Question 1: What is the definition of porosity?
Question 2: Name 3 types of seismic waves. Describe the particle motion of each wave relative to it's propagation (travel) direction.
Question 3: The Earth's upper mantle is mainly composed of:
- granite
- basalt
- iron
- olivine
Question 4: The San Andreas Fault is a:
- left-lateral strike-slip fault
- thrust fault
- right-lateral strike-slip fault
- normal fault
Question 5: The elastic rebound theory explains:
- folding of rocks
- the behavior of seismic waves
- the sudden release of stored strain in rocks, causing movement along a fault
- none of the above
Question 6: In the example of ground rock shown to the right, where is the best place to drill a well?
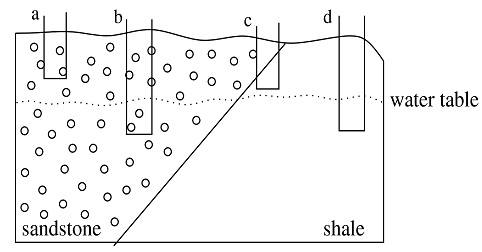
Question 7: What kind of tectonic structure occurs between the Santa Susana Mtns, the San Fernando Valley, and the Santa Monica Mnts?
- anticline
- fold and thrust belt
- mountain uplift
- extensional tectonics
Question 8: Draw a sketch of the geologic structure beneath which an oil reservoir forms. What is the name of this folded structure? Indicate the location of oil, gas, and water layers.
Question 9: If you experienced an earthquake of magnitude 5.5 and your friend in Japan experienced a magnitude 6.5, how much more ground shaking did your friend experience than you?
- 2 times more
- same
- 10 times more
- 20 times more
Question 10: What type of fault is the San Andreas Fault?
- thrust
- normal
- strike-slip
- abnormal
Question 11: Why are there large earthquakes (magnitude 6-8) on the San Andreas Fault?