The following molecule is chloroethane.
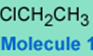
It is unreactive towards hydroxide and most nucleophiles under normal conditions, i.e., the chlorine-carbon bond is not a very good electrophilic center, hence 1 is not a good alkylating agent and does not transfer the CH3CH2 group easily.
On the other hand, there is a class of drugs that contain a chloroethyl group which are good alkylating agents and have been used clinically to treat cancer. An example of this class of drugs is melphalan.
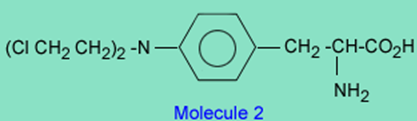
The reason melphalan, is a good alkylating agent, and 1 is not, is due to the formation of the intermediate 3 caused by the close proximity of a basic nitrogen to the carbon-chlorine bond in 2. Reaction of 3 with a nucleophile (Nuc) gives the alkylated nucleophile, 4.
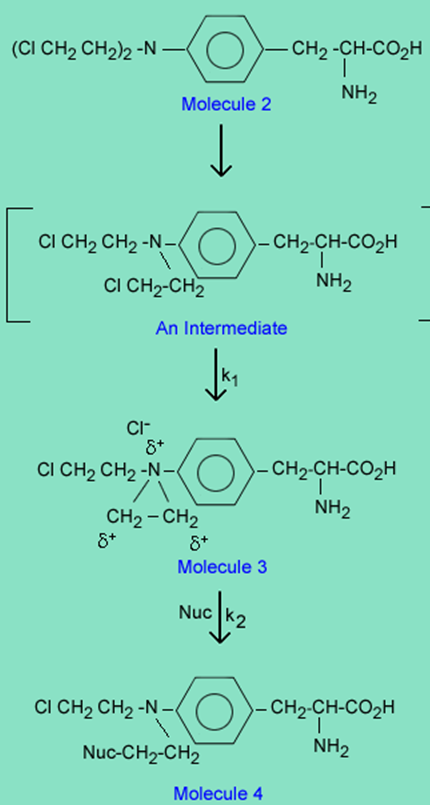
In vivo, in a therapeutic setting, the Nuc is specifically a nitrogen or oxygen on a purine in a DNA strand, which once alkylated cleaves from the DNA strand to create errors in reading the DNA code and ultimately death of a cancer cell. The alkylation takes place in two steps defined by the rate constants k1 and k2.
1. If k1 > k2, is the overall reaction of molecule 2àmolecule 4 an SN1 or SN2 reaction?
2. Conversely, if k2 > k1 is the overall reaction SN1 or SN2? Explain why.
3. If the basic pKa of the nitrogen in the -N-(CH2 CH2 Cl)2 in molecule 2 is 1.5 and the basic pKa in the -N-(CH2 CH2 Cl)2 in Molecule 5 is 6.5, which drug, (molecule 2 or molecule 5) is more likely to go by an SN1 reaction with the nucleophile and why? Note that the rate or ease of reaction k1 for 2à3 will depend on how basic is the nitrogen in -N-(CH2 CH2 Cl)2.
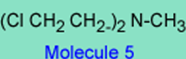
Assignment Two:
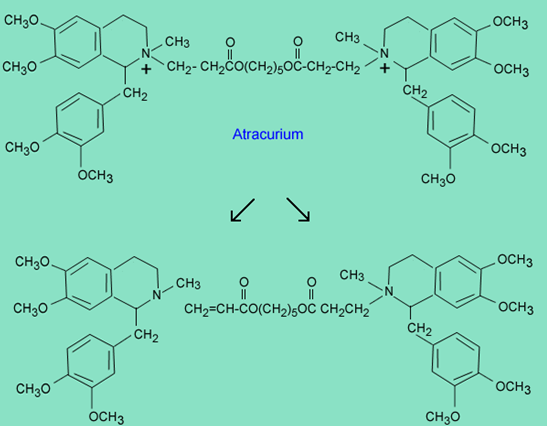
The following molecule, atracurium, is a very complex drug. It is a neuromuscular blocking agent and is related to the natural product tubocurarine. Atracurium exhibits a very short half-life (20-min). The products of the fastest inactivation process are shown below.
Explain what mechanism is responsible for the formation of the products.
Hint: The acidic pKa of CH3(C=O)CH3àCH3(C=O)CH2 - is 20.