Problem 1. Which of the following statements is false?
a. The supply curve for a normal good normally slopes upwards.
b. The quantity supplied of a normal good is positively related to the price of the good.
c. The demand curve for a normal good always slopes downwards.
d. An inferior good is defined as a good where an increase in the price of that good increases the demand for that good.
Problem 2. Under which of the following assumptions would an increase in the price charged by firms lead to a decrease in total revenue collected by firms?
a. Supply is elastic.
b. Supply is inelastic.
c. Demand is elastic.
d. Demand is inelastic.
Problem 3. The demand curve for salted fish is given by the equation QD = 200 – 5P. The supply curve is given by the equation QS = 5P. The government places a $10 per unit excise tax on producers of salted fish. What is the deadweight loss resulting from this government action?
a. $75
b. $100
c. $125
d. $150
Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
The following figure shows the production possibilities frontier for an economy that produces only corn and wheat.
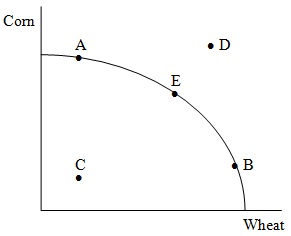
Problem 4. The bowed out shape of this PPF implies that
a. this economy has a comparative advantage in the production of corn.
b. this economy has an absolute advantage in the production of corn.
c. as the amount of corn produced increases, the opportunity cost of producing corn increases.
d. as the amount of corn produced increases, the opportunity cost of producing corn decreases.
Problem 5. Which of the following statements is false?
a. Points A and B are feasible and efficient.
b. Point E is always preferable to points A and B.
c. Point C is feasible, but inefficient.
d. Point D is not feasible.
Problem 6. A price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price. Then,
a. there will be a leftward shift in the demand curve.
b. there will be a leftward shift in the supply curve.
c. quantity demanded will be greater than quantity supplied.
d. quantity supplied will be greater than quantity demanded.
Problem 7. Which of the following statements is a normative statement?
a. New York City is the capital of the United States.
b. Italy won the world cup in 2006.
c. The world cup was in Berlin in 2006.
d. The world cup should be in Germany again.
Problem 8. Which of the following statements is false?
a. Good A and good B are complements. When the price of good A decreases, the demand for good B increases.
b. Good A and good B are complements. When the price of good A increases, the demand for good B increases.
c. Good A and good B are substitutes. When the price of good A decreases, the demand for good B decreases.
d. Good A and good B are substitutes. When the price of good A increases, the demand for good B increases.
Problem 9. The following figure shows the initial production possibility frontiers for countries A and B, each of which only produce 2 goods: cotton and milk.
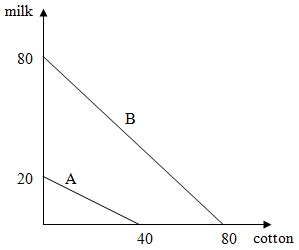
Suppose that technology in country A improves, improving their ability to produce milk. Now, if they produce 0 units of cotton, they can produce 90 units of milk. Their ability to produce cotton does not change (so that if they produce 0 units of milk, they still can only produce 40 units of cotton). Nothing changes in country B. Assume that the initial PPFs and the new PPF in country A are linear. Which of the following statements is true?
a. Country B has the absolute advantage in the production of both goods, before and after the change in country A’s technology.
b. Country A initially had the absolute advantage in the production of cotton, but after their technological improvement, they had the absolute advantage in the production of milk.
c. Country A initially had the comparative advantage in the production of cotton, but after their technological improvement, they had the comparative advantage in the production of milk.
d. Country A initially had the comparative advantage in the production of milk, but after their technological improvement, they had the comparative advantage in the production of cotton.
Use the following information to answer the next three questions.
Countries A and B only produce 2 goods, sweatshirts and jackets. The following table shows how many units can be produced in each country per week at two different production points. Assume that the production possibility frontier in both countries is linear.
Country A Country B
Sweatshirts Jackets Sweatshirts Jackets
0 50 0 20
30 0 30 0
Problem 10. What is the opportunity cost of producing a jacket in country B?
a. 5/3 sweatshirts
b. 3/5 sweatshirts
c. 2/3 sweatshirts
d. 3/2 sweatshirts
Problem 11. Which of the following statements is true?
a. Country B has the absolute advantage in the production of jackets and country B has the absolute advantage in the production of sweatshirts.
b. Country A has the comparative advantage in the production of jackets and country B has the comparative advantage in the production of sweatshirts.
c. Country A has the comparative advantage in the production of sweatshirts and country B has the comparative advantage in the production of jackets.
d. Neither country has the comparative advantage in the production of sweatshirts.
