Question 1: How does the marginal social benefit curve of a common resource compare to the marginal social benefit curve of positive externality from a mixed good? Highlight the differences via graphs.
Question 2:
a) Assume that the demand for saline solution is perfectly inelastic for contact lens wearers. If the government imposes a tax on saline solution, what occurs? Be sure to tell what happens to the price paid by the buyers and discuss the incidence of the tax.
b) If income tax rates on labor income are reduced, what is the effect on the labor supply and the labor supply curve? What is the effect on the equilibrium quantity of labor hired?
Question 3: Describe:
a) Tragedy of commons.
b) Free rider problem.
c) Diminishing marginal utility.
d) Diseconomies of scale.
e) Tax incidence.
f) Elasticity.
g) Gains from trade.
h) Rent- seeking in monopoly.
i) Public goods.
Question 4:
a) If the price elasticity of supply for corn is 3.12, then is the supply of corn elastic or inelastic?
b) If the cross elasticity of demand between peanut butter and milk is -1.11, then are peanut butter and milk substitutes or complements?
c) The income elasticity of demand for movies in the United States is 3.41. If people's incomes decrease by 1 percent, what is the decrease in the quantity of movies demanded?
Question 5: Ayanna grows herbs. Last year she grew 2,000 pounds of herbs in a year while using 250 square feet of land and 1 worker. This year she doubled her land to 500 square feet, doubled her workers to 2, and grew 4,500 pounds of herbs. She sells her rare, organic herbs for $50 a pound. She pays her a worker $25,000 a year and rents her land for $100 per square foot for a year. These are her only costs.
a) What was Ayanna's total cost last year and this year?
b) What was Ayanna's average total cost last year and this year?
c) Did Ayanna experience economies or diseconomies of scale?
Question 6:
a) What is a prisoner's dilemma?
b) Why would a firm in a monopolistically competitive industry advertise?
Question 7: Through graphs describe the relationship between the price, P and the average total cost, ATC, for a firm in perfect competition when it earns an economic profit; earns a normal profit or zero economic profit and; incurs an economic loss? Why can't the firm continue making economic profits in the long run?
Question 8:
a) To maximize the utility, why does a consumer consume the combination of goods which equates marginal utility per dollar from the different goods instead of just equating the marginal utility of the different goods?
b) Why does gold, which is a relatively non-essential item, have a higher price than water, which is essential to life?
Question 9: Describe what are price ceilings and price floors and how they affect the market for a good or service. As well show through graphs, if they cause any inefficiency in a perfectly competitive market.
Question 10: Before first Gulf War, Kuwait had the capacity to produce a certain amount of oil from its oil wells. After the war, it found that capacity greatly diminished as the oil wells were on fire. Draw Kuwait's PPF before and after the war, assuming that the only two goods produced are oil and food. Further assume that setting the oil wells on fire did not affect Kuwait's ability to produce food. Explain why the PPF before the war is distinct from the PPF after the war. If instead, Kuwait had faced economic growth how would it reflect on the PPF?
Question 11: "Price discrimination permits a monopoly to raise its economic profit by capturing part of the consumer surplus and turning it into economic profit. Such a situation though leads to a deadweight loss to the society as a whole in the long run." Is the previous statement correct or incorrect? If the statement is correct, why is it important in understanding firms' behaviors?
Question 12: Describe the three arguments used to promote trade barriers and two instruments to impose these trade restrictions in a country.
Question 13: How can a nation and its producers determine whether or not it has a comparative advantage in producing a particular good or service?
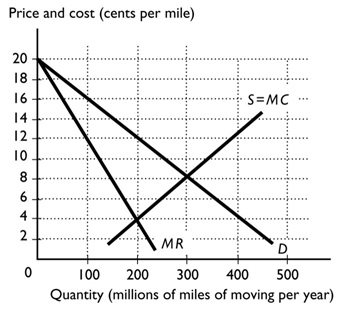
Question 14: The above figure displays the market for the three moving companies in a small nation. If the movers act as perfect competitors, what is the price per mile and the number of miles per year? If the movers collude and act as a single monopoly, what is the price per mile and the number of lines per year?
Question 15:
a) "The marginal rate of substitution of the good measured along the x-axis increases as a consumer moves downward along an indifference curve." Is the previous statement correct or not?
b) Explain the consumer equilibrium in the indifference curve or budget line model.