Assignment 1:
1. Discover the IP address of a client device on the home network. The steps involved will vary depending on the device. You may use any device such as a computer, or mobile device. Refer to these links for help: Windows 7 or 8, Mac OSX, iPhone/iPad, or Android.
a. What is the IP address you located?
b. Is this address public or private?
c. What is this address called when using NAT terminology?
2. Discover the IP address the client device appears as when using the Internet. There are a variety of sites that will provide this information, but perhaps the easiest way to find this information is to use a search engine such as Bing or Google and use the search term ‘my ip address’. The search engine will return the public IP address your device is using when communicating on the Internet.
a. What is the address of your device as it appears to the Internet?
b. Is this the same address as the address assigned to the device that you discovered in step 1?
c. What is this address called when using NAT terminology?
3. Discover the IP address of https://www.schoolcraft.edu, or another website you visit frequently. To do so, navigate to the DNS Lookup Tool and enter the name of the website you chose to use for the exercise into the search field. Click submit for the results.
a. What is the IPv4 address used to contact the website?
b. Assuming the client device you are using to contact this website is being translated by a router using NAT, what is this IP address called when using NAT terminology?
4. Given the scenario where you use the computer and IP address from step 1 to visit the website you chose in step 3, fill in the following NAT table by entering each IP address you discovered as well as the correct NAT term that describes each IP address
Enter IP Address here Enter IP Address here Enter IP Address here
5. Describe how a router will utilize this table when providing for two-way communication between your client device and the website destination IP address.
Assignment 2:
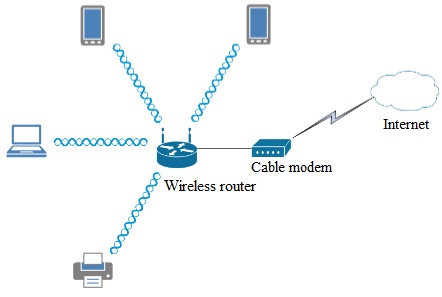
1. After reviewing the planned topology above, you know that the devices are located throughout the home and may move from one place to another. Also, the signal from the router’s antennas should have an equal opportunity to reach throughout the home.
a. What type of antenna should you look for and use on the router?
b. What specific type of WLAN does this topology represent and what mode will the router be functioning in when it acts as the access point for the network?
2. The home owner is concerned about interference from other wireless networks in the neighborhood. When performing your survey you discovered that several of the neighbors are running 802.11g networks across all available non-overlapping channels (1, 6, and 11). However, the home owner still has a device that must be able to communicate using the older protocol.
a. What standard(s) should be used in this network, why?
b. How can using this standard also help to reduce interference from the neighbors’ wireless devices?
After performing a more detailed wireless survey you have discovered that some of the building materials in the home obstruct the wireless signal from the router and reception is not acceptable in some portions of the house. Therefore you have modified the topology of the network.
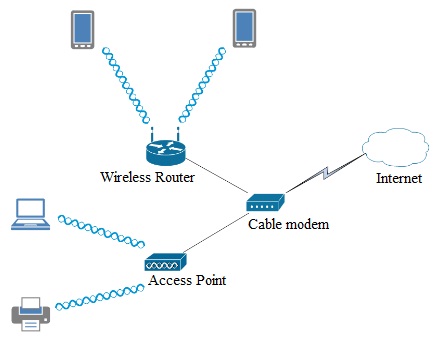
3. The devices are not tied to using either the router or the AP. They are still free to move about the house and will connect to either the wireless router or the access point depending on signal strength because the router and the access point are using the same SSIDs.
a. What specific type of WLAN does this new topology represent?
4. Now that you have adequate signal coverage throughout the house you need to plan your channel allocation to reduce interference and improve performance.
a. Should the router and access point utilize the same channel, or each use a different channel? Why or why not?
Next, perform the following steps:
Step #1:
Access the wireless router from Dlink.com. (There is no password required to login).
If 802.1x is required during any of your configurations, utilize the following information:
Server IP address: 10.10.10.100
RADIUS server Shared Secret: Rad1usIsRAd!
Step #2:
Navigate the user interface and manually configure the 802.11 and security settings you select to match the following requirements. (Note: It often helps to consult the help or support information when you are configuring a device.) After performing the configurations, you need to provide two screenshots where indicated.
Requirements:
- The wireless network should have the maximum amount of bandwidth available on both the 2.4ghz and 5ghz bands.