Problem 12. Suppose countries A and B were to specialize and trade with each other. For which of the following prices would both countries agree to trade?
a. 1/2 sweatshirts for a jacket
b. 2/3 sweatshirts for a jacket
c. 1/2 jackets for a sweatshirt
d. 3/5 jackets for a sweatshirt
Problem 13. Consider the market for bicycles in New York City. Due to negotiations with the labor union, the wages for the workers who produce bicycles increase. At the same time, the price of riding the bus in New York City decreases. What will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity in the bicycle market?
a. Quantity will decrease, and price will increase.
b. Quantity will increase, and price will decrease.
c. Quantity will decrease, and the effect on price is indeterminate.
d. Price will increase, and the effect on quantity is indeterminate.
Problem 14. Andi is a construction worker in Madison and earns $15 per hour. On Friday, he is scheduled to work an 8 hour shift. However, his favorite band is playing at a club in Madison on Friday, and he is considering skipping a full day of work to see the show. A ticket for the concert costs $30. What is the opportunity cost for Andi to attend the show?
a. $30
b. $45
c. $120
d. $150
Problem 15. The price elasticity of demand measures
a. how often the price of a good changes.
b. the slope of a budget line.
c. how sensitive the quantity demanded is to changes in demand.
d. the responsiveness of the quantity demanded to changes in price.
Use the following information to answer the next three questions.
The demand for cars is described by the equation 3QD = 450 – 9P. The supply of cars is described by the equation 3QS = 6P - 150
Problem 16. What is the equilibrium price and quantity in the market for cars?
a. Price is 40, and quantity is 30.
b. Price is 40, and quantity is 90.
c. Price is 30, and quantity is 50.
d. Price is 30, and quantity is 60.
Problem 17. What do the consumer and producer surplus equal in this case?
a. Consumer surplus equals 150, and producer surplus equals 225.
b. Consumer surplus equals 150, and producer surplus equals 600.
c. Consumer surplus equals 300, and producer surplus equals 225.
d. Consumer surplus equals 300, and producer surplus equals 600.
Problem 18. Public transportation becomes cheaper and the demand for cars falls by 20 units at each price. Furthermore, there is a new innovation that makes car producers more efficient. Now, car producers can supply 30 more units at each price. What is the new equilibrium price and quantity after these changes?
a. Price is 30, and quantity is 40.
b. Price is 30, and quantity is 30.
c. Price is 35, and quantity is 20.
d. Price is 35, and quantity is 135/3.
Problem 19. The supply curve for wheat is given by the equation QS = 5P. The demand curve for wheat is given by the equation P = -(1/5)QD + 10. Suppose the government wants to use a price support to allow for 40 units of wheat to be produced. Assume that storage costs are $0. How much will this program cost the government?
a. $40
b. $200
c. $240
d. $320
Problem 20. Demand is price-inelastic if:
a. a large change in quantity demanded causes a small change in price.
b. the quantity demanded is very responsive to changes in price.
c. the price elasticity of demand is less than 1.
d. the price elasticity of demand is greater than 1.
Problem 21. Economics is primarily the study of:
a. scarcity.
b. money.
c. business.
d. greed.
Use the following information to answer the next three questions.
Workers in Boston and in Chicago produce 2 goods: red and white socks. The following table shows different combinations of red and white socks that a worker in Boston or Chicago can produce in each hour. Assume that the production possibility frontiers in both cities are linear.
Pairs of Red Socks per Pairs of White socks per
Worker per hour worker per hour
Boston 5 4
Chicago 2 3
Problem 22. Which of the following statements is false?
a. The opportunity cost of producing one pair of red socks in Boston is 0.8 pairs of white socks.
b. The opportunity cost of producing one pair of white socks in Boston is 1.25 pairs of red socks.
c. The opportunity cost of producing one pair of red socks in Chicago is 1.5 pairs of white socks.
d. The opportunity cost of producing one pair of white socks in Chicago is 1.5 pairs of red socks.
