Discuss the below in detail:
The Speed of Nitrogen Molecules
The kinetic theory of gases states that the kinetic energy of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas. A relationship between the microscopic properties of the gas molecules and the macroscopic properties of the gas can be derived using the following assumptions:
• The gas is composed of pointlike particles separated by comparatively large distances.
• The gas molecules are in continual random motion with collisions being perfectly elastic.
• The gas molecules exert no long-range forces on each other.
One of the most important microscopic properties of gas molecules is velocity. There are several different ways to describe statistically the average velocity of a molecule in a gas. The most obvious measure is the average velocity . However, since the molecules in a gas are moving in random directions, the average velocity is approximately zero. Another measure of velocity is ,v2(avg) the average squared velocity.
Since the square of velocity is always positive, this measure does not average to zero over the entire gas. A third measure is the root-mean-square (rms) speed,vrms, equal to the square root of v2(avg) . The rms speed is a good approximation of the the typical speed of the molecules in a gas.
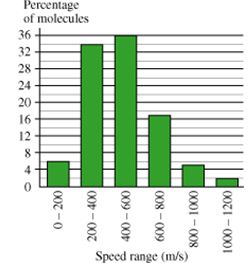
This histogram shows a theoretical distribution of speeds of molecules in a sample of nitrogen (N2) gas. In this problem, you'll use the histogram to compute properties of the gas.
A. What is the average speed of the molecules in the gas?Express your answer numerically to three significant digits.
B. Because the kinetic energy of a single molecule is related to its velocity squared, the best measure of the kinetic energy of the entire gas is obtained by computing the mean squared velocity, , or its square root . The quantity is more common than because it has the dimensions of velocity instead of the less-familiar velocity-squared. What is the rms speed of the molecules in the nitrogen gas?
Express your answer numerically to three significant digits.
C. What is the temperature of the sample of gas described in the histogram. Express your answer in degrees Celsius to three significant figues.