- Any settings specific to an 802.11 standard that can be used to increase bandwidth should be used.
- Older devices not supporting the latest 802.11 standard should be supported on the 2.4ghz band but NOT on the 5ghz band
- Client devices accessing the 2.4ghz SSID must be able to use a PSK and should use the setting that allows the best security for both newer devices and older devices not capable of using the latest standards.
- Client devices accessing the 5ghz SSID must utilize the username and password of the user that is using the device. The latest and most secure settings must be used.
Step #3:
When you have completed the required configurations, take a screenshot or snipping tool snip of the settings for each SSID and paste them below. If you are unsure how to take a screenshot you can refer to the guides for the Snipping Tool in Windows 7 or Windows 8, the Grab application or these keyboard shortcuts (for Mac OS X), or Jing (both Mac and Windows compatible).
a. Wireless Network Settings for the 2.4 ghz Band
Despite the continuing rise in cybercrime, there has been rapid growth of wireless technology in new devices like cars, televisions, and even light bulbs! Consumer demand for these new applications of wireless technology drives the market for manufacturers, but it also creates an ever-increasing pool of new targets for attackers. It doesn’t help that many of these devices favor ease of setup over better security.
On the business side, many leaders are concerned about wireless security and are potentially spending large sums to keep their businesses safe. This doesn’t change the fact that security breaches and related incidents still occur more often than a business or their customers would be comfortable with. Stories detailing these incidents can be seen regularly in evening news and web-based media.
Using the Internet, search for a news article that relates to one of the following scenarios below. You will use your research to further explore the scenario in this assignment.
- A security breach that involved a problem inherent to WLAN technologies.
- A security breach that involved misconfiguration or lack of configuration of WLAN technologies.
- A new type of attack seeking to use WLANs as a means of attack.
- A home user that was a victim or a wireless attack.
- A home wireless network that was used to perform illegal activity.
- Wireless devices (routers, APs, NICs) that were vulnerable to attack or were exploited before receiving updates
In a Microsoft Word Document Write a short description of your chosen scenario, making sure to include the following information:
1. Provide the URL(s) where you found information about the incident
2. Briefly summarize the security breach or incident and its impact (or potential impact) to the business or home user.
3. Make sure to address security approaches or security standards, vulnerabilities in the software of the device and how it was or could be exploited.
4. Explain how you would configure your own wireless network or a wireless network at your workplace to prevent this same event from happening.
Assignment 3:
You have just been assigned a network trouble ticket and have started the troubleshooting process. The following diagram represents the current design of the network involved.
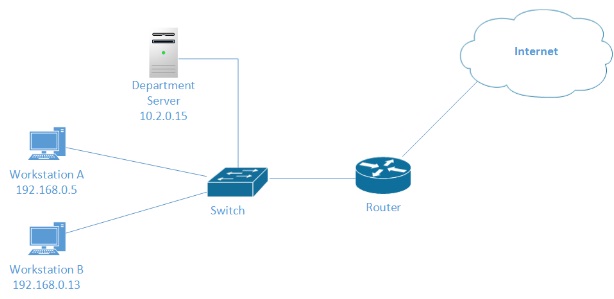
Within the trouble ticket, you notice the following updates:
- The user of Workstation A stated that they cannot access the departmental server in the server subnet, or the Internet.
- The helpdesk technician who visited the computer has stated that the link light is active on the network interface card in Workstation A and that Workstation A was able to successfully communicate with Workstation B through the network.
Answer the following questions as if you were troubleshooting the issue in an actual situation. The focus should be on the process used during the troubleshooting process as different answers are possible. Include information specific to the scenario above in your responses.
1. Describe the first step you should take in troubleshooting the problem. Specify any actions that need to be taken or questions that need to be asked.
2. Assume that you were able to successfully complete the first step to your satisfaction. What is the next step in the process?
Make sure to include any information within the network diagram or trouble ticket that you took into account for your response and whether or not these indicate to you that the problem is at layer 1, layer 2, layer 3, or a combination.
3. You should now be getting closer to solving the problem. After completing Step 2, what must you now do before making changes to the network?
Describe any actions you can take to make sure you are ready to make changes to the network. Indicate whether or not these actions relate to layer 1, layer 2, layer 3 or a combination.
4. Assuming you were successful in Step 3, what should be done in the next step? Indicate any actions you should take on the network (if any) and describe what the output from Step 4 should be.
