Question 1: Describe the independent and dependent sources with the help of V-I characteristics.
Question 2: Differentiate between ideal and practical sources and draw their characteristics.
Question 3: A 25 ohms resistor is connected across a voltage source V (t) = 150 Sin ωt. Find out the current I (t) and the instantaneous power P(t) and as well the average power. Draw the relevant waveforms.
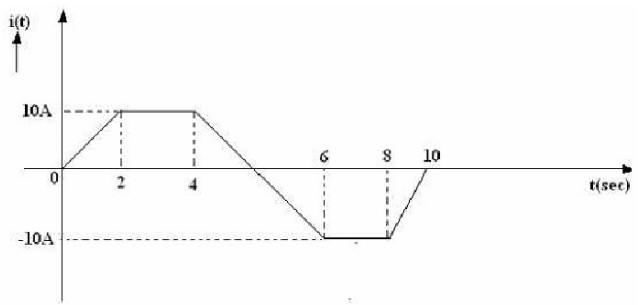
Question 4: A series RLC circuit with R= 4 ohms, L = 2mH and C = 500 micro-farads is carrying a current waveform as shown in figure below. Find out the voltage across each element and sketch each voltage to same time scale.
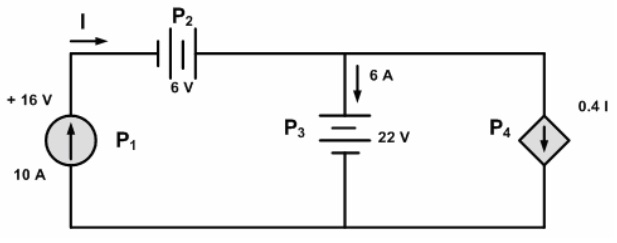
Question 5: Compute the power absorbed by each component in the circuit as shown in figure below:
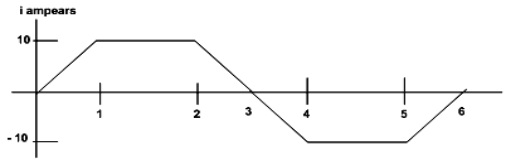
Question 6: A pure inductance of 3 mH carries a current of the wave form shown in figure below. Sketch the waveform of V(t) and P(t). Find out the average value of power.