BINARY CHOICE QUESTIONS:
Problem 1) A country produces only Teddy Bears and I-Pods using labor. Some workers are really skilled at producing Teddy Bears while others are really good at producing I-Pods. Say that the production of Teddy Bears has to be increased so much that some workers formerly producing I-Pods now have to start producing Teddy Bears. In this case, the opportunity cost of producing a Teddy Bear will
a. Increase
b. Decrease
Problem 2) Suppose that the city government in Madison sets an effective price ceiling on apartment rental prices. What can be said regarding the effect of this price ceiling on the apartment rental market?
a. There will be a shortage in the housing market.
b. There will be a surplus in the housing market.
Problem 3) If we are initially at a point on the demand curve where the demand is inelastic, then an increase in price will result in a (an)
a. Decrease in revenue.
b. Increase in revenue.
Problem 4) If the government pays a $1 subsidy to the farmers on every pound of apples sold, the farmers receive a dollar more per pound of apple than they would have without the subsidy. This statement is ______.
a. True
b. False
Problem 5) Suppose Australia produces more toothbrushes per hour and fewer envelopes per hour than Indonesia. These countries only produce these two goods. Thus, Australia will have a comparative advantage in producing toothbrushes.
a. True
b. False
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
Use the following graph to answer the next two questions.
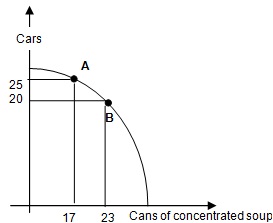
Problem 6) Human-like creatures living in Mars produce two goods only: cars and cans of concentrated soup. The Martians’ production possibility frontier (PPF) is given above. Their current production is at point A on the PPF. If the Martians reallocate their resources and move from A to B on the PPF, what can be said about the new production bundle?
a. The new point is efficient and the opportunity cost of cars has increased.
b. The new point is not efficient and the opportunity cost of cars has increased.
c. The new point is efficient and the opportunity cost of cars has decreased.
d. The new point is not efficient and the opportunity cost of cars has decreased.
e. none of the above
Problem 7) What is the opportunity cost of producing 1 car in terms of cans of concentrated soup when this economy moves from point A to point B?
a. 6/5 cans of concentrated soup.
b. 5/6 cans of concentrated soup.
c. 20/23 cans of concentrated soup.
d. 23/20 cans of concentrated soup.
e. None of the above.
Use the following information and graph to answer the next three questions.
Kenya and Laos produce only soybeans and robots. The following graph (not to scale) shows the linear production possibility frontiers for both Kenya and Laos:
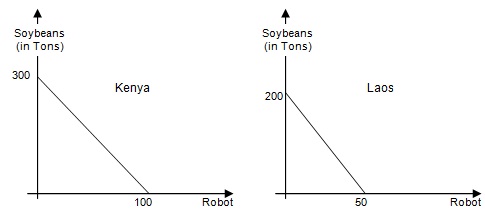
Problem 8) Which of the following statements is true?
a. Laos has the comparative advantage in the production of robots but no absolute advantage in production of either good.
b. Laos has the comparative advantage in the production of robots and the absolute advantage in the production of soybeans.
c. Kenya has the comparative advantage in the production of robots and the absolute advantage in the production of soybeans.
d. Both Kenya and Laos have absolute advantage in the production of soybeans.
e. None of the above
Problem 9) Kenya produces 150 tons of soybeans and 45 robots. Laos produces 100 tons of soybeans and 25 robots. As a result,
a. Kenya’s production is inefficient and Laos’ production is efficient.
b. Kenya’s production is efficient and Laos’ production is inefficient.
c. The production in both countries is efficient.
d. The production in both countries is inefficient.
e. None of the above
Problem 10) Kenya produces 150 tons of soybeans and 50 robots. Laos produces 100 tons of soybeans and 25 robots. As a result,
a. There are no possible gains from trade.
b. There are gains from trade, but only for Laos.
c. There are gains from trade, but only for Kenya.
d. There are gains from trade, both for Laos and Kenya.
e. None of the above
Problem 11) Reducing a tariff will ______ the domestic production of the good and ______ the total domestic consumption of the good.
a. increase; increase
b. increase; decrease
c. decrease; increase
d. decrease; decrease
e. no effect on; no effect on
Use the following information and table to answer the next two questions.
Germany and Portugal are two countries producing peanuts and mirrors. Both of them have 40 hours of labor. The following table shows the number of hours of labor needed to produce one pound of peanuts or one mirror.
