Binary Choice:
Problem 1) Alice is in charge of the statistics bureau in the small nation of Wonderland, and part of her job is computing GDP for Wonderland. Until this year, Wonderland had a closed economy for widgets with a domestic price of $5 per widget. This year, however, Wonderland entered the international market for widgets, where the world price of widgets is $2. Given this information, what can Alice expect to happen to Wonderland's nominal GDP this year relative to last year's nominal GDP in Wonderland? Assume production in all other markets is unaffected by this change.
a. Nominal GDP will decrease.
b. Nominal GDP will increase.
Problem 2) 1,000,000 people live and work in Someland. Of these 1,000,000 people, half are citizens of Someland. Additionally, there are 10,000 citizens of Someland, who live and work overseas in Finland. All residents and citizens of Someland produce $20,000 of output per year per person.Given this information, what can we say about the relationship of Someland'sGDP to Someland'sGNP?
a. Someland'sGDP will be higher than Someland'sGNP.
b. Someland'sGDP will be lower than Someland'sGNP.
Problem 3) "Investing in early childhood education will have positive effects on the child's future income." This is an example of a _______ statement.
a. Positive
b. Normative
Problem 4) If we want to find the market demand curve for a private good, should we vertically sum or horizontally sum the individual demand curves?
a. Vertically sum
b. Horizontally sum
Problem 5) A researcher collects data on real GDP and the CPI for each US state for the year 2014. We say that she has collected _________ data.
a. Cross-sectional
b. Time-series
Problem 6) Suppose that a researcher at UW has shown that lettuce is healthier than previously believed, leading consumers to develop a stronger preference for lettuce. At the same time the drought in California has resulted in reductions in lettuce production. Holding everything else constant, we can conclude that:
a. The equilibrium price of lettuce is indeterminate.
b. The equilibrium quantity of lettuce is indeterminate.
Problem 7) Suppose when operating efficiently, a furniture factory can produce 5 tables and 10 chairs, or it can produce 8 tables and 4 chairs. Assuming constant opportunity cost, is it feasible for the factory to produce 3 tables and 16 chairs?
a. Yes. This production combination is feasible.
b. No. This production combination is not feasible.
Use the following information for the next two (2) questions:
Robinson Crusoe works 8 hours a day. It takes him 2 hours to collect one coconut and 4 hours to catch a fish. His friend, Friday, works 12 hours a day. Friday needs 1.5 hours to collect a coconut and 2 hours to catch a fish. Assume that both Robinson Crusoe and Friday each have constant opportunity costs.
Problem 8) Given the above information, who hasthe comparative advantage in catching fish?
a. Robinson Crusoe
b. Friday
Problem 9) Suppose that Robinson Crusoe decides to work 12 hours a day as well. Now given this new information, who has the comparative advantage in collecting coconuts?
a. Robinson Crusoe
b. Friday
Problem 10) Use the following graph to answer this question. The graph shows a joint PPF for Adam and Ben who both produce pencils and erasers.
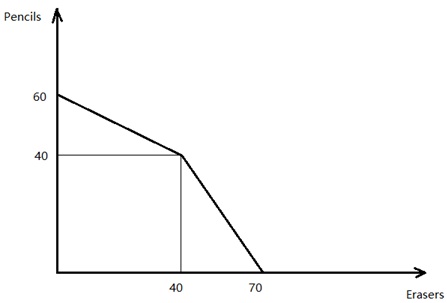
Suppose that when producing efficiently, Ben could at most produce 30 erasers. Given this information and the above graph, who has the comparative advantage in producing erasers?
a. Adam
b. Ben
Multiple Choice:
Problem 11) McDonald's and Burger King both make burgers (B) and Fries (F). Suppose they have the following PPFs:
McDonald's PPF: B = -(1/4) F+3
Burger King's PPF: B = - (1/2) F +5
Now, consider the joint PPF for McDonald's and Burger King. Which of the following combinations of burgers and fries is efficient if both firms work together?
