Problem 1 . Suppose you had the following information regarding the economy:
Year Nominal wage CPI
1991 $15.00 100
1992 $16.50 110
1993 $20.00 150
Which of the following answers best describes what is happening to the real wage rate over the time period represented in the data?
a) It increased from 1991 to 1992 and increased further from 1992 to 1993.
b) It dropped from 1991 to 1992 and then increased from 1992 to 1993.
c) It increased from 1991 to 1992 and then dropped from 1992 to 1993.
d) It remained the same from 1991 to 1992 and then dropped from 1992 to 1993.
Problem 2. Consider an economy in which the only three items in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) are food, cars, and guns. Listed below are the quantities and prices of these items consumed in two diffe rent years, 1995 and 1996. The market basket for calculating the CPI is comprised of 10 units of food, 5 cars and 2 guns.
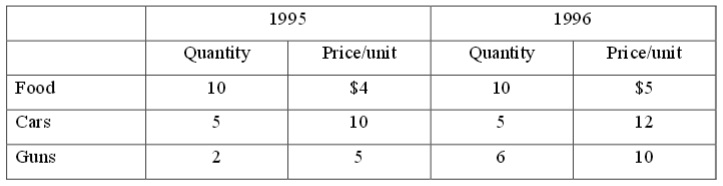
Using the information i n the table, what is the inflation rate between 1995 and 1996 as measured by the CPI?
a) 20%
b) 30%
c) 70 %
d) 120%
e) Since there was no given base year, it cannot be determined.
Problem 3. Joe and Mary live in Zimbabwe and in recent years have been frustrated by the very high rates of inflation. Joe, who runs an office supply store recently gave up printing a price list because prices changed so frequently that it was hard for his printed list to be up to date. Mary finds that she is spending significant time trying to figure out which grocery stores offer the best prices for the household's usual purchases of bread, jam, and peanut butter. The costs of inflation represented here are
a) Menu costs and unit - of - account costs
b) Unit - of - account costs and shoe leat her costs
c) Menu costs and shoe leather costs
d) Hyperinflation costs
Refer to the following table to answer the next TWO questions.
The following table presents all of the production and the prices for a hypothetical economy. That is, GDP is comprise d entirely of Coffee, Jelly Beans and Economics Textbooks.
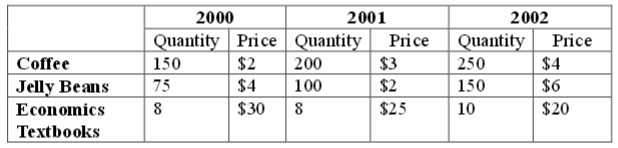
The next TWO questions refer to the table above. The market basket for the CPI is the quantities produced in the year 2001. Take 2001 to be the base year, and use 100 as the scale factor for the CPI.
Problem 4. Using the information in the table, calculate the value for the CPI in 2002.
a) 156
b) 161.5
c) 210
d) 117.3
Problem 5 . Using the information in the table, what is the value of the GDP deflator in 2000?
a) 95.2
b) 105
c) 100
d) 121.2
Problem 6. John worked as a typist for over twenty years and was laid off one day in 1995 after his company impl emented new computers. He tried very hard to find another job but failed because the demand for typists was shrinking sharply because of the introduction of computers. According to the above information, which of the following statements best describes what happened to John?
a) John became a discouraged worker.
b) John became cyclically unemployed.
c) John became structurally unemployed.
d) John became frictionally unemployed.
Problem 7. The following information is given as percentages of the total population in a small country. Consider a country with 5000 people in the population.
Full - time workers: 40%
Part - time workers: 20%
Discouraged workers: 10%
Unemployed workers: 10%
(Hint: this includes the cyclically unemployed workers) Cyclically unemployed workers: 3%
What is the natural rate of unemployment in this country?
a) 5%
b) 6%
c) 7%
d) 8%
e) 10%
Problem 8. Monica, Ross, Joey and Chandler worked together but they all lost their jobs last month. The following list describes what they have been doing since then.
- Monica has been taking care of her baby at home
- Ross went on to pursue a master’s degree in paleontology
- Joey has been reading the job posts on Newspapers and sending his resumes out
- Chandler was frustrated and has been watching TV to kill time Which of the friends (if any) are considered unemployed?
a) Monica
b) Ross
c) Joey
d) Chandler
e) None of these individuals are unemployed
Problem 9. The government increases unemployment insurance to help those who are unemployed, so that they can take mor e time to find a better job. Which of the following side - effects would you expect to happen?
a) The frictional unemployment rate will increase.
b) The structural unemployment rate will increase.
c) The cyclical unemployment rate will decrease.
d) The unemployment rate will decrease.
Problem 10. Bakery A produces bread. Annually, Bakery A uses $15 million worth of sugar, flour, and eggs (assume all three of these ingredients are produced in the same year that the bread is produced) to produce its bread. Wages a nd salaries in Bakery A for the year are equal to $30 million; the bakery's only other annual expense is $10 million in interest that it pays on its bonds. The annual profits for the owner of the bakery are $15 million. What is Bakery A’s contribution to GDP this year?
a) 70 million
b) 60 million
c) 55 million
d) 40 million
e) It cannot be determined from the information given
Problem 11. Laura, who lives in Kansas, finds a briefcase with $60,000 cash inside of it at the casino. Instead of reporting it to th e authorities she decides to start her own business. To do so she buys $32,000 worth of equipment from Torcidos Ltd. in Canada and $28,000 from Tornado Ltd. in Madison, Wisconsin. Both purchases are made during this year and all the equipment was produced during this year. The change in GDP in the United States due to Laura’s actions is equal to:
a) 0
b) $60,000
c) $28,000
d) $32,000
Problem 12. Maryland produces only two goods: crab cakes and waffles. Use the output information in the following table to answ er the next question. Use 2010 as the base year.