5. Explain any remaining steps in the troubleshooting process. Be specific as to the value in completing each remaining step and include any information from the scenario that you deem as relevant to each step.
NOTE: Actions taken in the remaining steps will vary, but they must coincide with your previous responses.
Type your answer here
Step #1: Gather information
1. On a computer, issue the correct command to display its IP configuration.
a. What command did you use?
b. Take a screenshot and paste it.
2. Describe the purpose of each setting or configuration shown in the output of this command.
3. Identify and describe two different ways the information provided by this command could alert you to a configuration problem on the device.
Step #2: Test connectivity
4. Choose one IP address within the same subnet as the device you are using and issue the appropriate command to test connectivity to that device.
a. If the command was successful, does this conclusively determine that the device you are using is configured correctly? Why or why not?
b. How does testing connectivity within the same subnet as the device you are using assist the troubleshooting process?
5. Issue the appropriate command to test the ability to reach and communicate with the default gateway configured on the device you are using.
a. Provide a screenshot of the results of this command below:
b. Identify and describe the repercussions to the ability of this device to communicate with other devices if this command is not successful.
c. List one other way that a misconfiguration can cause this to happen
6. Assume that your device was able to successfully communicate with the default gateway (if it could not in actuality, assume it was indeed successful), but that it could not communicate with computers in other subnets. What tool could you use to determine which router in the path may be causing the problem?
Use the tool you specified in Step 6 to test the network path between the device you are using and a common site, such as Google or Microsoft. Provide a screenshot below:
8. Identify two pieces of information within the output of this command that would be helpful in troubleshooting connectivity to the site you chose.
Step #3: Examine Active Communication
9. What tool can be used to determine any active communication, open ports, or applications that could accept connections on the device you are using?
10. Use this tool to display any active communication or applications that can accept connections on the device you are using. Provide a screenshot below:
11. Identify any two active communication sessions, or applications that will accept connections and provide two pieces of information about the communication or application that you were able to discern from the command output.
12. Describe one way the information in this command can be useful in the troubleshooting of a network problem.
Assignment 4:
Question 1: Which of the following is NOT a source of routing information?
- Networks discovered by using Automatic IP Addressing (APIPA)
- Networks learned from another router
- Networks manually added by an administrator
- Networks connected to a router
Question 2: Routers using a distance vector routing protocols typically share ________, whereas routers using a link state routing protocols share ________
- Routes to only private IP address destinations; routes to either private or public IP address destinations
- Information only about distances they know firsthand; an entire database of all known links in the network
- Entire routing tables; Information about their own links
- Hop advertisements; Link state advertisements
Question 3: Order the following routing information sources from the lowest to highest administrative distance.
- RIP
- Static route
- Connected network
- OSPF
- EIGRP
Question 4: Based on the figure, which of the following paths represents the path most likely chosen by a series of routers running a Link State routing protocol for traffic sent from PC1 to PC2?
- E-A-D-G-C
- E-B-A-D-C
- E-A-F-C
- E-A-C
Question 5: Why is a statically configured route considered to be more believable than a dynamically learned route?
- It involves using information explicitly specified by an administrator, which is more reliable than second hand information
- It is not more believable because dynamically learned routes are not prone to human error
- It involves using a network that is directly connected to the router being configured, which is more reliable than second hand information.
- It is entered into the routing table that is stored in permanent storage as opposed the one kept in temporary storage
Question 6: Match each routing protocol with the set of characteristics that most closely defines it.
A. Distance vector - limit of 15 hops
B. Link state - scalable and popular
C. EGP - controls routes for the Internet
D. Proprietary - hybrid routing protocol
E. Djikstra's algorithm - not popular
Question 7: Based on the figure, which of the following paths represents the path most likely chosen by a series of routers running a Link State routing protocol for traffic sent from PC1 to PC2?
- E-B-A-D
- E-B-A-C
- E-A-D-G-C
- E-A-F-C
Question 8: Which of the following routing protocols is NOT an interior gateway protocl (IGP)?
Question 9: Which of the following piece of information is required for a router to route traffic correctly?
- Speed of next hop link
- Number of hops to the destination
- Destination IP address
- Source IP address
Question 10: Based on the figure, which of the following paths represents the path most likely chosen by a series of routers running a Distance Vector routing protocol for traffic sent from PC1 to PC2?
