Use the following information to answer the next TWO (2) questions.
Arrow and Debreu are leading economists working in the same field. Both of them are able to produce research papers and presentation slides. The maximum number of each that they can produce if they do not produce any of the other good is shown in the table below:
|
Maximum Number of Papers |
Maximum Number of Slides |
|
| Arrow |
20 |
15 |
|
| Debreu |
5 |
10 |
|
Question 1. Who has the absolute advantage in producing presentation slides?
a. Arrow
b. Debreu
Question 2. Who should specialize in producing presentation slides if Arrow and Debreu trade with each other?
a. Arrow
b. Debreu
Question 3. Alice and Bob both work in the same restaurant, cleaning the floor and washing dishes. Initially they work independently, both washing an equal number of dishes and cleaning an equal area of the floor. A few days later, they make a deal where Alice cleans some parts of the floor for Bob, and Bob washes some dishes for her. From this information we can infer that ________ has a comparative advantage in washing dishes.
a. Alice
b. Bob
Question 4. Which of the following agricultural market programs implemented by the government to maintain a target price may also involve storage costs?
a. A price guarantee program
b. A price support program
Question 5. Fireflowers are a normal good for Super Mario. If his income rises then his demand for fireflowers
a. Decreases.
b. Increases.
Question 6. Jackie spends her days planting apple trees and cacao trees. If her PPF for these trees is plotted with the number of apple trees planted on the vertical axis and the number of cacao trees planted on the horizontal axis, then the absolute value of the slope at some point along this PPF represents
a. Jackie's opportunity cost of planting one apple tree at that point.
b. Jackie's opportunity cost of planting one cacao tree at that point.
Question 7. Which of the following is a positive statement?
a. Badgers games should always start at 2pm on Saturdays.
b. Based on their recent play, the Badgers should defeat the team they will face this Saturday.
Question 8. Before an election, 1 million individuals are randomly picked and interviewed about which candidate they support. The data collected from these interviews is:
a. Cross sectional data.
b. Time series data.
Question 9. An effective minimum wage is an example of a
a. Price ceiling.
b. Price floor.
Question 10. Use the following supply and demand equations to find the equilibrium quantity (Q) and the equilibrium price (P).
Demand: P = 31 – (10)Q
Supply: P=10 + (1/2)Q
a. Q = 2, P = 11
b. Q = 3, P = 1
Question 11. Whenever there is an increase in _____ and a decrease in _____ we cannot tell which direction the _____ moves in the new equilibrium.
a. Demand, supply, price
b. Supply, demand, quantity
Question 12. The "law of demand" states that increasing the price of a good or service, all else equal, results in
a. A reduction in demand.
b. A reduction in the quantity demanded.
Question 13. Suppose the market for paper is in equilibrium. One day there is a large fire that burns down several tree plantations that are the source of the wood that the producers of paper use when producing paper. Given this information and holding everything else constant, consumer surplus in the market for paper will
a. Increase.
b. Decrease.
Question 14. Suppose the market for eggs is initially in equilibrium. Then a popular documentary causes consumers to be worried about salmonella, a foodborne illness sometimes present in eggs. Given this information and holding everything else constant, the market price of eggs will:
a. Increase.
b. Decrease.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (20 QUESTIONS)
Question 15. Suppose both Madison and Eau Claire can only produce two kinds of dairy products, yogurt and ice cream. Which of the following situations is impossible?
a. Madison has an absolute advantage in the production of both yogurt and ice cream.
b. Eau Claire has a comparative advantage in the production of yogurt and an absolute advantage in the production of ice cream.
c. Eau Claire has a comparative advantage in the production of both yogurt and ice cream.
d. Madison has an absolute advantage in the production of ice cream and a comparative advantage in the production of yogurt.
Question 16. Consider the following four linear demand curves. Joey is trying to figure out which demand curve is the one that has the smallest change in the quantity demanded of the good if the price decreases by $1 for that good. Is it the apple market, the banana market, the coconut market, or the durian market?
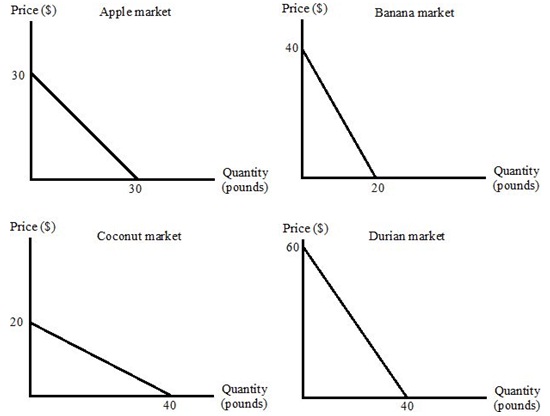
a. The apple market
b. The banana market
c. The coconut market
d. The durian market
For the next TWO (2) questions use the following information:
Castor, Pollux and Helen spend their days fishing and hunting boar. Their PPF's are given by the following equations (where F is the number of fish caught and B is the number of Boars hunted):
Castor: B = 20 - 2F
Pollux: F = 10 - 0.5B
Helen: B = 10 - 0.2F
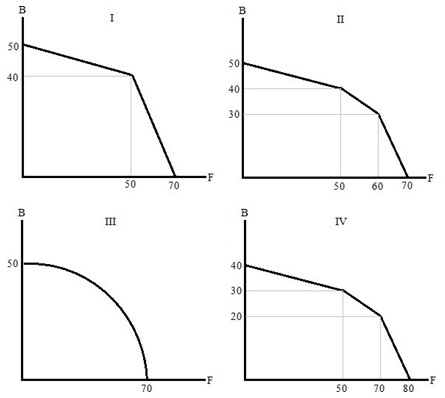
Question 17. Which of the following diagrams represents the possible combinations that can be produced by these three individuals if Castor, Pollux and Helen work together? (None of the graphs below have been drawn to scale.)
