PART 1: BINARY CHOICE
Question 1. Suppose the economy of Macroland is in long-run equilibrium and that aggregate production in Macroland can be described by the following aggregate production function: Y = 20K 1/2 L1/2. The labor supply of Macroland suddenly doubles as a result of a change in immigration laws. Holding everything else constant, what will happen to capital productivity in Macroland?
a. It will increase
b. It will decrease
Question 2. Assume the unemployment rate is initially less than 100%. Holding everything else constant, counting prisoners as part of the labor force in this economy would ______ the unemployment rate.
a. decrease
b. increase
Question 3. An increase in the prevalence of labor unions with successful bargaining power would likely affect the unemployment rate through an increase in the _________.
a. structural unemployment rate
b. frictional unemployment rate
Question 4. From 2000 to 2001, the GDP deflator increased by 10% and real GDP decreased by 10%. Nominal GDP in 2001 must therefore be
a. as high or higher than nominal GDP in 2000.
b. lower than nominal GDP in 2000.
Question 5. As certain goods become relatively more expensive, consumers tend to substitute away from these goods towards goods that are relatively cheaper. This will cause the CPI to ___________ the impact of rising prices.
a. overstate
b. understate
Question 6. Over time suppose the rate of inflation from one period of time to the next period of time is increasing. Given this scenario I am
a. Less likely to spend money today and instead wait to spend money until a later point in time.
b. More likely to spend money today instead of waiting to spend money at a later point intime.
Use the following diagram of the circular flow diagram of monetary flows in an economy for the next two questions:
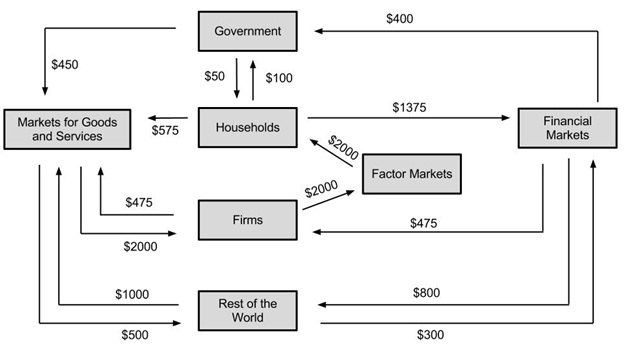
Question 7. Consider the expenditure approach to calculating GDP. Which of the following is larger in this economy?
a. Government Spending
b. Investment Spending
Question 8. What is the level of consumption spending in this economy?
a. $1375
b. $575
Question 9. Nick has $50 and gets an annual interest rate of 7% on this money. James has $300 and gets an annual interest rate of 3.5%. Who will be better off in 40 years? Assume that neither individual spends any of these funds or the accumulation of interest from these funds over the entire 40 years.
a. James
b. Nick
Question 10. Suppose that real GDP per capita in the U.S. in 2013 is approximately $50,000 while real GDP per capital in China in 2013 is approximately $5,000. Furthermore, suppose that real GDP per capita in the U.S. grows at a constant 3.5% a year while real GDP per capita in China grows at a constant 7% a year. (We are using "easier" numbers than the real numbers in this example.) Holding everything else constant, in twenty years China's real GDP per capita will be equal to __________ of the U.S.'s real GDP per capita.
a. 20%
b. 10%
PART 2: MULTIPLE CHOICE
Question 11. Kruglandia is a small country with a total working-age population of 500 people. It has an unemployment rate of 5% and a labor force participation rate of 80%. How many individuals are employed in the labor market of Kruglandia?
a. 370 people
b. 380 people
c. 375 people
d. 400 people
Question 12. Bob invested $100 dollars in a bond (this is similar to an IOU that promises the holder of the IOU a yearly interest payment) that has an annual interest rate of 5%. How long does it take for Bob's investment to reach $400?
a. 28 years
b. 42 years
c. 30 years
d. 56 years
13. Which of the following would be included in calculations of US GNP?
a. Pierre, from France, comes to New York to work in a bookshop.
b. Ralph,who is from Great Britain but living in New York, imports goods from China that were manufactured by a Chinese owned company.
c. Sonoko, from Seattle, is getting her degree at the University of Madrid, in Spain.
d. Philip, from Madison, works for Michelin (a French company), as a salesrepresentative for their tires.
Question 14. Hanna is writing an essay arguing that Macroland's reported GDP per capita overestimates the true quality of life of its poorest citizens. (Assume Macroland follows the usual rules for calculation of GDP.) Which of the following topics would least help her argument?
a. Pollution externalities
b. Wealth Inequality
c. Lack of social programs for the poor in Macroland
d. Economic transactions not reported to the IRS (the Internal Revenue Service, thetax collection agency in Macroland)
Question 15. Which of the following is NOT included in the Natural Rate of Unemployment?
a. Cyclical Unemployment
b. Frictional Unemployment
c. Structural Unemployment
d. All of the above are included in the Natural Rate of Unemployment.
