Multiple Choice Questions:
Use the information provided in the table below to answer the next three questions. Suppose there are only three firms in the economy: Wisconsin Racquet Co., which produces tennis racquets; Wisconsin Metal Co., which produces the various metals that go into racquet production; and Wisconsin Ore Co., which mines the ores needed for the manufacture of the metal.
|
|
Wisconsin
Racquet Co.
|
Wisconsin
Metal Co.
|
Wisconsin
Ore Co.
|
Total
factor income
|
|
Value of sales
|
$5000
|
$3000
|
$500
|
|
|
Intermediate goods
|
$A
|
$B
|
$0
|
|
|
Wages
|
$1200
|
$1600
|
$300
|
$C
|
|
Interest payments
|
$100
|
$50
|
$20
|
$D
|
|
Rent
|
$500
|
$100
|
$50
|
$E
|
|
Profit
|
$200
|
$750
|
$130
|
$F
|
|
Total expenditures by firm
|
$5000
|
$3000
|
$500
|
|
|
Value added per firm
|
$G
|
$H
|
$I
|
|
Problem 1. The GDP of this hypothetical economy is equal to
a. $5000
b. $8500
c. $3500
d. $980
Problem 2. If we use the factor payments approach to measuring GDP, which entries would you combine to get a measure of GDP?
a. G, H, and I
b. C, D, E, and F
c. A and B
d. A, B, C, and D
Problem 3. Suppose we use the value added approach to measuring GDP. Which of the following values are correct for the missing entries in the table?
a. A=$3000, B=$3000, G=$2000, H=$0, I=$500
b. A=$3000, B=$3000, G=$0, H=$4500, I=$500
c. A=$3000, B=$500, G=$2000, H=$2500, I=$500
d. A=$3000, B=$500, G=$0, H=$4500, I=$500
Use the information given in the following table to answer the next three questions. Suppose 2007 is the base year and the market basket for purposes of constructing a price index consists of 200 units of rice, 100 units of apples, and 100 units shampoo.
|
|
Prices in 2007
|
Prices in 2008
|
|
Rice
|
.5
|
.4
|
|
Apples
|
.25
|
.4
|
|
Shampoo
|
.4
|
.5
|
Problem 4. Using 2007 as the base year, the consumer price index in 2007 is
a. 1.15
b. 165
c. 190
d. 100
Problem 5. Using 2007 as the base year, the consumer price index in 2008 is
a. 103
b. .97
c. 1
d. 100
Problem 6. Using 2007 as the base year, the inflation rate between 2007 and 2008 in this economy is
a. 0%
b. 3%
c. 103%
d. 67%
Problem 7. The population in an economy increases and this leads to an increase in the supply of labor. Assume the economy's aggregate production function exhibits diminishing marginal productivity of labor. If there are no changes in technology and in the capital market, then in this economy
a.) the equilibrium quantity of labor and the aggregate output level decrease while the equilibrium wage and the productivity of labor increase.
b.) the equilibrium quantity of labor, the equilibrium wage, the aggregate output level, and the productivity of labor increase.
c.) the equilibrium quantity of labor and the aggregate output level increase while the equilibrium wage and the productivity of labor decrease.
d.) the equilibrium quantity of labor, the equilibrium wage, the aggregate output level, and the productivity of labor decrease.
Problem 8. Suppose an economy experiences technological improvement, so that the marginal productivity of labor increases at the current level of labor usage. Assuming that the equilibrium level of capital is constant, which of the following statements describes the impact of this technological change on this economy?
a.) The technological change will result in a higher equilibrium wage level while output remains constant since there is no change in the level of capital.
b.) The technological change will result in a higher level of output for this economy.
c.) There will be no change in the equilibrium wage rate but labor productivity will decrease while the level of output in this economy increases.
d.) There will be no change in the equilibrium wage rate but labor productivity will increase while the level of output in this economy decreases.
Problem 9. Consider a country whose economy is a closed economy. Suppose the government of this country decides to increase both the level of taxes and the level of government spending by the same amount. According to the Classical Model,
a.) there will be no change in the equilibrium interest rate and no change in the level of investment in this economy as a result of this change in government policy.
b.) the change in the equilibrium interest rate and the equilibrium level of investment are ambiguous.
c.) there will be a decrease in the equilibrium interest rate and an increase in the equilibrium level of investment.
d.) there will be an increase in the equilibrium interest rate and a decrease in the equilibrium level of investment.
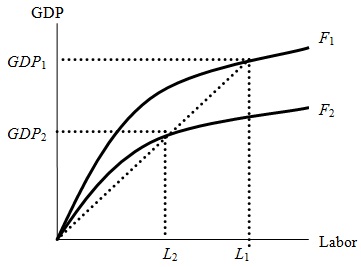
Problem 10. The graph above depicts the aggregate production function with respect to labor for Iraq. Due to the war and its destruction Iraq has experienced a decrease in its level of available technology as well as its working age population. Due to these changes Iraq's aggregate production function has shifted from F1 to F2 while its equilibrium level of employment has decreased from L1 to L2. These changes caused the equilibrium level of output to decrease from GDP1 to GDP2. According to the graph, labor productivity in Iraq has
a.) increased.
b.) decreased.
c.) remained unchanged.
d.) changed, but it is impossible to know with certainty the direction of the change without more information.