Problem 23. Which of the following statements is true?
a. Boston has the comparative advantage in producing white socks.
b. Chicago has the comparative advantage in producing red socks.
c. Chicago has the absolute advantage in producing white socks.
d. We cannot determine who has the absolute advantage in the production of white socks with the information given.
Problem 24. Suppose these two cities trade with each other. Which of the following trades will both cities agree to?
a. 1 pair of red socks for 3 pairs of white socks
b. 1 pair of red socks for 2 pairs of white socks
c. 1 pair of red socks for 1 pair of white socks
d. 2 pairs of red socks for 1 pair of white socks
Problem 25. The following graph shows supply and demand in the market for textbooks.
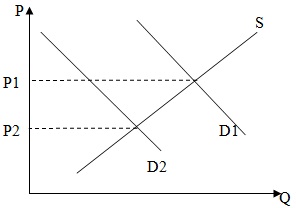
The demand curve in this economy will shift from D1 to D2 if
a. the government imposes a price floor at P1.
b. the government imposes a price ceiling P2.
c. firms in this economy adapt new technology that allows them to produce more textbooks.
d. student enrollment in school decreases.
Problem 26. Assume country A’s production possibilities frontier can be expressed as 2x + y = 80, where x denotes units of coffee and y denotes units of wheat. What is the opportunity cost of 1 unit of coffee in terms of wheat in country A?
a. 1/3 units of wheat
b. 1/2 units of wheat
c. 1 unit of wheat
d. 2 units of wheat
Problem 27. Assume that good A is a normal good. Tom’s consumer surplus from good A will
a. increase if the supply curve for good A shifts to the left.
b. increase if the price of good B, a substitute for good A, decreases.
c. increase if Tom’s income increases.
d. decrease if the price of good C, a complement in consumption for good A, decreases.
Problem 28. The demand curve for milk is given by the equation QD = -2P + 20. When the price equals $8, what is the point elasticity of demand?
a. 0.5
b. 1
c. 2
d. 4
Problem 29. Consider the market for shampoo in a country. A new technology is invented such that the productivity of shampoo production doubles. As a result, the supply curve moves from line S1 to line S2 in the figure below (assume that this is a parallel shift, so that the slope of the supply curve does not change). However, this shampoo pollutes the environment, and the government wants to restrict output to the level at the initial equilibrium (Q1).
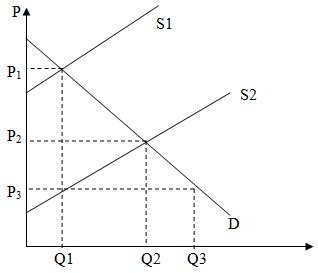
If the government levies an excise tax to reach this goal, what should the per-unit tax equal?
a. P1- P2
b. P1- P3
c. P2- P3
d. P1+ P3-P2
Problem 30. Consider the market of ice cream in Newmadison. The demand curve is given by the equation P = -Qs + 10. Points A and B are 2 points on the demand curve, as shown in the figure below.
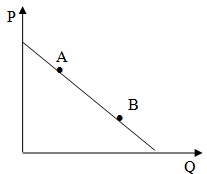
Which of the following statements is true?
a. Demand is more price-elastic at point A than at point B.
b. Demand is less price-elastic at point A than at point B.
c. Point A and point B have the same price elasticity of demand.
d. We need more information to determine whether the price elasticity of demand is larger or smaller at point A compared to point B.
Problem 31. What will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity in the market for hamburger buns if hamburgers become cheaper?
a. Price will increase, and quantity will decrease.
b. Price will increase, and quantity will increase.
c. Price will decrease, and quantity will decrease.
d. Price will decrease, and quantity will increase.
Problem 32. A 10 percent increase in the price of gasoline decreases the demand for cars by 30 percent. Thus the cross-price elasticity of demand between cars and gasoline is
a. -1/3
b. 1/3
c. -3
d. 3
Problem 33. Consider the market for grapes. Suppose that there is bad weather in California and farmers are not able to produce as many grapes as usual. Also, at the same time, wages for the workers who pick grapes increase. What will happen to the equilibrium quantity and price in the market for grapes?
a. Quantity will decrease and price will increase.
b. Quantity will decrease and price will decrease
c. Quantity will decrease and the effect on price is indeterminate
d. Price will increase and the effect on quantity is indeterminate.