Assignment Problem I: Surface Mining Operations and Equipment
Problem 1: A new coal mining operation is to be worked employing surface mining using blasting to clear an overburden of Shale using 150mm holes and 11m benches. Dry rock conditions are anticipated and the decision is to use bulk ANFO with emulsion cartridges as a primer. The density of compacted ANFO = 0.85 g/cm3 and the PF is expected not less than 0.65 kg/m3. You are required to do the blast design to facilitate the production request of stripping 2,000,000 m3 overburden annually, including the followings,
(1) Drilling and blasting schedule and production;
(2) Blasthole drilling pattern;
(3) Details of blasthole parameters, e.g. burden and spacing, subdrill and inclination;
(4) Details of blast control techniques employed;
(5) Blast circuit / initiation pattern.
Please include a design drawing whenever appropriate for each of the design.
Problem 2: Illustrate with suitable cross-section sketches showing ore and waste components, how overall stripping ration can be;
a. Constant
b. Increasing
c. Decreasing over the life of an open-pit mine.
Problem 3: Two surface mines are considering the use of a conveyor in conjunction with their current fleet of trucks and shovels. The mines are;
i. a strip mine operation in which coal is transported out of the strip from a depth of 37m to a coal plant on surface, at a rate of 1.2 million tons per month.
ii. an open-pit operation in which coal and waste are transported from a depth of 300m to either a waste dump or a processing plant on surface, at a rate of 1.22 million tons per month (ore) at a stripping ratio of 3:1.
Give advice to the mines concerning the practicality and utility of using a conveyor to either replace or supplement the existing systems with proper justification.
Give advice to the mines as to what extra additional equipment they may need if they were to combine existing and new conveyor systems with proper justification.
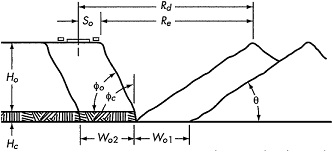
Problem 4: A coal strip mining is designed to use dragline operation as illustrated below. The swell of the spoil is 1.25 to 1.30. You are required to design the effective radius Re and select a dragline that is suitable to the mine. Ho = 16 m, Hc = 4.5 m, pit width = 40 m, Φo = Φc = 70°, θ = 40°.
Assignment Problem II: Surface Mining Operations and Equipment
Problem 1: Explain the terms
- Bench and overall slope angles
- Overall, breakeven and immediate stripping ratios, with reference to the open pit mining method.
- Mineral resource and Ore reserve
- Cut-off grade
- Powder factor
- Charge density
Problem 2: An open pit mine employs ANFO at a density of 0.8 g/cc as its explosive. Given the following details, determine the blasthole spacing.
- Blastholes are vertical and bench height is 12m.
- Burden and spacing of blastholes are the same, i.e. B = S.
- The specific gravity of the rock is 2.5.
- The powder factor is 0.5 kg of explosive per m3 of rock.
- Hole diameter is 225 mm.
- Stemming column length is 3 m and subdrill is 2m.
If ANFO has a cost of $1050 per tonne, what will be the cost of explosives per tonne of rock?
Problem 3: Explain various deciding factors related to choice of surface mining over underground mining methods.
Problem 4: Discuss the concept of stripping ratio and how haul road gradient, bench, stack and overall slope angles affect it.
Problem 5: Illustrate with a suitable diagram, how waste overburden and orebody geometry dictates the choice of surface mining method.
Problem 6: What is meant by "break-even stripping ratio" and what factors would you consider when you need to determine its value?
Problem 7: What is difference in opencast, open pit and quarry mining?
Problem 8: Briefly describe frontal cut, drive-by and stop-and-reverse parallel operations.
Problem 9: Explain the following terms with the aid of sketches, as they apply to an open-pit operation;
(a) Overall slope angle
(b) Bench stack slope angle
Problem 10: Why is the individual bench slope angle steeper than the stack slope angle, which is steeper than the overall pit slope angle?
Problem 11: A dragline is to be selected to remove overburden at a rate of 395,000 cubic meters per month. If it will be scheduled to operate 720 hours per month with an operating efficiency of 0.80, its bucket factor is 0.85 and its cycle time is 54 seconds, what should be the size of its bucket?
Problem 12: Describe briefly how the operational life of a mine can influence the choice of transport equipment. Refer in your answer to a new open-pit mine and a deep open-pit mine that is near the end of its production lifetime.
Problem 13: Briefly describe the applications of the below equipments in surface mining. What are the major factors affecting the selection?
(a) Mining shovel,
(b) Dragline
(c) Bucket wheel excavator
(d) In-pit crusher
(e) Rail haulage
(f) Truck
(g) Conveyor belt
Problem 14: Explain the importance of slope angle in economics of surface mines by some example.
Problem 15: A discontinuity is found fully developed from the toe to the bench surface on a 20 m high slope, slope angle 63? The discontinuity (frictional angle 32? and cohesion 20 kN/m2) is planar and its strike is parallel to the slope face with a dip 42?. Determine the factor of safety in case of a planar slope failure assuming drained conditions. Unit weight of the rock is 2.7 t/m3.
Problem 16: Illustrate bench width. Why should we provide safety bench? What are the factors affecting the width of safety bench?
Problem 17: What is pit limit? Describe a procedure to determine pit limits.
Problem 18: Estimate the unit profit in mining and processing a 0.80% copper ore deposit if the selling price of copper in concentrate is $1.73/kg and overall unit costs are $6.5/ton. Overall recovery is 82%. Calculate the cut-off grade of the copper deposit.
Problem 19: A surface mine operators needs to purchase a front-end loader that will be used to load ripped coal onto on-highway dump trucks. The mine operates two 7 hour shifts per day, 5 days per week, and 50 weeks per year. The daily production of coal is 1500 tons. The desired cycle time is 1.0 min or less. The density of loose coal is approximately 1.0 t/m3. Assume that the load factor is 0.65, the bucket factor is 1.23 and the operating factor is 0.75. What bucket size is required?
Problem 20: Assume an underground mining cost of $25.5/ton ore for an ore body. Assume open pit mining costs at $0.0028/kg ore removal and $0.0035/kg waste removal. Determine the stripping ratio for an open operation that results in break-even cost differential between the two mining methods.
Problem 21: What is the purpose of pit limit optimisation and typical computerized optimisation methods?
Problem 22: What are typical mine wastes? Describe measures to safely contain mine wastes.
Problem 23: Briefly describe:
a). Objectives of production planning;
b). Taylor's mine life rule;
c). Sequencing by nested pits;
d). Production scheduling.
For all the students of this university, our Surface Mining Operations and Equipment Assignment Help service is always available to assist all the students, who are in academic needs.
TAGS: Surface Mining Operations and Equipment Assignment Help, Surface Mining Operations and Equipment Homework Help, Surface Mining Operations and Equipment Coursework, Surface Mining Operations and Equipment Solved Assignments, Mining Engineering Program Assignment Help, Mining Engineering Program Homework Help, Blasthole Assignment Help, Blasthole Homework Help, Break-Even Stripping Ratio Assignment Help, Break-Even Stripping Ratio Homework Help, Mining Method Assignment Help, Mining Method Homework Help