BINARY CHOICE QUESTIONS:
Question 1. The lines y = 5 + 2x and 3y + x = 30 do not intersect.
a. True
b. False
Question 2. Which of the following statements is a positive statement?
a. Sam and Hans should produce the number of apples and oranges at the kink point of their joint PPF graph.
b. Sam has an absolute advantage in the production of apples, while Hans has an absolute advantage in the production of oranges.
Question 3. Kate is a junior in high school and is deciding whether or not she should attend college. The full-time salary that Kate forgoes to attend college is considered an accounting cost.
a. True
b. False
Question 4. Tom owns a bakery. He uses two secret ingredients “A” and / or “B” to prepare his world-famous cookies. In a particular year, you observe that his demand curve for “A” shifts right. Which of the following statements might be consistent with this shift?
a. “A” and “B” are complements, and the price of “B” has gone up.
b. “A” and “B” are substitutes, and the price of “B” has gone up.
Question 5. Consider that fast food is an inferior good for Beth. She will reduce her consumption of fast food if she receives a 15% wage increase.
a. True
b. False
Question 6. Apartment rent in Madison is currently $1,000 per month. The government is planning to establish a price ceiling of $1,200 per month for apartment rent. This policy will most likely create a shortage of apartments in Madison.
a. True
b. False
Question 7. Brazil and Colombia both produce soy beans and coffee beans. Suppose we observe Brazil imports coffee beans from Colombia, and they export their soy beans to Colombia. Which of the following statements may be false given this information?
Assume that the coffee beans and soy beans grown by the two countries are identical.
a. Colombia has the absolute advantage in the production of coffee beans.
b. Colombia has thecomparative advantage in the production ofcoffee beans.
Question 8. In the financial crisis, the value of the houses owned by American citizens collapsed. How would you represent this event in the T-account of American citizens?
a. As a decrease in the value of assets and a decrease in net worth.
b. As a decrease in the value of liabilities and an increase in net worth.
Question 9. Suppose that you have a market with a downward sloping demand curve and an upward sloping supply curve. The implementation of an excise tax in this market will always reduce the value of
both the consumer surplus and the producer surplus.
a. True
b. False
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Question 10. (Warning: this problem will either be easy for you or VERY HARD-do not spend too much time on this question!) As of 2016, the European Union comprised 28 member states. The GDP (gross domestic product) per capita of the European Union is equal to $40,000, and the average population of these 28 countries is 20million inhabitants. Eight additional countries (Albania, BosniaHercegovina, Croatia, Iceland, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Turkey) have applied to join the European Unionin the last decade. Suppose that the current GDP per capita of these eight countries is equal to $20,000. Finally, consider that the average population of the eight countries that are looking forward to joining the European Union is equal to 10million inhabitants. Approximately, what would be the new GDP per capita of the European Union, if the current member states decide to accept the applications to join the European Union of these eight countries?
a. $ 30,000
b. $ 33,300
c. $ 34,400
d. $ 37,500
Use the following information to answer the next two (2) questions.
Susan is working on the family farm. She has two main responsibilities: picking apples and collecting eggs. Susan can collect 30 eggs in 2 hours, and can pick 60 apples in 1 hour.
Question 11. What is Susan’s opportunity cost of collecting 1 egg (in terms of picking apples)?
a. 1/2 apples
b. 2 apples
c. 4 apples
d. 6 apples
Question 12. Suppose a new technology is introduced on the farm that allows Susan to pick apples at a faster rate.
Holding everything else constant, how does this affect Susan’s opportunity cost of collecting 1 egg (in terms of picking apples)?
a. Her opportunity cost of collecting 1 egg increases.
b. Her opportunity cost of collecting 1 egg decreases.
c. There is no effect on her opportunity cost of collecting 1 egg.
d. Her opportunity cost of collecting 1 egg may have increased, decreased, or remained the same.
Question 13. Mark, Kim, and Larry are students at the computer engineering department at UW Madison. Besides studying, each of them can work 800 hours per year. Each of them can use their time to design either websites (w) or Android apps (a).
Assume that each of these individuals has a linear production possibility frontier in the production of these two goods. Mark can design a website in 100 hours and an Android app in 200 hours, Kim can design a website in 80 hours and an Android app in 200 hours, and Larry can design a website in 100 hours and an Android app in 100 hours. Assume that they decide to create a companytogether. Which graph (these graphs are NOTdrawn to scale) represents most accurately the joint PPF of their company?
