Question 1: Consider the given two probability distributions for sales:
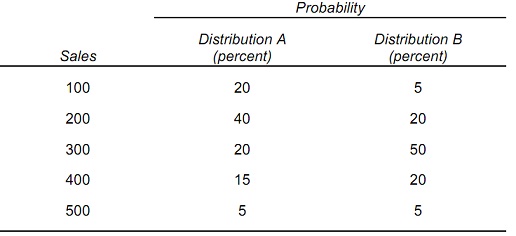
a) Compute the expected sales for both of these probability distributions.
E(SalesA) = __________
E(SalesB) = __________
b) Compute the variance and standard deviation for both of the probability distributions.
σA2 = __________ and σ A = __________
σB2 = __________ and σ B = __________
Distribution _____ is more risky than distribution _______.
c) Compute the coefficient of variation for both distributions:
vA = __________
vB = __________
Distribution _____ has greater risk relative to its mean than distribution _____.
Question 2: Texas Petroleum Company is a producer of crude oil which is considering two drilling projects with the given profit outcomes and associated probabilities:
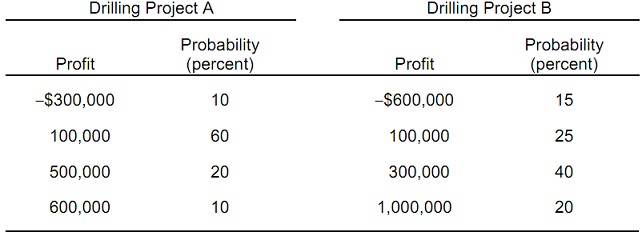
a) Evaluate the expected profit for both drilling projects.
E(ProfitA) = __________ and E(ProfitB) = __________
b) Based on the expected value rule, Texas Petroleum should choose drilling project _______.
c) Calculate the standard deviations of both projects:
σ A = __________ and σ B = __________
d) Which drilling project has the greater (absolute) risk?
e) Use mean-variance rules, if possible, to decide which drilling project to undertake. Describe.
f) Calculate the coefficient of variation for both projects:
vA = __________ and vB = __________
By using the coefficient of variation rule, Texas Petroleum should choose project _____.
Question 3: A manager’s utility function for profit is U(π ) = 35π, where π is the dollar amount of profit. The manager is considering a risky decision with the four possible profit outcomes shown below. The manager makes the given subjective assessments regarding the probability of each and every profit outcome:
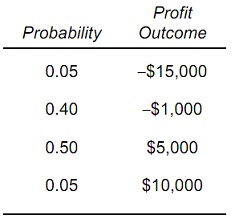
a) The expected profit is _______________.
b) The expected utility of profit is _____________.
c) The marginal utility of an extra dollar of profit is ________.
d) The manager is risk ___________ as the marginal utility of profit is ____________.
Question 4: Assume that the manager of a firm has a utility function for profit U(π ) = 12ln(π ), where π is the dollar amount of profit. The manager is considering a risky project with the following profit payoffs and probabilities:
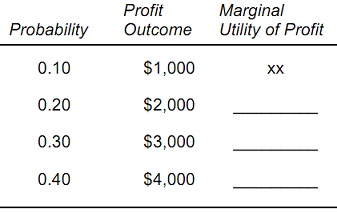
a) The expected profit is _______________.
b) The expected utility of profit is _____________.
c) Fill in the blanks in the following table showing the marginal utility of an additional $1,000 of profit.
d) The manager is risk _________ because the marginal utility of profit is __________.
Question 5: A firm is making production plans for next quarter, but the manager doesn't know what the price of the product will be next month. She believes there is a 30 % chance that price will be $500 and a 70 percent chance that price will be $750. The four possible profit outcomes are:
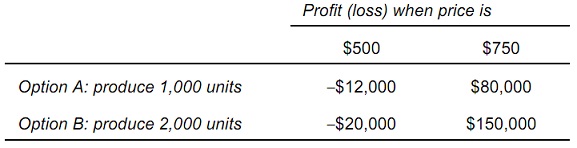
a) Option ______ maximizes expected profit.
b) Option ______ is the riskier of the two options.
c) The manager _____________ (can, cannot) apply mean-variance rules in this decision. If the manager can use mean-variance rules, the manager would choose Option ______.
d) Using the coefficient of variation rule, the manager chooses Option _____.
Question 6: Suppose the manager in Problem 5 has absolutely no idea about the probabilities of the two prices occurring. Which option would the manager choose under each of the following rules?
a) Maximax rule _________________
b) Maximin rule _________________
c) Minimax regret rule _________________
d) Equal probability rule _________________