Response to the following problem:
In the osmotic pressure apparatus depicted in Fig. , let the pressure of the pure solvent be Poand that of the dilute solution be P, the temperature being T throughout the system. The molar Gibbs function of the pure solvent is s".
(a) Show that, at equilibrium,
g"(T,P0) = g"(T,P) + RT In (1 - x),
Where x is the mole-fraction of the solute.
(b) For an infinitesimal change of x at constant T, show that
0 = v" dP + Rtd In (1 - x)
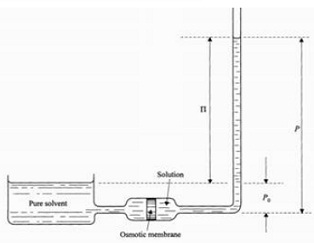
(c) Integrating P from P0 to P, and x from 0 to x, show that
IIv" = xRT,
when II = P - P0.Compare this equation with the ideal-gas law.