a. 0 burgersand 20 packets of fries
b. 3 burgers and 10 packets of fries
c. 5 burgers and 10 packets of fries
d. 7 burgers and 4 packets of fries
Problem 12) Both Casey and Dorothy produce erasers and pencils. It takes Casey 2 hours to make one eraser and 1 hour to make one pencil. It takes Dorothy 3 hours to make either one eraser or one pencil. Now, imagine that Casey and Dorothy engage in trade with one another. The acceptable range of trading prices for one pencil in terms of erasers is:
a. Between 2/3 eraser and 1 eraser.
b. Between 1 eraser and 2 erasers.
c. Between 1/2 eraser and 1 eraser.
d. Between 1/3 eraser and 2/3 eraser.
Problem 13) Pentos and Westeros are two nations that produce swords and silk. Pentos and Westeros both have linear PPFs: at most, Pentos could produce a maximum of 300 swords or 600 pieces of silk annually;Westeros could produce a maximum of 2000 pieces of silk annually, but it keeps a secret and does not reveal the maximum number of swords it could produce.
As a spy from Pentos, you want to know the maximum number of swords Westeros can produce annually. You notice that when Pentos and Westeros engage in trade, the acceptable range of trading prices for one sword is between 4/3 pieces of silk and 2 pieces of silk.
Given this information, the maximumnumber of swords Westeros can produce in a year is:
a. 4000swords.
b. 3000swords.
c. 1500swords.
d. 1000swords.
Problem 14) The supply and demand for inline skates are represented by the following equations where P is the price per pair of inline skates and Q is the quantity of pairs of inline skates.
Supply: P = (1/10)*QS + 60
Demand: P = 360 -(1/5)*QD
Given the above information and holding everything else constant, what is the equilibrium price?
a. $180 per pair of inline skates
b. $160 per pair of inline skates
c. $210 per pair of inline skates
d. $1000 per pair of inline skates
Problem 15) Sarah's monthly demand for coffee is P = 6 - 1/4*Q. She has trouble falling asleep, so she decides to cut back her intake by 4 coffee drinks at every possible price. Given this information and holding everything else constant, her new demand for coffee is:
a. P = 10 - (1/4)*Q
b. P = 7 - (3/10)*Q
c. P = 5 - (1/4)*Q
d. P = 2 - (1/4)*Q
Problem 16) Kiril and Anna are the only consumers of mangoes in Slavia. Their demand curves are:
Kiril's Demand: P = 5 - Q
Anna's Demand: 3P = 9 - Q
Given the above information and holding everything else constant, which of the following equations represents the market demand for mangoes in Slavia?
a. Q = 8 - (4/7)P
b. Q = 5 - P for 3 ≤ P ≤ 5
Q = 14 - 4P for 0 ≤ P ≤ 3
c. P = Q - 5 for 3 ≤ P ≤ 5
P = (1/4)Q - (7/2) for 0 ≤ P ≤ 3
d. P = 5 - Q for 0 ≤ P ≤ 3
P = (7/2) - (1/4)Q for 3 ≤ P ≤ 5
Problem 17) The following graph represents real GDP for the dictatorship of Gruyovia from 2007 to 2014 measured in billions of US dollars. What happened to real GDP from 2013 to 2014?
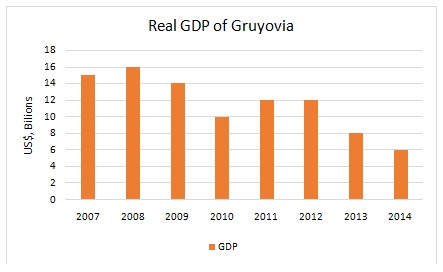
a. Real GDP decreased by 33.33%.
b. Real GDP increased by 33.33%.
c. Real GDP decreased by 25%.
d. Real GDP decreased by 20%.