- E-A-C
- A-B-A-C
- E-A-F-C
- E-B-A-D-C
Question 11: Choose the two main types of routing protocols
- Distance Vector
- Link Vector
- Routing Information Protocols
- Link State
Question 12: True or False - A router must know an entire path from beginning to end to successfully route traffic
Question 13: Distance vector routing protocols base their decisions primarily on _______, whereas Link state routing protocols base their decisions primarily on ________
- Link speed; router capacity
- The number of hops to the destination; The quality of a link
- The lowest cost path; the nuber of hops to the destination
- Administrator input; information from neighoring routers
Question 14: Which of the following addresses is NOT involved in routing traffic to a destination
- Next hop IP Address
- IP address of the device sending the traffic
- IP address of the device the traffic is intended for
- Next hop MAC address
Question 15: Based on the figure, which of the following paths represents the path most likely chosen by a series of routers running a Distance Vector routing protocol for traffic sent from PC1 to PC2?
- E-B-A-D-G
- E-A-C
- E-A-C-G
- E-A-F-C-G
Question16: True or False - Cable modem and DSL WAN technologies are both popular in home networks because they make use of the already existing coaxial media from cable TV networks.
Question 17: Digital circuits like T1 or T3 are terminated by a device called a _________ that processes the incoming signals into bits the router can understand
- CSU/DSU
- SDSL/VDSL
- CSI/NCIS
- ISDN/HSPA
Question18: Which of the following WAN technologies utilizes fiber optics exclusively?
Question 19: Choose the item that represents a commonality between MPLS, Frame Relay, and MPLS connections.
- Each of them utilizes cell switching, featuring fixed length data fields for predictable latency performance
- Each of them is a dedicated leased line for point-to-point connections
- Each of them forms connections between sites utilizing a service provider network (or WAN cloud)
- Each of them utilizes circuit switching for higher reliability
Question 20:
Which of the following protocols can be used to perform authentication of devices in WANs? (choose two).
Question 21: Match each WAN technology with the correct connection type (more than one technology can use the same connection type)
- Frame Relay
- ATM
- ISDN
- T1
- T3
A. Packet switched connection
B. Packet switched connection
C. Circuit switched connection
D. Dedicated leased line
E. Dedicated leased line
Question 22: True or False - MPLS utilizes its own special use header that is inserted between the native layer 2 and layer 3 headers of a packet.
Question 23: Each of the following WAN technologies features packet switching capabilities EXCEPT
- MPLS
- Frame Relay
- ATM
- ISDN
Question 24: Which of the following physical mediums are NOT used in WAN connections?
- Coaxial cable
- Fiber Optics
- UTP
- Satellite
- None of the above.
- Each of the choices is a valid medium for WAN connections.
Question 25: Order the following WAN connections from the slowest to the fastest.
Question 26: Match each WAN technology with the characteristic that best matches that technology.
- DSL
- T1
- Cable Modem
- Frame Relay
- ISDN
A. Asymmetric or symmetric
B. Dedicated leased line
C. DOCSIS
D. Packet switched
E. Bearer and Data Channels
Question 27:What is the main differentiation between a T1 and an E1 connection?
- T1 connections utilize 32 channels, whereas E1 connections utilize 23 channels
- T1 connections utilize telephone lines, whereas E1 connections use electrical lines
- T1 connections are used in the Unitied states, whereas E1 circuits are used in Japan
- T1 connections utilize 24 channels, whereas E1 connections utilize 32 channels
Question 28:
True or False - Frame Relay identifies each virtual circuit by its VCI (Virtual Circuit Identifier).
Question 29: Choose the best description of the term 'demarc'
- The point of demarcation, where responsibility passes from the service provider to the subscriber of the service
- An identifier of virtual circuits in Frame Relay or ATM networks
- An authentication protocol used in point-to-point circuits or DSL implementations
- The process by which MPLS packets have their labels removed as they exit the provider network
Question 30: Why is it that a service provider could be considered the most important WAN component?
- They're not that important. Most organizations manage the entirety of their own WAN connections between locations.
- WAN connections will typically cost a large one-time fee, so it's important for the provider to be trustworthy.
- They will be the ones responsible for the IP addressing your devices.
- They form the WAN connection and are held responsible for its function between locations and the technologies available can vary by provider.
Question 31: While maintaining cabling in an IDF with hundreds of patch cables, you are having trouble locating the other end of a cable that is connected to a patch panel. What tool will be he most helpful to you?
- Loopback plug
- Toner probe
- Cable analyzer
- Certifier probe
Question 32: After starting a new job you want to get familiarized with and document the current configuration and behavior of the network before making any changes. What is this activity called?