Labor hours needed to produce one
pound of peanuts mirror
Germany 4 8
Portugal 8 20
Problem 12) What is the opportunity cost of producing a mirror in Germany?
a. 1/2 pound of peanuts
b. 2 pounds of peanuts
c. 2/5 pounds of peanuts
d. 5/2 pounds of peanuts
e. It cannot be determined from the information given.
Problem 13) Which of the following statements is true?
a. Germany has the comparative advantage in the production of mirrors but no absolute advantage in the production of either good.
b. Portugal has comparative and absolute advantage in the production of peanuts.
c. Germany has the comparative advantage in the production of peanuts and absolute advantage in the production of mirrors.
d. Portugal has the comparative advantage in the production of peanuts, but no absolute advantage in the production of either good.
e. Portugal has no comparative advantage in the production of either good.
Problem 14) If Derek can produce green tea at a higher opportunity cost that Ignacio, then
a. Ignacio has a comparative advantage in the production of green tea.
b. It is obvious that Ignacio is capable of producing more green tea than Derek.
c. Derek does not have the absolute advantage in the production of green tea.
d. Derek has a comparative advantage in the production of green tea.
e. It is impossible to answer the question without knowing the available resources that Derek and Ignacio have.
Problem 15) A fall in the price of sugar from $10.50 to $9.50 per pound increases the quantity demanded from 188 to 212 pounds. The price elasticity of demand (using arc elasticity) is
a. 0.8
b. 1.0
c. 1.2
d. 8.0
e. 0.2
Please use the following graph to answer the next four questions.
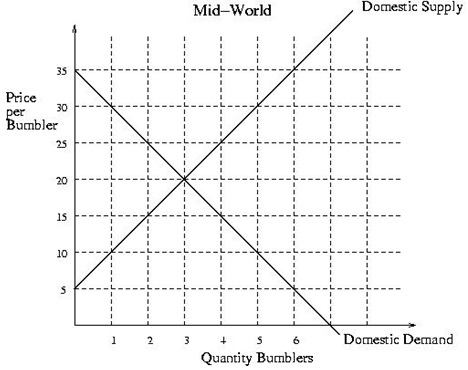
Problem 16) The above figure shows the domestic supply and domestic demand in Mid-World for Bumblers. Mid-World is open to free trade. If the world price for Bumblers is $10 then Mid-World will produce ____________ Bumblers and consumers will purchase _________ Bumblers, and the difference between these two quantities will be Mid-World’s _________.
a. 2; 4; exports
b. 5; 1; exports
c. 4; 2; imports
d. 1; 5; imports
e. 3; 3; imports
Problem 17) Again, referring to the same figure, Mid-World is open to free trade and the world price of Bumblers is $10. The consumer surplus is
a. $22.5
b. $35
c. $40
d. $62.5
e. $2.5
Problem 18) Again, referring to the same figure, Mid-World is open to free trade and the world price of Bumblers is $10. Let PS1 denote the producer surplus in Mid-World with an open economy with no tariff. Suppose now that a $5 tariff is imposed on the Bumblers. Let PS2 denote the producer surplus in Mid-World with an open economy with the tariff. Then, the change in the producer surplus due the imposition of the tariff is (PS2 - PS1). Please calculate this amount.
a. $2.5
b. $5
c. $7.5
d. $10
e. $15
Problem 19) The government wants to implement an import quota program that will have the same effect on the market as the $5 tariff program. The size of the import quota that would have achieved this same effect on trade as the tariff is
a. 1 unit
b. 2 units
c. 3 units
d. 4 units
e. 5 units
Use the following information to answer the next three questions.
Consider the cigarette market. The market demand for cigarettes is given by P = 50 - QD. The market supply of cigarettes is given by P = 10 + 4QS. Suppose that the government designs a tax program to reduce the number of smokers; it imposes an excise tax of $5 per pack on cigarette producers.
Problem 20) What is the change in consumer surplus due to this tax program?
a. $32
b. $49
c. $24.5
d. $17.5
e. $7.5
Problem 21) What is the tax incidence on producers?
a. $7
b. $8
c. $28
d. $32
e. $35
Problem 22) What is the deadweight loss that results from the tax program?
a. $5
b. $2.5
c. $1
d. $3
e. $4
Problem 23) The figure below shows three linear demand curves. Which point has the same point elasticity of demand as point B?
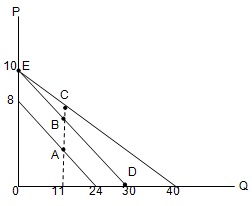
a. A
b. C
c. D and E
d. A and C
e. None of the above.