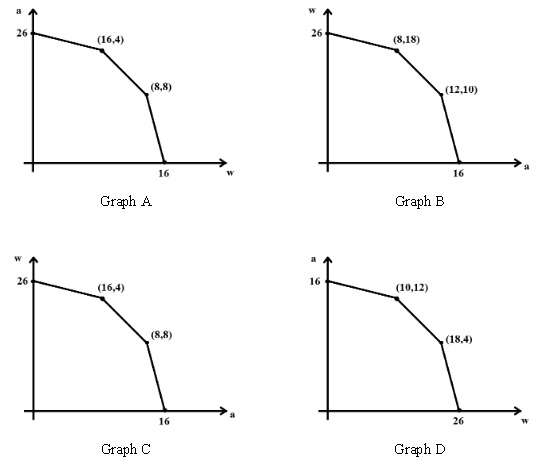
a. Graph A
b. Graph B
c. Graph C
d. Graph D
Use the following information to answer the next three (3) questions.
Every Japanese or American worker can produce 5 cars per year. Each American worker can produce 2 tons of rice and each Japanese worker can produce 3 tons of rice per year. Assume that each country has 10 million workers.
Question 14. Which of the following statements is true, given the above information and holding everything else constant?
a. Neither country has a comparative advantage in the production of cars. Japan has a comparative advantage inthe production of rice.
b. Japan has the comparative advantage in the production of both rice and cars.
c. Japan has the comparative advantage in the production of cars, and the US has the comparative advantage in the production of rice.
d. Japan has the comparative advantage in the production of rice, and the US has the comparative advantage in the production of cars.
Question 15. What is the equation for their joint PPF? Consider that c represents millions of cars and r represents millions of tons of rice
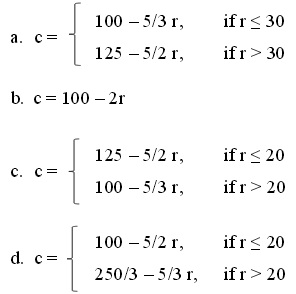
Question 16. Which of the following is an acceptable price to both countries for one car in terms of tons of rice assuming that both countries are specializing in the production of the good for which they have a comparative advantage?
a. 1/8 tons of rice
b. 1/4 tons of rice
c. 1/2 tons of rice
d. 1 ton of rice
Question 17. Which of the following events will most likely NOT cause a shift to the left in the supply curve of tomatoes in Florida? Holding everything else constant,
a. The publication of a scientific study that links tomato consumption and stomach cancer.
b. A financial crisis in Florida that forces the majority of tomato harvesters to go bankrupt.
c. An increase in the price of fertilizers required to harvest tomatoes.
d. A hurricane that destroys a big percentage of tomato fields.
Question 18. Suppose that the price of leather shoes has not changed in the last month, but the quantity sold has increased dramatically. Which of the following combination of events is consistent with this information?
a. The cost of leather has increased, and the price of wool socks (a complement of leather shoes) has also increased.
b. The cost of leather has increased, and the price of tennis shoes (a substitute of leather shoes) has increased.
c. The cost of leather has decreased, and the price of tennis shoes (a substitute of leather shoes) has also decreased.
d. The cost of leather has decreased, and the price of wool socks (a complement of leather shoes) has also decreased.
Question 19. Suppose that you are a policymaker that wants to increase the consumption of milk in your economy. Which of the following policies could help you achieve your goal without having to intervene directly inthe milk market? (Assume milk and cereal are complements, while milk and soy milk are substitutes.) Holding everything else constant, enact a policy that
a. Reduces the price of cereal.
b. Increases the supply of soy milk at every price.
c. Reduces the price of soy milk.
d. Increases the price of cereal.
Use the following information toanswer the next three (3) questions:
Consider the market of airplane tickets from Madison to Chicago, in which only two companies offer tickets: American Airlines and United Airlines. An analyst is analyzing the whole market using the available data.
The analyst knows that the following equations describe the individual supply curves for the two firms where P is the price per ticket and Q is the number of tickets.
American Airlines supply curve: P = 100 + 1/4 Q
United Airlines supply curve: P = 300 + Q 20.
Question 20: Given this information and holding everything else constant, the market supply curve (include the supply from both airlines) is given by:
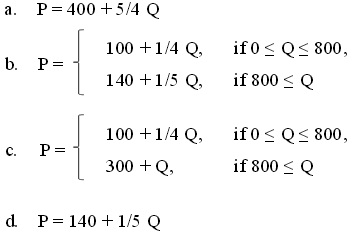
Question 21. Hint: This is a challenging question and you need to be careful in your analysis! The analyst also has the following demand schedule representing the demand for airplane tickets for men and women.