a. I
b. II
c. III
d. IV
Question 18. Castor, Pollux and Helen agree to trade. In order for all parties to agree to trade the price of a fish must be more than _____ boars and less than ____ boars.
a. 0.2; 0.5
b. 0.2; 2
c. 0.5; 5
d. 0.5; 2
Use the following information to answer the next FOUR (4) questions.
The market for olive oil in Athens has the following demand and supply curves, where Q is the quantity of olive oil in bottles and P is the price in drachmae.
Demand: P = 20 - 0.01Q
Supply: P = 5 + 0.01Q
Question 19. When this market is in equilibrium the value of consumer surplus is
a. Less than 500 drachmae.
b. Between 500 drachmae and 1000 drachmae.
c. Between 1000 drachmae and 1500 drachmae.
d. More than 1500 drachmae.
Question 20. The Athenian government is considering a price support program. If the target price is 15 drachmae, how many bottles of olive oil will the government have to purchase directly?
a. 250 bottles
b. 500 bottles
c. 1000 bottles
d. 1500 bottles
Question 21. Suppose the Athenian government instead of a price support program decides to use a price guarantee program to achieve the target price of 15 drachmae per bottle. What would be the total cost of this subsidy to the government of Athens?
a. 2,500 drachmae
b. 5,000 drachmae
c. 7,500 drachmae
d. 10,000 drachmae
Question 22. As the Athenian government is debating which policy to implement a messenger arrives with news from the Oracle at Delphi: the message from the Oracle is that this will be a particularly good year to grow olives. Assume that this is an accurate weather forecast and the government still wants to achieve through implemented policy a price of 15 drachmae per bottle of olive oil. The number of bottles the government will need to buy to implement a price support program given this news will be _____ than compared to before they received the news. The total cost of implementing a price guarantee program given this news is now _____ than compared to before they received the news.
a. Higher; higher
b. Higher; lower
c. Lower; higher
d. Lower; lower
Question 23. Mr. R recently started his life in Madison as an economics graduate student. Before he came here, he had (mutually exclusive) job offers from two different companies with salaries of $50,000 and $70,000 per year, respectively. Mr. R is not paid for being a graduate student. Mr. R's living expenses for the year are $15,000 regardless of where he lives. What is Mr. R's opportunity cost of being a graduate student for a year?
a. $50,000
b. $55,000
c. $70,000
d. $120,000
Question 24. King Pyrrhus is considering a price guarantee program in a market. His economic advisers tell him that (5, 115) and (10, 105) are two points on the linear demand curve (where the first number in each pair represents the quantity demanded), while (15, 45) and (20, 60) are two points on the linear supply curve. Given this information and holding everything else constant, what per-unit subsidy would be required to support a price of 90?
a. 25
b. 20
c. 10
d. There is no need to pay a per-unit subsidy since the equilibrium price is 90.
Use the diagram below to answer the following question
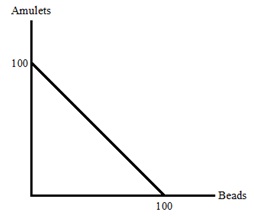
Question 25. Mycenae is a city that produces amulets and beads. Suppose initially Mycenae's PPF is as given in the diagram above. Then their supply of copper, a material used to produce amulets but not beads, is reduced due to one of their copper mines being exhausted. At the same time they discover a technology that makes it easier to produce beads. Which of the following new PPF's could represent this information?
Use the following information to answer the next THREE (3) questions.
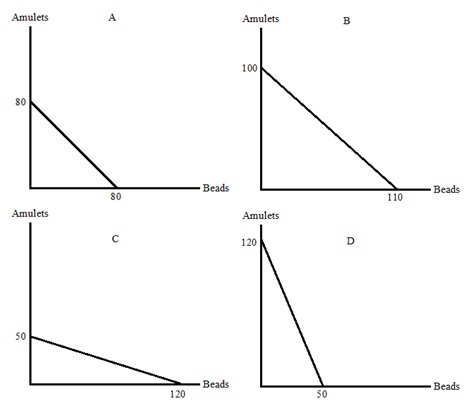
Emilio and Yoshi work in the same office to produce ECON101 questions and coffee. Emilio's opportunity cost of writing an ECON101 question is three cups of coffee. Yoshi's opportunity cost of one cup of coffee is two ECON101 questions. They both have linear production possibility frontiers.