- Reconnoitering
- SNMP Get
- Baselining
- E-Discovery
Question 34: Match each network maintenance tool with the purpose that is most closely identified with that tool
- Loopback plug
- Protocol analyzer
- Throughput tester
- Time Domain Reflectometer (TDR)
- Locating a specific cable
A. Confirm interface functionality
B. Analyze network traffic
C. Measure link speed
D. Determining the location of cable fault
E. Toner probe
Question 35:
As your network has grown to include many network devices, it has become almost impossible to investigate the status of these devices by checking them individually, or to correlate network events using log information from network devices. What tool should you employ to optimize these network management tasks by allowing your network devices to send their log information to a central server?
- Remote Log Connection
- Log Transport Protocol
- Syslog
- Secure log shell
Question 36:
Based on some weird network behavior, the IT director asks you to investigate whether or not the firewall experienced any unsual traffic patterns or high utilization. What monitoring tool is most likely to contain the information needed to provide the IT director with necessary information?
- Secure Shell
- Rulebase
- System logs
- SysMon
Question 37: Which of the following technologies can be used to improve both the availability and the performance of a network?
- Multiple power supplies in every network device
- LACP/NIC Teaming
- QoS
- Optimizing network device configurations to use less memory
Question 38: True or False - Unlike network diagrams, policies are only useful for management and not network technicians
Question 39: Choose two ways that the ToS byte in IP packets can be used to mark packets as belonging to a certain classification of traffic.
- IP Precendence
- IntServ
- Random Early Detection
- Differentiated Services Code Point
Question 40: Choose 2 tasks that must be completed before configuring QoS on a network?
- Categorize network traffic
- Filter network traffic
- Identify network traffic
- Load balance network traffic
- Policing network traffic
Question 41: Which of the following tools can be used to test cables or connectors? (Choose 3)
- Punch-down
- Crimper
- Time Domain Reflectometer (TDR)
- Multimeter
- Certifier
Question 42: Choose each technology that can improve the availability of a network (choose 3)
Question 43: True or False - SNMP can be used to configure a network device or tell it to perform an action.
Question 44: You have been tasked with implementing Qualiy of Service (QoS) on the organizational network. Which of the following network maintenance tools will be the most helpful for this activity?
- Protocol analyzer
- Throughput tester
- Time domain reflectometer
- Toner probe
Question 45: Which type of network documentation is essential in order to escalate high priority issues to the correct team or person?
- Security Policy
- Contact information
- Simple Network Management Procedure
- Support resource map
Question 46: Both packet filtering firewalls and circuit-level gateways can filter based on IP addresses and TCP or UDP port numbers. What then is the main difference between them?
- Packet filtering firewalls monitor active communication sessions and can allow valid return traffic without an explicit rule.
- There is no difference, both terms describe the same type of firewall.
- Circuit-level gateways are only capable of filtering traffic on dedicated point-to-point WAN circuits.
- Circuit-level gateways monitor active communication sessions and can allow valid return traffic without an explicit rule.
Question 47: Order the following firewall types from least capable to most capable.
- Stateful Inspection
- Packet Filtering
- Circuit-level gateway
Question 48: An online business website suddenly receives identical requests from thousands of zombie computers around the world all at once. What type of attack are they likely facing?
Question 49: Choose the activity that best defends against known vulnerabilities in applications or operating systems.
- Patching
- Firewalls
- User training
- Vulnerability scanners
Question 50: A firewall will typically be placed __________ the untrusted network and the trusted network.
- In front of
- Inside
- between
- Separate from
Question 51: True or False - Unlike a firewall, IDS/IPS devices can be located within a network to protect traffic between devices in the same subnet.
Question 52: In addition to using encryption to protect the confidentiality of network information, VPNs will often use _________ to ensure that secure connections are only made to trusted devices.
- Filtering
- Integrity checking
- Tunneling
- Authentication
Question 53: Intrusion detection systems are said to be ___________, whereas intrusion prevention systems are considered ___________.
- active-passive
- obsolete - highly recommended
- passive - active
- The best defense - obsolete
Question 54: Which 3 of the following options are fundamental goals of network security?
- Performance
- Encapsulation
- Availability
- Integrity
- Confidentiality
- Tunneling
Question 55: Modern firewalls no longer combine packet filtering with the ability to identify and track active sessions.