Problem 24) A quota is:
a. a tariff imposed on goods that are dumped in the country.
b. a law that prevents ecologically damaging goods from being imported into a country.
c. a market-imposed balancing factor that keeps prices of imports and exports in equilibrium.
d. a government-imposed restriction on the quantity of a specific good that can be imported.
e. none of the above
Problem 25) Consider the coca-cola market. Assume that coca-cola and water are substitute goods. Suppose that the government decides to impose an excise tax on producers in the coca-cola market. Simultaneously, the price of water increases. Then, the equilibrium price of coca-cola will ____ , and the equilibrium quantity of coca-cola will _______.
a. fall, fall
b. rise, rise
c. rise, not be determined
d. not be determined, fall
e. fall, not be determined
Problem 26) Consider the orange juice market. Assume that oranges are an input to orange juice production and that oranges are also a substitute good in consumption of orange juice. Suppose that there is an effective price floor in the orange juice market. Furthermore, suppose that the price of oranges falls. The equilibrium price of orange juice will ____ and the quantity of orange juice that is traded will _____. (Warning: This is a though question and we are certain that the correct answer is among the choices below.)
a. rise, rise
b. fall, rise
c. fall, fall
d. change in an ambiguous amount, fall
e. stay the same, fall
27) Lazy Luke has the option to work at the Memorial Union or beg money from his parents. He cannot do the two tasks at the same time. The hourly wage at the Memorial Union is $8. If Lazy Luke begs money from his father for one hour he gets $6. If he begs money from his mother for one hour he gets $9. However, if he begs money from his mother and father together for one hour he gets $7.5. What is the opportunity cost of having a 3-hour nap for Lazy Luke?
a. $24
b. $51
c. $27
d. $45
e. none of the above.
The next four questions are based on the following information.
Suppose that the market for wheat in the U.S. is characterized by the following demand and supply functions:
Supply: QS = 5 + 4P
Demand: QD = 30 - P
where quantity is measured in billions of bushels and price in dollars per bushel.
Problem 28) Find the market equilibrium.
a. Price= $10, quantity= 20 billion bushels
b. Price= $8, quantity= 12 billion bushels
c. Price= $5, quantity= 25 billion bushels
d. Price= $6, quantity= 24 billion bushels
e. None of the above
Problem 29) The government introduces a subsidy program where a subsidy of $5 per bushel is granted to wheat producers. What quantity will be traded in the market under this subsidy program?
a. 29 billion bushels
b. 28 billion bushels
c. 27 billion bushels
d. 26 billion bushels
e. 25 billion bushels
30) How much deadweight loss will arise as a result of the subsidy program?
a. $2 billion
b. $4 billion
c. $5 billion
d. $10 billion
e. $20 billion
Problem 31) Now the government revises its agricultural policy and adopts a price support program rather than a subsidy program. The government implements the price support program by using a price floor equal to $7. What is the (direct) cost of the price support program to the government?
a. $30 billion
b. $45 billion
c. $70 billion
d. $161 billion
e. $210 billion
Problem 32) Suppose that the government introduces a price floor in a particular agricultural market. If demand for the agricultural product is _______ and supply is ________, the resulting excess supply associated with the price floor will become larger.
a. inferior; normal.
b. elastic; elastic
c. inelastic; inelastic
d. elastic; inelastic
e. inelastic; elastic
Problem 33) Takeshi consumes two goods: A and B. Which of the following observations imply that good A is an inferior good for Takeshi?
a. Takeshi’s demand for good A falls as his income falls.
b. Takeshi’s demand for good A falls as his income increases.
c. Takeshi’s demand for good B falls as his income falls.
d. Takeshi’s demand for good A rises as the price of good B falls.
e. Takeshi’s quantity demanded of good A falls as the price of good A falls.
Problem 34) Suppose that market supply for grapefruit is given by QS =3P and the market demand is given as QD = 10 - 2P. Which of the following would lead to an increase in total revenue for the producers?
a. The price of grapefruit juice (a substitute good in consumption) goes down.
b. A storm destroys the grapefruit orchards.
c. Good weather helps the farmers to harvest more grapefruit.
d. The number of farmers who grow grapefruit increases.
e. Both (c) and (d).
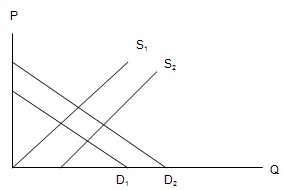
Problem 35) The above picture shows the demand and supply curves in the wooden table market. Which of the following statement is false?
a. A decrease in the price of wood causes a shift in the supply curve from S1 to S2.
b. An improvement in wood carving technology causes a shift in the supply curve from S1 to S2.
c. An increase in the price of wooden chairs causes a shift in the demand curve from D2 to D1.
d. An increase in the price of aluminum tables causes a shift in the demand curve from D1 to D2.
e. If consumers tend to prefer wooden tables more than they did before, the demand curve will shift from D2 to D1.