Question 1: Sketch the transition state for the first step in oxidative addition of a benzyl halide and a square planar complex ML4.
Question 2: Describe the following. The cis isomer of L2Pd(Et)2 decomposes instantly to give butane, however the trans isomer produces a 1:1 mixture of ethene and ethane.
Question 3: The reaction of L2Pd(Me)2 with PhC*HDBr produced PhC*HDMe. Determine the other product and do you expect retention or inversion at chiral carbon?
Question 4: SO2 can insert into an LnM-CR3 bond. The reaction is thought to proceed by an SE2 pathway to form an ion pair, [LnM]+[OS(O)R]–. Collapse of the ion pair produces the O-sulfinate (formally a 1,2-insertion of SO2), which can re-arrange to the S-sulfinate (formally a 1,1-insertion of SO2). Draw the transition state, the ion pair, and the O- and S-sulfinates.
Question 5: Give a mechanism for the reaction:
LnZr–H + E–2-butene → LnZr–CH2CH2CH2CH3
Question 6: Binding of Cr(CO)3 to an achiral arene:
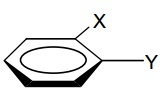
gives a chiral complex. Describe this. What about for meta- and para- substituted arenes? How might this be helpful?