Problem 11. Consider a country with a closed economy. The government of this country is initially running a balanced budget. Suppose the government then decides to increase its spending so that it will have a budget deficit. Holding everything else constant, which of the following statements is true given this increase in government spending?
a.) The equilibrium interest rate, the level of private saving, and the equilibrium level of investment will increase.
b.) The equilibrium interest rate and the level of private saving will decrease, while the equilibrium level of investment will increase.
c.) The equilibrium interest rate and the level of private saving will increase, while the equilibrium level of investment will decrease.
d.) The equilibrium level of interest rate and the equilibrium level of investment will increase, while the equilibrium level of private saving will increase.
Problem 12. Suppose we have data for the CPI where 2001 is the base year for this index: thus, the CPI for 2001 is equal to 100. Furthermore, suppose that the CPI in 2008 is equal to 100 while the CPI in 2009 is equal to 125. If we recalculate the CPI using 2009 as the index's base year, what is the inflation rate between 2008 and 2009?
a.) 20%
b.) 80%
c.) 25%
d.) There is not enough information given in this problem to calculate this inflation rate.
Problem 13. In China, a small steel company purchases iron ore from a mining company, and sells all of the steel products it produces to a Chinese automobile company. In this case,
a.) only the value of the iron ore is counted as a part of China's GDP.
b.) the value of both the steel products and the automobiles are counted as part of China's GDP.
c.) the value of the iron ore, the steel products and the automobiles are all counted as part of China's GDP.
d.) only the value of the automobiles is counted as part of China's GDP.
Problem 14. Suppose there is an increase in the government budget deficit in a country with a closed economy. Holding everything else constant, this will
a.) increase the equilibrium level of the interest rate and the level of investment in this country; and, in the next time period output in this economy will increase.
b.) decrease the equilibrium level of the interest rate and the level of investment in this country; and, in the next time period output in this economy will decrease.
c.) decrease the equilibrium level of the interest rate while the level of investment will increase in this country; and, in the next time period output in this economy will increase.
d.) increase the equilibrium level of interest rate while the level of investment will decrease in this country; and, in the next time period output in this economy will decrease.
The following table shows information of Taiwan.
|
Population (16 years or older)
|
10000
|
|
Number of employed workers with full time jobs
|
4200
|
|
Number of employed workers with part time jobs
|
3000
|
|
Number of people not searching for a job
|
1000
|
Problem 15. Given the information in the above table, what is the unemployment rate in Taiwan?
a) 30%
b) 20%
c) 40%
d) 58%
Binary Choice Questions :
Problem 16. Suppose the GDP of a country increased by 8% from 2007 to 2008. Suppose this increase in GDP was accompanied by extensive pollution that created serious health issues. In this case GDP per capita for this country
a.) will overstate the standard of living.
b.) will understate the standard of living.
Problem 17. Suppose that last year in an economy the GDP increased while the GDP per capita decreased. Then it must be true that
a.) the labor force in this economy decreased last year.
b.) there was population growth in this economy last year.
Problem 18. Madison's inflation rate between 2008 and 2009 is 10%. However, the nominal wage in Madison did not change between 2008 and 2009. Which of the following statements is true?
a.) The real wage in 2009 is lower than the real wage in 2008.
b.) The real wage in 2009 may be higher, lower, or equal to the real wage in 2008.
Problem 19. Initially, the loanable funds market is in equilibrium and aggregate expenditure is equal to aggregate income. After an increase in investment spending at every interest rate, the loanable funds market attains a new equilibrium with a higher level of investment. With this change in investment spending,
a.) aggregate expenditure is higher than aggregate income since investment spending is part of aggregate expenditure.
b.) aggregate expenditure is equal to aggregate income since the loanable funds market is in equilibrium.
Problem 20. Suppose the nominal GDP in China in 2009 is only 92% percent of the level of nominal GDP in China in 2008. With this information, one can conclude that China must be producing fewer goods in 2009 than it produced in 2008.
a.) True
b.) False
Problem 21. Suppose the unemployment rate of a country is 8% and there are 92 million employed people. At the time this unemployment rate was calculated this economy had 1 million discouraged workers. Suppose all of these discouraged workers reenter the job market to search for jobs. This change in the behavior of these discouraged workers will cause the
a.) unemployment rate to increase.
b.) unemployment rate to decrease.
Problem 22. In 2009, Japanese real GDP is $9 billion while the nominal GDP for Japan is $18 billion. Given this information, the value of the GDP deflator in Japan is equal to
a) 200
b) 50.
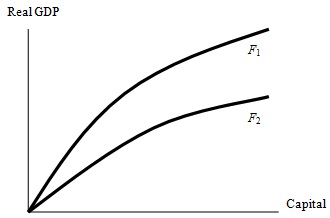
Problem 23. The above diagram shows the aggregate production function of a country shifting from F1 to F2. Such a shift in the aggregate production function could be caused by
a.) A decrease in the country's physical capital.
b.) A decrease in the country's labor force.
Problem 24. If the loanable funds market is in equilibrium, then
a.) injections are equal to leakages.
b.) injections are equal to the sum of leakages plus the trade deficit.
Problem 25. We may calculate GDP by the factor payment (income) approach or the value-added approach, and we know the two approaches will give us the same answer. However, for an individual firm, the total factor payments made by the firm are not necessarily equal to the value-added by the firm.
a.) True
b.) False
Problem 26. Suppose in an economy there is no change in the number of employed people, while at the same time some of the unemployed people in this economy decide to stop searching for jobs. This will cause the
a.) employment rate to increase in this economy.
b.) employment rate to remain unchanged in this economy.
Problem 27. In 2008, Paula bought 1000 shares of AT&T's stock in the stock market through a broker. Paula's purchase of this stock is
a.) counted in the value of GDP in 2008 as is the value of the stockbroker's services.
b.) not counted in value of GDP in 2008 while the value of the stockbroker's services is counted.