PART I: TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS
Question 1) If tuition for all classes is $500 per course then the opportunity cost of taking the course is the same for all students.
Question 2) Talented people that are the best at everything have a comparative advantage in the production of everything.
Question 3) If trade benefits one country, its trading partner must be worse off due to trade.
Question 4) Poor countries gain from trade with rich countries.
Question 5) Specialization in production only occurs in developed countries.
Question 6) A simultaneous increase in demand and supply leads to an increase in prices.
Question 7) The value of the automobiles produced by a General Motors plant in Spain is not included in U.S. GNP.
Question 8) Since the value added approach and the expenditure approach are different approaches to calculating GDP, they will give different values for it.
Question 9) Imposing effective minimum wage legislation tends to reduce the number of low skilled workers employed.
Question 10) It is possible to see the prices of some goods and services decreasing while the CPI is increasing.
Question 11) Less developed countries with very low growth rates typically suffer from poor infrastructure and very low population growth rates.
Question 12) According to the classical view, the economy needs the government's help in achieving full employment.
Question 13) A binding price ceiling (when it is lower than the equilibrium price) causes deadweight loss.
Question 14) With a vertical demand curve (a perfectly inelastic demand curve), consumers bear the full economic burden of an excise tax.
Question 15) GDP is the value of everything sold within a given year within the borders of a country.
Question 16) If some unemployed workers become discouraged workers while other factors remain unchanged, the unemployment rate will go down.
PART II: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Question 17) Which of the following is a positive statement?
a) An unemployment rate of 7 percent is a national disgrace.
b) Unemployment is not so important a problem as inflation.
c) When the national unemployment rate is 7 percent, the unemployment rate for inner-city youth is often close to 40 percent.
d) Unemployment and inflation are equally important problems.
e) An increase in the inflation rate is unacceptable.
Question 18) All of the following would tend to increase a nation’s production possibilities EXCEPT:
a) The culture becomes more accepting of women who work.
b) A new hybrid for wheat is discovered.
c) A government program is instituted that encourages college education.
d) The nation decides (by whatever method) to increase production of investment goods and decrease production of consumption goods.
e) All of the above would tend to expand a nation’s production possibilities.
Question 19) The table below shows how many hours each superhero, Batman and Robin, needs to save a life or a city.
|
|
Hours to Save a Life
|
Hours to Save a City
|
|
Batman
|
2
|
1
|
|
Robin
|
6
|
2
|
Then:
a) Batman has absolute and comparative advantages in both saving lives and cities.
b) Robin has absolute and comparative advantages in both saving lives and cities.
c) Batman has an absolute advantage in both saving lives and cities, and Robin has a comparative advantage in both saving lives and cities.
d) Batman has a comparative advantage in saving lives, but Robin has a comparative advantage in saving cities.
e) Robin has a comparative advantage in saving lives, but Batman has a comparative advantage in saving cities.
Question 20) Suppose that beside the information in the previous question we know that Batman & Robin have 12 hours to spend on saving lives and/or cities, and each of them are currently spending half of their time on each activity. Then:
a) There is no way to increase the total number of cities and lives saved.
b) Since Robin does not have an absolute advantage in producing either good, there will be more saved cities or lives if he stops working.
c) If Robin tends to specialize in saving Cities, and Batman tends to specialize in saving lives, then there will be an increase in production.
d) If Batman tends to specialize in saving Cities, and Robin tends to specialize in saving lives, then there will be an increase in production.
e) If Robin and Batman both specialize in saving cities, then there will be an increase in production.
Use Figure to answer questions below.
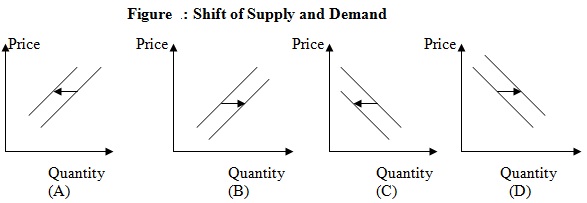
Question 21) The above graphs represent the supply or demand (depending on which graph you view) for steel. Which of the graphs above best describes the effect of the introduction of environmental restrictions by the government on the dumping of wastes from processing steel?
a) (A)
b) (B)
c) (C)
d) (D)
e) Either (A) or (C).
