Discuss the below:
BASCS OF RAY OPTICS
Q1. A microscope has an objective with f = 1 cm, an ocular with f = 2.5 cm, and a distance s = 10 cm between them. Taking the best viewing distance as 25 cm,
a) Find the magnification of a microscope
b) Plot the picture of the rays to scale using the graph paper.
OPTICAL FIBRES - RAY OPTICS
Q2.Model a parabolic graded-index fibre with n (r) = n 1 [1-(r/a)² delta] for r is less than or equal to a , with n 1 = 1.5, a = 0.1 mm and delta = 0.01 , by the equivalent multiple-step approximation. Divide the radius into 10 equal parts. Consider a ray inside the fibre crossing the fibre axis at 5° with respect to that axis. Using the graph paper, plot the progress of the ray through the fibre until it turns back and re-crosses the fibre axis. (Angles can be magnified on the plot.) At what value of r/a will the ray turn back? Does it depend on the value of a ?
BASICS OF WAVE OPTICS
Q3. Find the superposition of two plane waves of equal amplitudes which have close but not equal frequencies. Plot a sketch of the resulting wave. Hint: Take the angular frequency of the waves as ω + Δω and ω - Δω, respectively. Consider the superposition at the point x = 0 and neglect the phase difference.
OPTICAL FIBRES - WAVE OPTICS
Q4. In a step-index fibre, the refraction coefficients of the core and the cladding layer are 1.500 and 1.505, respectively. Provide explanations.
1) Find the radius of the core, at which the fibre would perform as a single-mode at the wavelength of 1.3 µm, using a typical design criterion of v = 2
2) Find the cut-off wavelength for this fibre.
BASICS OF OPTICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS
Q5. Explain in your own words the difference between photoluminescence and electroluminescence.
SEMICONDUCTOR LIGHT-EMITTING DIODES
6. Explain, why an LED operating at the fixed current would be more stable than that operating at the fixed voltage. Consider the effect of the device heating on the I(V) characteristics. Explain under which condition there would be positive or negative feedback from the heating.
SEMICONDUCTOR LASER DIODES
Q7. A laser diode has a threshold current of 10mA and a slope of its optical power versus input current of 2mW/mA. The diode current is I = A + B sin ωt. Plot the output power as a function of time if:
[a] A = 20 mA; B = 2 mA;
[b] A = 10 mA; B = 2 mA;
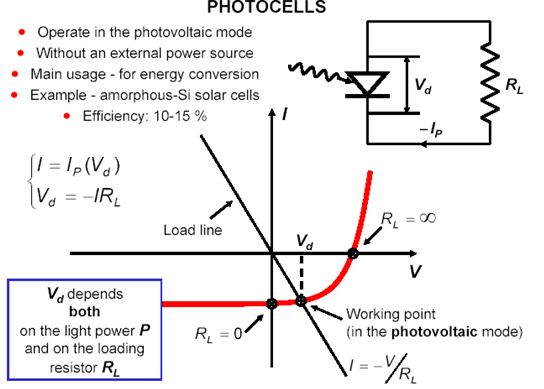
SEMICONDUCTER LIGHT DETECTORS
Q8. A p-n photodiode acts as a photocell, the circuit is shown below. Outline the band profile of the diode for infinitely large RL for different levels of illumination.