2010 Quantity Price 2011 Quantity Price
Crab cakes 50 $2 80 $4
Waffles 100 $3 80 $4
What was Maryland’s growth rate of Real GDP from 2010 to 2011?
a) 0%
b) 100%
c) 33.3%
d) 60%
Problem 13. In Finland, real GDP was lower in 2009 than in 2010. The GDP deflator was the same in 2009 and 2010. Therefore, we can conclude that nominal GDP in 2010 is
a) Lower than nominal GDP in 2009.
b) Higher than nominal GDP in 2009.
c) The same as nominal GDP in 2009.
d ) There is not enough information available to determine the trend of nominal GDP.
Problem 14. Suppose that last year real GDP increased while real GDP per capita decreased in an economy. Therefore, it must be the case that
a) The labor force decreased last year .
b) The labor force increased last year.
c) The economy experienced population growth last year.
d) The economy experienced a decrease in population last year.
Problem 15. Consider the following production function that relates levels of capital (K) and labor (L) to output (Y).
Y = K√L
Further, assume that capital (K) is fixed at 100. Does this function exhibit diminishing marginal returns to labor?
a) Yes it does.
b) No it does not.
Use the following information and the table below for the next TWO questions.
Consider an economy in which the labor force consists of the entire population. The following table summarizes values of population size, the level of capital and the level of real GDP in 3 consecutive years.
Year Population Capital Real GDP
1 100 40 900
2 130 44 1200
3 160 48.4 1600
Problem 16. What is the annual growth rate for capital in this economy?
a) 10%
b) 30%
c) 33%
d) The growth rate for capital between years 1 and 2 is different from the growth rate between years 2 and 3.
Problem 17. Which of the following best describes the pattern of Real GDP per capita growth in this economy?
a) There is growth in real GDP per capita between years 1 and 2, and also between years 2 and 3.
b) Real GDP per capita grows between years 1 and 2, but falls between years 2 and 3.
c) Re al GDP per capita falls between years 1 and 2, but grows between years 2 and 3.
d ) There is a decrease in real GDP per capita between years 1 and 2, and also between years 2 and 3.
Problem 18. Annual tuition rates are rising at a rate of roughly 5% a year. Curre ntly tuition at Harvard is roughly $35,000 per year. If tuition rates keep rising at 5% per year, what will the tuition at Harvard be in 14 years?
a) $55,000
b) $70,000
c) $85,000
d) $100,000
Use the following information for the next THREE questions .
The economy of Kansas is a closed economy. The loanable funds market is characterized by the following equations where r is the interest rate as a whole number (for example, if the interest rate was 5% then r would be equal to 5 in the equation) and Q is the quantity of loanable funds.
Private investment: r = 20 - (1/100)Q
Private savings: r = 5 + (1/200)Q
Problem 19. Suppose that initially the government runs a balanced budget (remember this is just a hypothetical world). What is the equilibrium quantity of private investment in this economy?
a) $500
b) $1000
c) $1250
d) $2250
Problem 20. Now suppose that the government acts more realistically and decides to run a massive deficit of $1500 dollars no matter what the interest rate is in the economy. What is the equilibrium quantity of savings in this economy?
a) $1500
b) $2000
c) $2500
d) $4500
Problem 21. Continue to assume that the government runs the $1500 deficit. How much private investment is crowded out because of the government deficit?
a) $500
b) $1000
c) $1500
d) Investment went up as a result of the deficit, there is no crowding out.
Problem 22. Consider the loanable funds market that is initially in equilibrium. As a result of the financial crisis, individuals began to increase their private savings at every interest rate. In addition, firms increase their investment expen ditures since the interest rate is decreasing. Which of the following best describes what happens to the equilibrium interest rate and the quantity of loanable funds?
a) The quantity of loanable funds increased and the interest rate decreased.
b) The qua ntity of loanable funds increased and the effect on the interest rate is indeterminate.
c) The quantity of loanable funds decreased as did the interest rate.
d) The quantity of loanable funds decreased and the effect on the interest rate is indeterminate.
Problem 23. The concept that asset prices embody all publicly available information is known as the
a) Complete information hypothesis.
b) Efficient markets hypothesis.
Problem 24. The country of Wyoming is a closed economy, whose loanable funds market is characteriz ed by the following equations. r is the real interest rate (so if r = 35, then the interest rate is 35%) and Q is the quantity of loanable funds.
Demand: r 20 - (1/5)Q
Supply: r = 5 + (1/10)Q
Initially, the government runs a balanced budget, but then decides to run a deficit in order to hire m ore policemen to deal with bank robberies. After running their deficit, the equilibrium interest rate in Wyoming jumps up to 15%. Holding everything else constant, how large must the government deficit be to increase the interest rate to 15%?
a) $25
b) $50
c) $75
d) $100
e) None of the above answers is correct.