Problem 1: The general elution problem can be addressed by:
a. Application of an elution gradient
b. Reduction of sample concentration
c. Increasing of flow rate
d. Use of a reference electrode
Problem 2: Gas Chromatography separates compounds in first instance by their:
a. Polarity
b. Molecular weight
c. Vapor pressure
d. Atomic number
Problem 3: What is the purpose of a degasser in an HPLC?
a. To release gas pressure downstream of the HPLC column
b. To avoid formation of gas bubbles in the HPLC column
c. To improve gaseous mobile phase flow
d. To increase inert gas loading in the mobile phase
Problem 4: Which component carries the ionic current in an electrochemical experiment?
a. The working electrode
b. The electrolyte
c. The external circuit
d. The reference electrode
Problem 5: Why do you need a reference electrode?
a. As a stable potential reference point in the experiment
b. As sink to charges generated at the working electrode
c. To carry electronic charges
d. To allow faradaic charge transfer
Problem 6: Reading the required values from the chromatogram below, calculate the selectivity factor for compounds A and B, calculate the number of theoretical plates and plate height. Consider accuracy of your read values in the calculated significant figures. (Column length L=25cm)
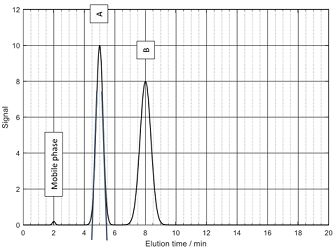
Problem 7: Describe the purpose of all three of the following components in an HPLC instrument:
a. Column guard
b. Pump
c. Injector
Problem 8: You have obtained very wide, overlapping peaks in a chromatography experiment. How can you reduce peak widths? Justify your response by explaining how your method affects peak width.
Problem 9: You are using a Ag/AgI sensing electrode to determine I- ion concentration in an aqueous analyte solution. You are measuring a potential of - 45.0 mV vs a Ag/AgCl/3.00M KCl reference electrode (E(Ag/AgCl/3M KCl) = 0.210 V vs. NHE). Determine the concentration of I- in the solution. (T = 25.0oC, Eo(Ag/AgI) = 0.152 V vs. NHE)
Problem 10: Sketch the current-potential behavior for one full cycle in the Cyclic Voltammetry of a reversible dissolved redox couple. How can you identify the redox species from this data?
Problem 11: Choose a separation or electrochemical method and justify your choice: you need to determine the diffusion coefficient of a redox-active species in water.
Problem 12: Bonus: Calculate the solubility product Ksp for AgI from the values given in question 9.
Avail Well-Crafted Assignment From The Professional Tutors Of Gas Chromatography Assignment Help Service At Nominal Prices To Secure Notable Grades With Ease!
Tags: Gas Chromatography Assignment Help, Gas Chromatography Homework Help, Gas Chromatography Coursework, Gas Chromatography Solved Assignments, Solubility Product Assignment Help, Solubility Product Homework Help, Cyclic Voltammetry Assignment Help, Cyclic Voltammetry Homework Help