Question 56:
Firewalls _________ traffic based on an access control list, whereas IDS/IPS devices detect network intrusions by comparing traffic to _________, ________, or _________
- Policies - filtering, signatures, anomalies
- anomalies - filtering, signatures, policies
- Signatures - filtering, anomalies, policies
- filter - signatures, anomalies, policies
Question 57: Which of the following would represent a useful defense against email viruses, password hacking, and social engineering
- Firewalls
- User training
- IDS/IPS
- Vulnerability scanners
Question 58:
A week after you installed a new wireless network for a customer's home they have contacted you with a problem where they appear to have a good connection but it experiences consistent performance problems and random drops. When you installed the 802.11n access point running at 2.4ghz, you measured the signal strength in each room of the house and tested network performance. The customer recently installed a new baby non-802.11 wireless monitoring system in the home. What is the most likely cause of the problem?
- The signal is being blocked by the high quality drywall in the house
- Recent power losses in the neighborhood have begun to impact the signal strength output from the access point
- RFI from the baby monitoring system is impacting the 802.11n signal
- The antenna on the access point is not powerful enough to cover the home
Question 59: A network administrator within the IT group you work for did not correctly configure spanning-tree protocol within the network. What problem is this likely to cause, and what layer of the OSI model will the problem affect?
- Layer 2 loops
- Crosstalk between switches at layer 2
- Layer 3 loops
- Mismatched MTUs at layer 3
Question 60: Put the following troubleshooting process steps in the correct order, beginning to end. Document your findings, the underlying cause, and problem resolution
- Verify solution was successful
- Implement your action plan
- Define the problem and gather information
- Establish a hypothesis for the probable cause
- Test your hypothesis
Question 61: Which of the following issues represents a potential data link layer (layer 2) issue?
- A Fiber optic cable run near high voltage factory equipment and motors
- A mistyped static route
- A switch port assigned to the wrong VLAN
- A UTP cable run near high voltage factory equipment and motors
Question 62: Choose the two problems that are NOT physical layer problems.
- Incorrectly configured VLAN
- Incorrectly configured subnet mask
- Electromagnetic interference
- A bad network interface card
- Incorrectly terminated RJ45 connector
Question 63: Match the following network problems with the most likely solution.
- There is no link light on workstation network interface card and the workstation cannot communicate across the network
- A user is unable to browse the Internet using website names, but when you are troubleshooting you are able to use the workstation to contact websites by IP address.
- A workstation is experiencing slow network performance even though it is showing a 1gbps connection status to the switch
- A workstation cannot communicate outside of its own subnet
A workstation cannot communicate with any other device in its own subnet or in other subnets. The IP configuration has been checked and the network interface card is showing the link is active
A. Bad cable
B. Incorrect DNS configuration
C. Port configuration issue – duplex mismatch
D. Incorrectly configured default gateway
E. Misconfigured VLAN on the switch port
Question 64:
A week after you installed a new wireless network for a customer's home they have contacted you with a problem where they appear to have a good connection but it experiences consistent performance problems and random drops. When you installed the 802.11n access point running at 2.4ghz, you measured the signal strength in each room of the house and tested network performance. The customer recently installed a new non-802.11wireless baby monitoring system in the home. Which of the following actions will most likely solve the problem?
- Change the 802.11n frequency from 2.4ghz to 5ghz
- Change the SSID of the wireless network
- Move the access point closer to the client devices
- Install a larger antenna on the access point
Question 65:
Which of the following issues represents a potential physical layer issue?
- A Fiber optic cable run near high voltage factory equipment and motors
- A switch port assigned to the wrong VLAN
- A UTP cable run near high voltage factory equipment and motors
- A mistyped static route
Question 66:
A workstation computer is not able to contact devices outside of its own subnet but can contact any devices within the local subnet. Before the trouble ticket was escalated to the networking team the helpdesk technician verified that the subnet mask was correct for the device's assigned VLAN. Which of the following potential issues is most likely the cause?
- The 100 meter distance limitation of the CAT6 cable that connects the workstation to the switch has been exceeded
- The port the workstation connects to has been assigned to the wrong VLAN
- The default gateway setting is incorrectly set or missing on the workstation
- The port the workstation connects to has malfunctioned
Question 67: Which of the following issues represents a potential network layer (layer 3) issue?
- A UTP cable run near high voltage factory equipment and motors
- A mistyped static route
- A switch port assigned to the wrong VLAN
- A Fiber optic cable run near high voltage factory equipment and motors