Solve the following problems:
1: A company reports the following information regarding its production cost:
|
Units produced
|
22,000 units
|
|
Direct labor
|
$31 per unit
|
|
Direct materials
|
$27 per unit
|
|
Variable overhead
|
? in total
|
|
Fixed overhead
|
$2,750,000 in total
|
Required: Perform the following independent calculations.
a. Compute total variable overhead cost if the production cost per unit under variable costing is $240.
b. Compute total variable overhead cost if the production cost per unit under absorption costing is $240.
2: Stonehenge Inc., a manufacturer of landscaping blocks, began operations on April 1 of the current year. During this time, the company produced 750,000 units and sold 720,000 units at a sales price of $9 per unit. Cost information for this period is shown in the following table:
|
Production costs
|
|
|
Direct materials
|
$1.80 per unit
|
|
Direct labor
|
$.30 per unit
|
|
Variable overhead
|
$496,000 in total
|
|
Fixed overhead
|
$450,000 in total
|
|
Non production costs
|
|
|
Variable selling and administrative
|
$18,000 in total
|
|
Fixed selling and administrative
|
$53,000 in total
|
a. Prepare Stonehenge's December 31st income statement for the current year under absorption costing.
b. Prepare Stonehenge's December 31st income statement for the current year under variable costing.
3: Dado, Inc. is preparing its budget for the second quarter. The following sales data have been forecasted:
|
|
April
|
May
|
June
|
July
|
Aug.
|
|
|
Unit sales....................
|
640
|
720
|
780
|
620
|
660
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional information follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inventory on March 31:
|
|
|
|
192 Units
|
|
|
Desired ending inventory each month:
|
|
|
|
30% of nt month's sales
|
|
Prepare a merchandise purchases budget for the total units to be purchased in the months of April, May, and June, as well as the total unit purchases for entire the quarter.
4: Lafayette Company's perience shows that 20% of its sales are for cash and 80% are on credit. An analysis of credit sales shows that 50% are collected in the month following the sale, 45% are collected in the second month, and 5% prove to be uncollectible. Calculate the following. Show all calculations!

5: Anniston Co. planned to produce and sell 40,000 units. At that volume level, variable costs are determined to be $320,000 and fixed costs are $30,000. The planned selling price is $10 per unit. Anniston actually produced and sold 42,000 units.
Using a contribution margin format:
(a) Prepare a fixed budget income statement for the planned level of sales and production.
(b) Prepare a flible budget income statement for the actual level of sales and production.
6: Engineworks Co. provides the following fixed budget data for the year:
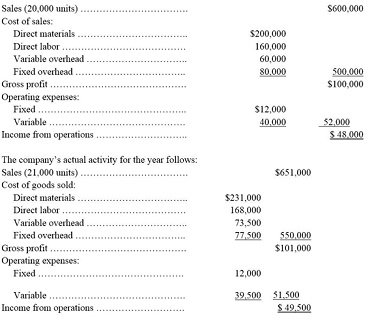
Required:
Prepare a flible budget performance report for the year using the contribution margin format.
7: City Park College allocates administrative costs to its teaching departments based on the number of students enrolled, while maintenance and utilities are allocated based on square feet of classrooms. Based on the information below, what is the total amount of penses allocated to each department (rounded to the nearest dollar) if administrative costs for the college were $180,000, maintenance penses were $70,000, and utilities were $85,000?
Teaching Size of
Department Students Classroom
Electronics 117 900 sq. ft.
Automotive 156 750 sq. ft.
Computers 429 1,200 sq. ft.
Plumbing 78 150 sq. ft
8: A company has just received a special, one-time order for 1,000 units. Producing the order will have no effect on the production and sales of other units. The buyer's name will be stamped on each unit, at a cost of $1.50 per unit. Normal cost data, cluding stamping, follows:
Direct materials................................. $ 10 per unit
Direct labor...................................... 16 per unit
Variable overhead.............................. 4 per unit
Allocated fixed overhead...................... 12 per unit
Allocated fixed selling pense............... 8 per unit
Prepare an analysis that indicates the selling price per unit this company will require to earn $3,000 on the order.
9: A company is considering two alternative investment opportunities, each of which requires an initial cash outlay of $110,000. The pected net cash flows from the two projects follow:
|
|
Project A
|
Project Z
|
|
Year 1
|
$ 30,000
|
$ 44,000
|
|
Year 2
|
44,000
|
70,000
|
|
Year 3
|
70,000
|
30,000
|
|
Totals
|
$144,000
|
$144,000
|
Required:
(1) Based on a comparison of their net present values, and assuming the same discount rate greater than zero is required for both projects, which project is the better investment?
(2) Use the table values below to find the net present value of the cash flows associated with Project A, discounted at 12%:
Periods Present value of 1 at 12%
1................... 0.8929
2................... 0.7972
3................... 0.7118
10 A company produces two boat models, Flyer and Skimmer. Both products are being considered for major investment projects nt year. Relevant data follow:
Flyer Skimmer
New investment .................... $424,000 $380,000
pected 3-year net cash flows:
Year 1 150,000 130,000
Year 2 160,000 130,000
Year 3 170,000 130,000
Required:
Use the payback period to evaluate these two investment projects.