Problem 18) The following graphs represent the market demand for avocados in Wisconsin. One of these demand curves provides different information from the other three. Which graph provides different information?
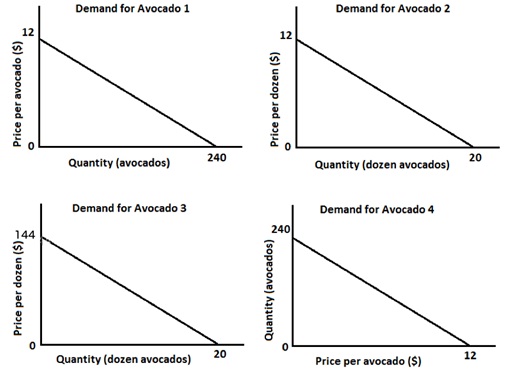
a. Demand for avocado 1
b. Demand for avocado 2
c. Demand for avocado 3
d. Demand for avocado 4
(Note: the above question originally had an error in resulting in two correct answers. This version has been corrected for future reference.)
Problem 19) The White Witch is the somewhat unscrupulous leader of Narnia. In order to convince people that her economic policies are working, she provides the following GDP data:
|
|
Real GDP...
|
...using Base Year
|
|
2012
|
$1,000,000
|
1980
|
|
2013
|
$1,100,000
|
1980
|
|
2014
|
$9,000,000
|
2014
|
Being a well-educated citizen of Narnia, Tumnus realizes something is amiss with the data, because the base year would normally not change. Searching his data tables, he finds that the GDP deflator for 2014 using a base year of 1980 was 900 (the scale factor is 100). Given this information, which of the following statements is FALSE?
a. Nominal GDP in 2014 was $9,000,000.
b. When using the base year of 1980, real GDP decreased between 2013 and 2014.
c. Price levels decreased between 1980 and 2014.
d. When using the base year of 1980, Real GDP in 2012 equals Real GDP in 2014.
Use the following information for the next two (2) questions:
Pirate Island is a small economy with a domestic market for cutlasses (a type of sword) that can be described by the following equations where P is the price per cutlass and Q is the quantity of cutlasses:
Domestic Demand: P = 100 - Q
Domestic Supply: P = Q
You are also told that the world price of cutlasses is $10 per cutlass.
Problem 20) George is the king of Pirate Island, a small economy. Perhaps not unsurprisingly for a Pirate King, George is rather corrupt, and wishes to enrich his friend Bob. To do this secretly, George decides to enact a quota limit in the cutlass market (under the pretense of protecting domestic suppliers) and grant the import license to Bob. If George wants Bob to earn $800, the import quota should be equal to:
a. 20 units
b. 40 units
c. 60 units
d. 80 units
Problem 21) Unfortunately for George, the pirates of Pirate Island are surprisingly well-educated in economic matters and realize that this import quota enriches Bob at the cost of generating deadweight-loss. George doesn't want to upset Bob, and thus doesn't want to eliminate the import quota, but also fears an uprising by the unhappy pirate citizens. Thus, he decides to change the import quota so that there is zero deadweight loss. Which of the following import quotas has zero deadweight loss? An import quota of:
a. 0 units
b. 50 units
c. 60 units
d. 90 units
Problem 22) Which of the following four options has an opposite effect on the demand for good X from the other three options? Assume that good X is a normal good.
a. an increase in the price of a substitute good in consumption
b. an increase in the price of a complement good in consumption
c. a decrease in income
d. a change in tastes against good X
Problem 23) How do deadweight loss and government revenue change as the level of an import tariff increases, assuming the tariff is effective?
a. Both deadweight loss and government revenue increase as the size of the tariff increases.
b. Deadweight loss increases, while government revenue initially decreases and then increases as the size of the tariff increases.
c. Deadweight loss increases, while government revenue initially increases and then declines as the size of the tariff increases.
d. Government revenue increases, while deadweight loss initially increases and then declines as the size of the tariff increases.
