares of AIG stock in the stock market through his broker. How would you describe the effect of Tim's stock purchase on GDP for 2010?
a) The value of the stock is counted in GDP; the value of the stock broker's services is counted in GDP.
b) The value of the stock is counted in GDP; the value of the stock broker's services is not counted in GDP.
c) The value of the stock is not counted in GDP; the value of the stock broker's services is counted in GDP.
d) The value of the stock is not counted in GDP; the value of the stock broker's services is not counted in GDP.
Question 20. The market for books has two producers with individual supply curves P = 5 + Q and P = (1/2)Q, where P is price and Q is quantity supplied. What is the market supply curve for books?
a) P = (1/2)Q for all pricelevels
b) P = (1/2)Q for 0 ≤ P ≤ 5 and P = 3Q - 5 for P ≥ 5
c) P = 2Q for 0 ≤ P ≤ 5 and P = 3Q - 5 for P ≥ 5
d) Q = 2P for 0 ≤ P ≤ 5 and Q = 3P - 5 for P ≥ 5
Question 21. Use the table below to answer the following question:
|
2010 UW-Madison Rental Car Market
|
|
Price ($US / hour)
|
Quantity Demanded
|
Quantity Supplied
|
|
5
|
50
|
15
|
|
10
|
40
|
30
|
|
15
|
30
|
45
|
|
20
|
20
|
60
|
|
25
|
10
|
75
|
What is the equilibrium price for this market?
a) $12
b) $16
c) $20
d) $23
Answer the next 3 questions using the diagram below, which shows the domestic market for computers in a small economy. Assume that this economy is initially closed to international trade (autarky).
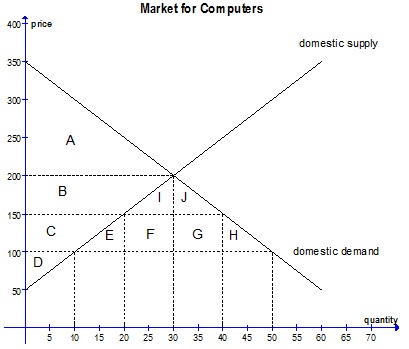
Question 22. The country opens its computer market to international trade and the world price for computers is $100. The increase in total surplus (consumer surplus + producer surplus) is equal to the area
a) E + F + G + H + I + J
b) C + E + F + G + H
c) E + F + G + H
d) I + J
Question 23. Suppose that the government is considering an import quota on computers that would have the same effect on domestic total surplus as an import tariff of $50. What import quota would achieve the government's goal?
a) An amount equal to E + H
b) 40 units
c) 20 units
d) 10 units
Question 24. After imposing an import tariff of $50, how much surplus does the economy as a whole lose (deadweight loss) relative to the free trade case?
a) $500
b) $750
c) $1000
d) $1250
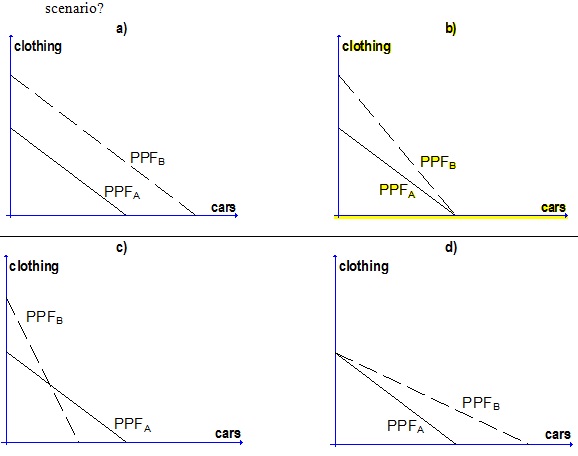
Question 25. A new technology is developed that increases the efficiency of the clothing industry. Assume that all other factors of production remain unchanged. The solid curve is the economy's PPF for cars and clothing before the change, and the dashed line is the PPF after the technology is adopted. Which of the following graphs is consistent with this scenario?
Question 26. Find the total surplus (consumer surplus + producer surplus) for the following market economy.
Supply: P = 15 + (1/2)Q
Demand: Q = 30 - P
a) $50
b) $75
c) $100
d) $150
Answer the next 2 questions using the table below, which shows the maximum amounts of coffee and rice that Cuba and Thailand can produce. Assume that both countries have constant opportunity costs of production.
|
|
Units of Coffee
|
Units of Rice
|
|
Cuba
|
60
|
30
|
|
Thailand
|
12
|
8
|
Question 27. The opportunity cost of producing one unit of coffee for Cuba is:
a) Higher than the opportunity cost of producing one unit of coffee for Thailand
b) Lower than the opportunity cost of producing one unit of coffee for Thailand
c) The same as the opportunity cost of producing one unit of coffee for Thailand
d) 2 units of rice
Question 28. Which of the following statements is true?
a) If Cuba and Thailand trade, Thailand will gain more from the trade because Cuba has the absolute advantage in both goods
b) If Cuba and Thailand trade, Cuba will gain more from the trade because Cuba has absolute advantage in both goods
c) If Cuba and Thailand trade, 0.6 units of rice would be a feasible price for coffee
d) If Cuba and Thailand trade, 1 unit of coffee would be a feasible price for rice
Question 29. The figure below represents the production possibilities frontier for carrots and bananas.
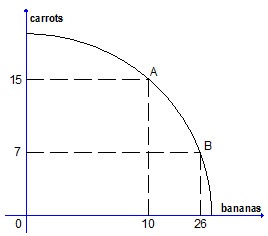
The opportunity cost of moving from point A to point B (along the PPF) is equal to
a) 8 units of carrots
b) 16 units of bananas
c) 2 units of bananas
d) (1/2) units of carrots
Question 30. The following table shows the PPF for milk and butter production in Wisconsin.
|
Milk
|
Butter
|
|
30
|
0
|
|
25
|
10
|
|
15
|
20
|
|
0
|
25
|
Assume that the PPF is linear between the points listed in the table. Which of the following production combinations is unattainable for Wisconsin (without international trade)?
a) 20 units of milk, 15 units of butter
b) 28 units of milk, 4 units of butter
c) 25 units of milk, 12 units of butter
d) 10 units of milk, 21 units of butter