Question 1. National saving is
I. Equal to the sum of private saving plus government saving.
II. Equal to the sum of investment spending and net exports.
III. Equal to aggregate disposable income minus consumption spending.
a. Statements I, II and III are true.
b. Statements I and II are true.
c. Statements I and III are true.
d. Statements II and III are true.
e. Statement I is true.
Question 2. In the Solow growth model with population growth and technological change, whenever the marginal product net of depreciation is greater than the sum of the rates of population growth and technological change, the omniscient and omnipotent policymaker should
a. Increase the economy’s rate of saving.
b. Decrease the economy’s rate of saving.
Question 3. In the Solow growth model with population growth and technological change, whenever the marginal product net of depreciation is greater than the sum of the rates of population growth and technological change the steady state level of capital is
a. Less than the golden rule level of capital.
b. Greater than the golden rule level of capital.
Question 4. A small open economy initially operates with balanced trade. Holding everything else constant, if this economy increases government spending then this will result in
a. Net exports rising.
b. Net exports falling.
Question 5. A country’s real exchange rate increases. Holding everything else constant, this implies that this country
a. Will export more goods and import fewer goods.
b. Will import more goods and export fewer goods.
Question 6. Unemployment that is due to wage rigidity is best described as
a. Frictional Unemployment.
b. Structural Unemployment.
Use the following graph of a small open economy with perfect capital mobility to answer the next question.
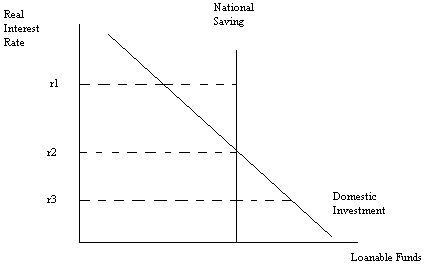
Question 7. Suppose this small, open economy finds that it has a negative trade balance. Given the choices of world real interest rate in the above graph, the world real interest rate that most likely occurs when this country has a negative trade balance is
a. r1
b. r2
c. r3
Question 8. Suppose the goal of policy makers in an economy is to reduce the NAIRU. Which policy is most likely to achieve this outcome?
a. Policy makers effectively reduce the rate of job finding in the economy.
b. Policy makers effectively reduce the rate of job separation in the economy.
Question 9. If the rate of job separation decreases holding everything else constant, this will result in
a. A decrease in the unemployment rate.
b. An increase in the unemployment rate.
Question 10. In the Solow growth model with no population growth and no technological change, the capital per worker increases when
a. Investment per worker is greater than depreciation of capital per worker.
b. Investment per worker is less than depreciation of capital per worker.