Problem 24) Suppose Alice, Bob, Charlie, and Sam can all produce coconuts and fish according to the following opportunity costs:
Alice: 10 coconuts per fish
Bob: 5 coconuts per fish
Charlie: 1/10 of a fish per coconut
Sam: 1/5 of a fish per coconut
If you were to graph the joint-PPF for these four individuals, how many "kink points" would the joint PPF have?
a. 1 kink point
b. 2 kink points
c. 3 kink points
d. 4 kink points
Problem 25) England and Portugal are producers of woolen cloth (C) and wine (W). Assume that in a given year, England could produce the following combinations of cloth and wine when producing efficiently:
|
|
Units of Woolen Cloth
|
Units of Wine
|
|
Combination 1
|
10
|
10
|
|
Combination 2
|
20
|
0
|
Portugal, benefiting from a more pleasant climate, could produce the following combinations:
|
|
Units of Woolen Cloth
|
Units of Wine
|
|
Combination 1
|
10
|
20
|
|
Combination 2
|
5
|
30
|
Assume both countries have constant opportunity costs of production for these two goods.
The joint PPF curve for England and Portugal is of the following shape:
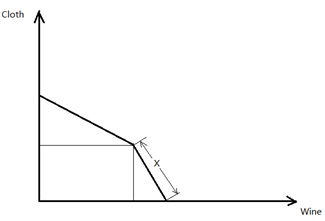
Given the above information, what is the function, or the equation, for the lower segment (labeled x in the graph) of the PPF? (Note: Wine is one the horizontal axis, and Cloth is on the vertical axis)
a. C = 60 - W
b. C = 40 - W
c. C = 60 - 2W
d. C = 40 - 2W
Use the following information for the next three (3) questions:
Suppose the market for lemons at the Capitol Square Farmer's Market can be described by the following demand and supply equations where P is the price of a lemonand Q is the quantity of lemons.
Demand: Q = 10 -P
Supply: Q = 3P-6
Problem 26) Calculate the equilibrium price and quantity for this market.
a. P=$5 per lemon and Q=5 lemons
b. P= $4per lemonand Q=6 lemons
c. P= $8 per lemonand Q=2 lemons
d. P = $10 per lemon and Q = 7 lemons
Problem 27) Calculate the producer surplus and consumer surplus in this market.
a. Producer surplus = $6 and Consumer surplus = $18
b. Producer surplus = $36 and Consumer surplus = $6
c. Producer surplus = $14 and Consumer surplus = $24
d. Producer surplus = $24 and Consumer surplus = $6
Problem 28) Suppose the Madison City Council attempts to help farmers by setting a price floor of $7 per lemon in the market for lemons. What is the deadweight loss of such a policy?
a. $12
b. $6
c. $3
d. $9
Problem 29) The US Census Bureau provides the following information on the share of household income held by each quintile of the income distribution in the years 1993, 2003, and 2013.
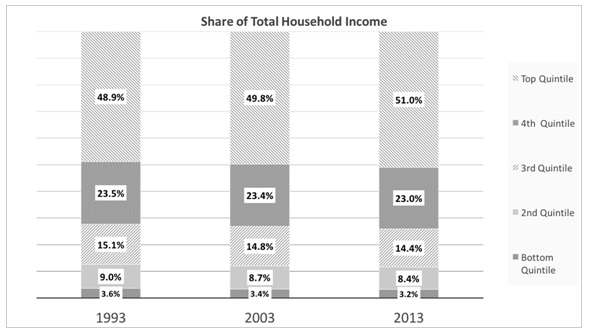
Which of the following statements about the income distribution is FALSE given the information in the graph above?
a. The share of total income held by the middle 3 quintiles increased between 1993 and 2013
b. Income has become less concentratedat the bottom of the distribution.
c. Income has become more concentrated at the top of the distribution.
d. The share of income held by the bottom two quintiles in 2003 was 12.1%.