Question 26. Emilio and Yoshi agree to trade one cup of coffee for x ECON101 questions. Which of the following CANNOT be true?
a. x = 1/3
b. x = 1
c. x = 2
d. x = 3
Question 27. Now suppose that Emilio can produce 10 cups of coffee per day and Yoshi can produce 20 cups of coffee per day, if neither of them write any ECON101 questions. What is the location of the kink point of their joint PPF?
a. 3.3333 ECON101 questions and 20 cups of coffee
b. 43.3333 ECON101 questions and 30 cups of coffee
c. 40 ECON101 questions and 10 cups of coffee
d. 3.3333 ECON101 questions and 18.3333 cups of coffee
Question 28. Yoshi and Emilio pool their production and then divide it between themselves. Which of the following allocations is inefficient?
a. Emilio gets 5 cups of coffee and 15 ECON101 questions, Yoshi gets 5 cups of coffee and 25 ECON101 questions.
b. Emilio gets 10 cups of coffee and 20 ECON101 questions, Yoshi gets 0 cups of coffee and 15 ECON101 questions.
c. Emilio gets 5 cups of coffee and 20 ECON101 questions, Yoshi gets 15 cups of coffee and 10 ECON101 questions.
d. Emilio gets 15 cups of coffee and 0 ECON101 questions, Yoshi gets 10 cups of coffee and 10 ECON101 questions.
Question 29. Consider a market in which the government has implemented a quota limit on the quantity supplied that results in the quantity traded in the market being less than the market equilibrium quantity. If the costs of production in this market fall, then holding everything else constant,
a. Producer surplus shrinks.
b. Price decreases and quantity increases.
c. Both price and quantity remain the same as they were before the change in the costs of production.
d. Consumer surplus increases.
Question 30. Suppose there are three firms producing macbooks and their respective supply curves are as follows where P is the price per macbooks and Q is the quantity of macbooks:
Firm 1: P = 1 + 2Q
Firm 2: P = 1 + 3Q
Firm 3: P = 2 + Q
Given the above information, how many kink points does the market supply curve have?
a. 0
b. 1
c. 2
d. 3
Question 31. Bucky Badger is the secret owner of the UW-Madison Bookstore. He just discovered a new technique that allows him to produce summer t-shirts at a lower cost. However he also knows that summer is over and people in Wisconsin do not buy summer t-shirts in winter. Given this information and holding everything else constant, Bucky anticipates that the quantity of summer t-shirts sold during the first quarter of the year (January, February and March)
a. Will increase.
b. Will decrease.
c. Will stay the same.
d. Is indeterminate.
Question 32. José is a Mexican student. He knows that he can trade 13 pesos for 1 dollar. Also he knows that 3.78 Liters is a gallon. José needs to figure out which of the following graphs represent the same information. Which ones are the same?
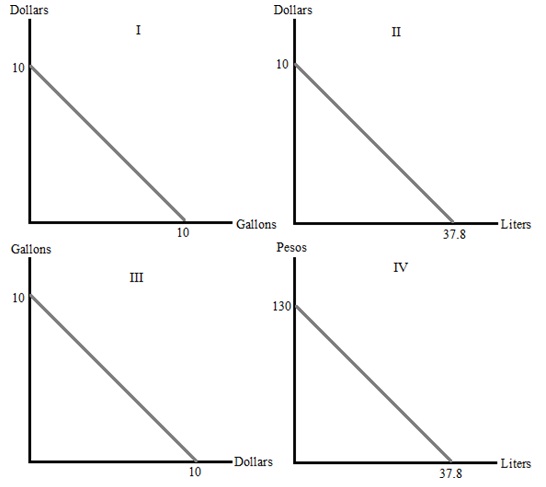
a. They are all providing the same information.
b. I and III
c. I,II, and III
d. I and II
Question 33. School officials would like to know the average sleeping time of students attending UW Madison. Which of the following sampling strategies is the best in terms of representing the whole population?
a. Randomly picking males passing by University Avenue and interviewing them about their sleeping time.
b. Randomly picking students entering College library and interviewing them about their sleeping time
c. Interviewing all students on State Street on Friday night about their sleeping time.
d. Randomly picking some locations on campus where during different time slots all the students passing by will be interviewed about their sleeping time.
Question 34. Suppose the USA can produce ships and planes, as shown in the PPF below. If the opportunity cost of moving from point I to point II is 2 ships, which of the following is a possible value of X?
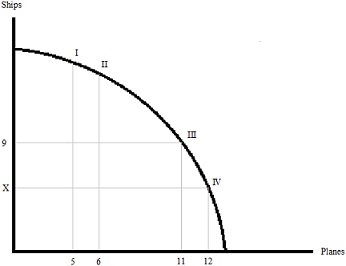
a. 8
b. 6
c. 4
d. Both answers (b) and (c) are possible values for X.