Price of ticket Q demanded by men Q demanded by women
$0 400 200
$300 250 50
$600 100 0
Assuming that the demand curves for men and women are linear, what are the coordinates of the kink point of the market demand curve?
a. (Q = 300, P = $300)
b. (Q = 200, P = $400)
c. (Q = 100, P = $600)
d. The market demand curve doesn’t have a kink point.
Question 22. Using all the previous information, which is the equilibrium quantity of airplane tickets?
a. 100 airplane tickets
b. 200 airplane tickets
c. 400 airplane tickets
d. We don’t have enough information to solve for the equilibrium quantity
Use the following information to answer the next two (2)questions.
In Oshkosh, Wisconsin the following equations describe the demand and supply for bananas where P is the price per banana and Q is the quantity of bananas:
Market demand: Qd = 9 - P
Market supply: Qs = 1/2 P
Question 23. Suppose that the government establishes a price floor of $8 per banana. At that price floor:
a. There is a shortage of 1 banana.
b. There is a shortage of 3 bananas.
c. There is a surplus of 3 bananas.
d. At a price floor of $8 per banana there is not a surplus nor a shortage of bananas.
Question 24. The government decides to repeal the price floor, so that the price and quantity are now determined by the market outcome. Which of the following statements accurately describes a consequence of the removal of the price floor?
a. Total surplus increases by $6.
b. The producer surplus is smaller in the market equilibrium than it was with the price floor.
c. Consumer surplus increases by $2.
d. Nothing happens. The equilibrium quantity and equilibrium price stay the same as they were with the pric
e floor.
Use the following information to answer the next two (2) questions.
Suppose that the state government is trying to promote apple production in Eau Claire, Wisconsin. To do this, they implement a “Price Support Program” in which the government sets up a price floor and agrees to buy any surplus generated in the apple market.
Assume that there are no storage costs to this program.
The following equations describe demand and supply in this market where P is the price per apple and Q is the quantity of apples:
Market demand: Qd = 10 - P
Market supply: Qs = P -225.
If the government has a limited budget of $54 to spend on this program and is trying to maximize as much as it can the producer’s surplus, which price floor would the government select?
a. A price floor set at $5 will maximize producer's surplus while staying within the budget constraint.
b. A price floor set at $7 will maximize producer's surplus while staying within the budget constraint.
c. A price floor set at $9 will maximize producer's surplus while staying within the budget constraint.
d. A price floor set at $11 will maximize producer's surplus while staying within the budget constraint.
Question 26. Suppose now that the government decides to change its policy and implement a “Price Guarantee Program” (a subsidy program) instead of a “Price Support Program”. If the government implements a price guarantee of $8, how much money would the government spend on this program?
a. $ 24
b. $ 30
c. $ 36
d. $ 48
Use the following information to answer the next three (3) questions. The state government wants to reduce the consumption of soda in Wisconsin. The following equations describe the market for soda in Wisconsin where P is the price per soda and Q is the quantity of sodas:
Market demand: Qd = 60 – 3P
Market supply: Qs = 2P
To reduce consumption of soda the government imposes an excise tax of $5 per soda that is levied on the consumers.
Question 27. This tax causes the quantity of soda consumed in equilibrium to decrease by approximately:
a. 16.67%
b. 25%
c. 33.33 %
d. 66.67%
Question 28. Fill in the following two blanks based on the information you have been given and holding everything else constant.
The tax revenue from this excise tax of $5 per soda is equal to __________ . If the government decided to increase the excise tax by an additional $15 per soda, the tax reve nue would __________.
a. $100; increase.
b. $90; decrease.
c. $70; increase.
d. $60; decrease.
Question 29. Suppose now that after establishing the excise tax of $5 per soda, the government plans to use the tax revenue to reduce the consumption of soda even further. Which combination of the following additional policies would best accomplish the government’s goal? Use the following assumptionsin doing your analysis:
1) sugar cane is an input in the production of soda;
2) soda and coffeeare substitutes in consumption;and
3) you use coffee beans to produce coffee.
a. Establish an effective Price Support Program for coffee beans.
b. Establish an effective Price Support Program for sugar cane where the government buys the surplus and then destroys the surplus.
c. Establish an effective Price Guarantee Program for sugar cane.
d. Either (b) or (c) would be policies that would diminish the consumption of soda