Binary Choice:
1. Real GDP and real GDP per capita always have different growth rates.
a. true
b. false
2. Credit lenders are better off if all inflation is anticipated.
a. true
b. false
3. If National Savings equals $120 billion and Investment is $ 140 billion, then Capital Inflow is positive.
a. true
b. false
4. The minimum wage is a price floor in the labor market. If the minimum wage is above the equilibrium wage, then
a. the employment level increases.
b. the unemployment level increases.
5. Country A’s production function is given by y = 2L0.5K0.5 while country B’s production function is given by Y = 2L + 0.5K . Suppose both countries have the same endowment of labor, L=16, and the same endowment of capital, K=100. Then, country A’s labor productivity is bigger than country B’s labor productivity when we have full employment.
a. true
b. false
6. Consider an open economy. In this economy net exports equal zero and the government is currently operating with a budget deficit. In this scenario, investment is less than private savings.
a. true
b. false
7. The nominal GDP growth rate from 2006 to 2007 in South Africa was 3%, so the real output (quantity of goods) produced in 2007 was larger than in 2006.
a. true
b. false
8. The GDP deflator is designed to adjust nominal GDP for changes in the quality of goods over time.
a. true
b. false
9. A price index like the CPI, which uses a fixed basket of goods from one year to the next, will tend to overstate inflation because
a. consumers will usually reduce their consumption of goods when they become relatively cheaper.
b. consumers will tend to substitute away from goods that become more expensive.
10. The type of unemployment caused by changes in the business cycle is natural unemployment.
a. true
b. false
Multiple Choice:
11. Rob is considered unemployed if he
a. has looked for a job in the last four weeks but has not found a job.
b. has worked at least 1 hour but not more than 15 hours as a paid employee last week.
c. does not have a job and stopped looking for a job at least two months ago.
d. has a part-time job but would like a full-time job.
12. A farm began the year with 1,000 pounds of milk in inventory, produced 10,000 pounds of milk during the year and ended the year with 1,100 pounds of milk in inventory. The 100 pounds added to his inventory will be classified as
a. consumption expenditures.
b. investment.
c. net exports of goods and services.
d. capital inflow.
13. In year 2005, US consumers spent $10 billion, interest payments were $1.5 billion, the government purchased $3 billion, net exports amounted to $2 billion, and investment was $8 billion. Hence the US 2005 GDP was
a. $21.5 billion.
b. $24.5 billion.
c. $23 billion.
d. $19.5 billion.
14. The Labor Force of Ithaca in 1325 BC consisted of 1200 people. The unemployment rate before the recession of 1325 BC was 25%, during the recession 400 employees were fired and half of them became discouraged workers. What was the after-recession unemployment rate in Ithaca?
a. 33%
b. 40%
c. 50%
d. 60%
15. In 2007 country A experienced an improvement in its technology. At the same time 1000 lawyers that were employed in country B migrated to country A. Given this information and holding everything else constant, the effect of these changes on the aggregate economy of country A will be
a. an increase in labor productivity and a decrease in aggregate production.
b. an increase in labor productivity and an increase in aggregate production.
c. an increase in aggregate production and an indeterminate impact on labor productivity.
d. an increase in labor productivity and an indeterminate impact on aggregate production.
16. Consider a country with a closed economy. Suppose the government then decides to increase its spending. Holding everything else constant, which of the following statements is NOT true given this increase in government spending?
a. The equilibrium interest rate will be higher.
b. Private saving will decrease.
c. The equilibrium level of investment will decrease.
d. National saving will decrease.
The following table provides information about production in some specific economy. Use this information to answer the next question. For this set of questions assume the market basket is defined as 10 oranges, 20 bananas, and 20 apples.
|
|
2008
|
2009
|
|
Price
|
Quantity
|
Price
|
Quantity
|
|
oranges
|
2
|
10
|
2
|
15
|
|
bananas
|
3
|
20
|
2
|
20
|
|
apples
|
1
|
20
|
3
|
10
|
17. Suppose 2008 is the base year. What is the value of the CPI in 2009?
a. 115
b. 90
c. 100
d. 120
18. Economic theory suggests that frictional unemployment would
a. decrease if methods of communicating job information among unemployed workers were improved.
b. increase if mothods of communicating job information among unemployed workers were improved.
c. decrease if the legally established minimum wage were increased.
d. decrease if unemployment benefits were increased.
19. The type of unemployment that occurs because of a recession is called
a. frictional unemployment.
b. seasonal unemployment.
c. natural unemployment.
d. cyclical unemployment.