Question 22) Assume that a series of forest fires reduces the supply of lumber, which is an input in the production of wooden bats. Baseballs and wooden bats are complements. Consumers can expect the price of wooden bats to:
a) Decrease and the demand for baseballs to decrease.
b) Decrease and the demand for baseballs to increase.
c) Increase and the demand for baseballs to decrease.
d) Increase and the supply of baseballs to increase.
e) Increase and the supply of baseballs to decrease.
Use the following demand and supply functions for questions 23 and 24:
Demand: Qd = 80 - p Supply: Qs = -10 + 2p
Question 23) Consumer surplus (CS) and producer surplus (PS) in equilibrium are:
a) CS = 625; PS = 625
b) CS = 2500; PS = 1250
c) CS = 1250; PS = 1250
d) CS = 1250; PS = 625
e) CS = 625; PS = 1250
Question 24) Suppose that the government imposes an excise tax of $3 per unit on producers. Which of the following is true?
a) $1 of the per unit tax is paid by consumers and $2 of it is paid by producers.
b) $1 of the per unit tax is paid by producers and $2 of it is paid by consumers.
c) The tax results in a deadweight loss of $3.
d) Both a) and c).
e) Both b) and c).
Question 25) In 1998, the country of Derf's imports equaled its exports. Derf's GDP was $500 million, its consumer expenditure was $385 million, and its investment was $14 million. Derf's government purchases were _______.
a) $500 million.
b) $899 million.
c) $101 million.
d) zero.
e) Equal to its imports.
Question 26) All of the following expenditures are included in investment expenditures except:
a) Business purchase of a fleet of new cars.
b) Household purchase of a new house.
c) A retail store's purchase of shoes to add to inventory.
d) A business firm financing a new plant by issuing stock.
e) A business firm buying the stock of a competing firm.
Question 27) In an economy, 20 million people are full-time workers, 5 million are part-time workers, 2 million are unemployed, and 6 million are not in the labor force. Assume that all people in this economy are 16 years or older. What is the employment-to-population ratio approximately?
a) 75 percent.
b) 83 percent.
c) 65 percent.
d) 85 percent .
e) cannot be determined from the information provided.
Question 28) The natural rate of unemployment ________.
a) Is the same from year to year.
b) Equals zero.
c) Is the unemployment rate when there is no cyclical unemployment.
d) Is greater than the actual rate of unemployment.
e) Is equal to the sum of cyclical, frictional and structural unemployment rates.
Question 29) Which of the following characterize index numbers?
a) Index numbers express observed data relative to some base value.
b) Index numbers indicate overall trends in an economy rather than specific detailed facts.
c) Index numbers often require that the individual items in the index be assigned some weight to reflect each item's overall importance to the final index number.
d) Index numbers are often used to measure aggregate macroeconomic variables.
e) All of the above.
Question 30) A typical family in Dref buys only oranges and pens. In the base year, it bought 400 oranges at $1.00 each and 800 pens at $0.75 each. This year, a family buys 500 oranges at $1.50 each and 850 pens at $1.00 each. The CPI this year is _________.
a) 62.5
b) 1.40
c) 160
d) 140
e) 1.60
Question 31) With the classical long run model we are trying to explain all of the following, BUT:
a) How real wages will be determined.
b) How total employment will be determined.
c) How much output will be produced.
d) Why short-run business fluctuations occur.
e) How consumer savings will be determined.
Question 32) In the classical model, with an increase in government purchases of goods and services we expect to see all of the following, BUT:
a) An increase in savings.
b) A decrease in investment.
c) An increase in GDP.
d) A decrease in consumption.
e) An increase in the interest rate.