Question 16. Macroville has only 2 companies: Macroville Lumber and Macroville Paper. The paper mill purchases all lumber produced by Macroville Lumber, and lumberis the only intermediate good that goes into the production of paper. Neither company incurs any expense from the hiring of capital. The following chart contains information on their inputs and expenditures. Note that a careless data analyst accidently left out some information.
|
|
Macroville Lumber
|
Macroville Paper
|
Total Factor Income
|
|
Intermediate Goods
|
$0
|
$150 (Lumber)
|
-
|
|
Wages
|
????
|
$90
|
|
|
Profit
|
|
|
$120
|
|
Rent
|
|
|
$100
|
|
Value Added
|
|
$300
|
|
What does Macroville Lumber pay in total wages?
a. $230
b. $80
c. $100
d. $140
Question 17. Mary spends $175 at the grocery store this week: she purchases $90 worth of canned goods that were produced in the U.S., $10 worth of cheese made in France, $20 worth of wine from Chile, $15 worth of Belgium-styled beer made in Wisconsin, and $40 of produce with half of this produce produced in Mexico and half produced in California. How much did Mary's expenditures at the grocery store this week affect the level of GDP in the U.S.?
a. GDP increased by $175 this week due to Mary's expenditures at the grocery store.
b. GDP increased by $125 this week due to Mary's expenditures at the grocery store.
c. GDP increased by $110 this week due to Mary's expenditures at the grocery store.
d. GDP decreased by $50 due to the imports that Mary purchased when shopping at the grocery store.
Question 18. When calculating its CPI, Econville uses a market basket that includes 4 apples and 2 bananas. In 2010, apples cost $0.40 and bananas cost $0.20. In 2011, apples cost $0.42 and bananas cost $0.18. If Ellen, a resident of Econville, had her money in the bank earning an annual interest rate of 1.5%during that time, what was the real interest rate approximately equal to on her deposit?
a. -0.5%
b. 0.5%
c. 2.0%
d. 3.5%
Question 19. Suppose in Wisconsin only beer and cheese are produced. In 2012, 20 kegs of beer and 30 pounds of cheese were produced. In 2012, the price for beer was $10/keg and for cheese $15/lb. In 2010, only 10 kegs of beer and 20 pounds of cheese were produced. Prices in 2010 were $5/keg for beer and $10/lb for cheese. If the GDP deflator is equal to 1 in 2012, what is the GDP deflator in 2010?
a. 1.625
b. 1.375
c. 0.625
d. 1.600
Question 20. Imagine an economy that only produces one good. 60 units were produced in 2004 and 75 units were produced in 2005. The nominal GDP increased by 25% from 2004 to 2005.What is the change in real GDP from 2004 to 2005?
a. Increased by 50%
b. Decreased by 50%
c. Increased by 25%
d. Stayed the same
Question 21. Mankiwville uses 1 slice of pizza and 2 sodas as its market basket. In 2010, pizza cost $0.50 and a soda cost $0.25. In 2012, a pizza cost $0.80 and a soda cost $0.26. If the inflation rate between 2010 and 2011 was 10%, what was theinflation rate between 2011 and 2012?
a. 10%
b. 22%
c. 20%
d. 14%
Question 22. Which of the following statements about unemployment is FALSE?
a. The unemployment rate is negatively related to the level of economic output.
b. Suppose actual real GDP is greater than full employment real GDP in an economy. Then, the unemployment rate in this economy is lower than the natural rate of unemployment in this economy.
c. The increase in employment during the summer is counted in measures of cyclicalunemployment.
d. Structural unemployment may result from labor unionization since labor unionization typically results in wage rates being set at levels above the equilibrium wage rate in the labor market.
Question 23. In Friedmanland, aggregate production is given by Y = √L √K. Friedmanland's labor market in 2000 is given by the following two equations, where L is the quantity of labor and W is the wage rate:
Labor Demand: W=72- 0.5L
Labor Supply: W=18+L
Suppose total output is equal to 300. What is the productivity of capital (K)?
a. 3 units of output per unit of capital
b. 4 units of output per unit of capital
c. 1 units of output per unit of capital
d. 5 units of output per unit of capital
Question 24. Suppose a country has a fixed level of technology and capital and that its hiring of labor is determined by the interaction of supply and demand in the market for labor. Suppose that nothing happens in this labor market, but the country experiences an increase in its level of capital. Holding everything else constant, we know that
a. Real GDP in this economy has increased and labor productivity has decreased.
b. Real GDP in this economy has increased and capital productivity has decreased.
c. Real GDP in this economy has decreased and labor productivity has increased.
d. Real GDP in this economy has decreased and capital productivity has increased.
Question 25. Suppose that there are two countries that are exact duplicates of one another with regard to resources, population, etc. And, these two countries are remarkably similar in all that they produce except that the first country has childcare provided by state agencies while the second country provides for all its childcare through each family utilizing its pool of grandparents. Holding everything else constant, GDP for the two countries
a. Will be the same since both countries produce the same level of output.
b. Will be different since GDP will include the state provided childcare in the firstcountry but not include the grandparent provided childcare in the second country.
c. Will be different since GDP will not include the state provided childcare in the first country but will include the grandparent provided childcare in the second country.
d. Will be different since GDP will be lower in the first country since it will need to devote resources to childcare production while the second country does not devote resources to childcare production.