20. Observe the following figure in which the aggregate production function of United States shifts from F1 to F2:
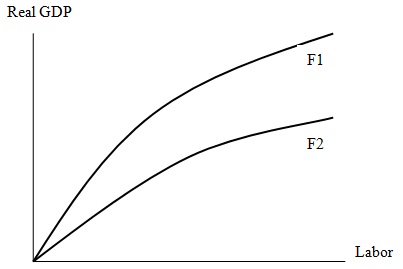
Which of the following could cause such a shift in the aggregate production function?
a. A decrease in the workday from 8 to 7 hours.
b. A less intensive use of installed capacity (less use of capital).
c. An decrease in the price of oil assuming that the US is a net importer of oil.
d. A subsidy per worker hired in the software industry.
21. Suppose that the government is currently running a big deficit and that it wants to close the gap between its revenues and expenditures. In order to reduce the deficit, the Government decides to cut subsidies that are applied to rural producers. In this situation we can observe
a. no shift of either the demand or supply curve.
b. a shift of the supply of loanable funds curve to the left.
c. a shift of the demand of loanable funds curve to the left.
d. a shift of the demand of loanable funds curve to the right.
Use the following Model to answer the next two questions:
Y=C+Sp+T–TR
Sg=T–TR–G
NS=Sp+Sg
NS=Y–C–G
KI=M–X
Y=C+I+G+(X–M)
In equilibrium, leakages=injections
Where Y = real GDP
C = consumption spending
Sp = private saving
T = taxes
TR = transfers
T – TR = net taxes
Sg = government saving
G = government spending
KI = capital inflows
M = Imports
X = exports
I = nvestment
Furthermore, suppose the government runs a balanced budget (that is, G – T + TR = 0) and collects $300 in tax revenue. Firms spend $55 on new capital and capital inflow equals $15. Income equals $450 and $220 of that income is spent on consumption. Furthermore, leakages equal injections in this economy.
22. What is the level of private saving in this economy?
a. $55 since private saving must equal investment in order for the loanable funds market to be in equilibrium.
b. $70 since businesses are spending $55 of their own money plus $15 provided via the foreign sector (i.e., capital inflows).
c. $40 since businesses are demanding $55 worth of loanable funds and the foreign sector is supplying only $15 worth of loanable funds.
d. $25 since the total demand for loanable funds is $40 and there are $15 of loanable funds being supplied through capital inflows.
23. What is the level of government transfers in this economy?
a. $0
b. $90
c. $110
d. $125
24. Binding minimum wages generally lead to:
a. cyclical unemployment since not everyone can find a job at the minimum wage rate.
b. frictional unemployment since the binding minimum wage results in longer job searches.
c. strucutural unemployment since more people want to work than can find jobs at the minimum wage.
d. all of the above answers are correct.
Use the following information to answer the next two questions:
Consider the market for loanable funds in a closed economy. The business demand for funds is given by r = 12 - (1/2)I, where I is investment (measured in millions of dollars) and r is the interest rate (measured as a percentage).
The private savings function is r = SP: , where Sp is private savings (measured in millions of dollars).
Assume that the government’s deficit changes from $0 to $6 million. (Note: deficit = G -(T - Tr))
25. How much business investment is crowded out as a result of this increase in government deficit?
a. $0
b. $2 million
c. $4 million
d. $6 million
26. How much does consumption change?
a. decrease by $2 million
b. increase by $4 million
c. decrease by $4 million
d. can’t determine
27. If there in an increase in exports holding everything else constant, the equilibrium interest rate in the loanable funds market will
a. fall.
b. rise.
c. no change.
d. be indeterminate.
28. There are 100 households in the economy. Half of these households save according to r = 2 + Sp/10 while the other half of the households save according to r = 5 + Sp/5 where each of these equations expresses the saving function for one household. What is the market private savings function?
a. r = 2 + Sp/500 for 2 < r < 5 and r = 5 + Sp/250 for r > 5
b. r = 2 + Sp/500 for 2 < r < 5 and r = 3 + Sp/750 for r > 5
c. r = 100 + 5Sp for 2 < r < 5 and r = 250 + 10Sp for r > 5
d. r = 3.5 + 3Sp/500
29. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
a. Infrastructure is typically provided by private companies.
b. Basic public health measures, like clean water, are not considered part of an economy’s infrastructure.
c. Countries with low levels of infrastructure typically experience low rates of economic growth.
d. Only local governments are allowed to invest in infrastructure in a specific city.
30. Suppose there are 100 working-age people, 80 of whom are in the labor force. Of these, 70 are employed and 10 are unemployed.
a. The unemployment rate is 10 percent.
b. The employment/population ratio is 80 percent.
c. The labor force participation rate is 80 percent.
d. The employment rate is 14.3 percent.