MARKETTING MANAGEMENT:
1) Define Marketing Management. Discuss the various management philosophies. Explain how the marketing and selling are contrasted and briefly explain the societal marketing concept.
2) Explain the various factors influencing a company’s marketing strategy with the help of suitable examples.
3) What is marketing research? Discuss the marketing research process with the help of an example. Briefly explain the different sources of data.
4) What do you mean by productivity analysis? Differentiate between productivity analysis and profitability analysis. What are the different steps in the direct and indirect approaches to marketing budgeting?
5) What do you mean by media scheduling? Explain the procedure for evaluating advertising programs with the help of suitable examples.
6) Define sales promotion and discuss the different elements of promotion-mix with the help of suitable examples.
7) Discuss the marketing plan for a consumer product of your choice and briefly explain the marketing planning process.
8) Write short notes on any three of the following
a) Relative Market Potential
b) Competitive Parity Analysis
c) Basic Elements of a Marketing Strategy
d) Product life cycle
e) Market segmentation
Accounting for managers:
1. (a) What do you understand by the concept of conservatism? Why it is also called the concept of prudence? Why it is not applied as strongly today as it used to be in the Past?
(b) What is a Balance Sheet? How does a Funds Flow Statement differ from a Balance Sheet ? Enumerate the items which are usually shown in a Balance Sheet and a Funds Flow Statement.
2. (a) Discuss the importance of ratio analysis for inter-firm and intra-firm comparisons including circumstances responsible for its limitations. If any (b) Why do you understand by the term ‘pay-out ratio’? What factors are taken into consideration while determining pay-out ratio? Should a company follow a fixed pay-out ratio policy? Discuss fully.
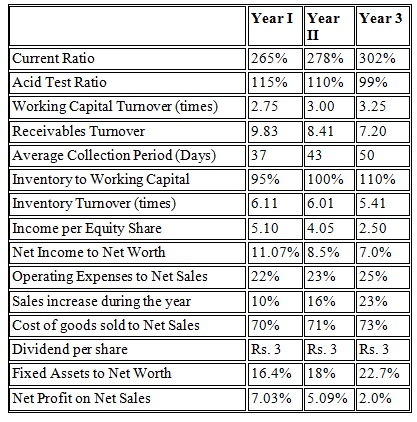
3. From the ratios and other data given below for Bharat Auto Accessories Ltd. indicate your interpretation of the company’s financial position, operating efficiency and profitability.
4. Bose has supplied the following information about his business to Summary of Cash book for the year ended 31st March, 2004 is as follows:
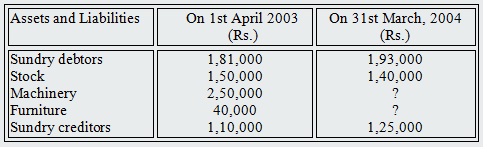
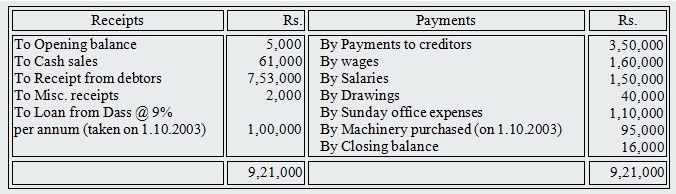
Discount allowed totaled Rs.7, 000 and discount received was Rs.4, 000. Bad debts written off were Rs.8,000. Depreciation was written off on furniture @5% per annum and machinery @10% per annum under the straight line method of depreciation. The office expenses included Rs.5, 000 paid as insurance premium for the year ending 30th June, 2004. Wages amounting to Rs.20, 000 were still due on 31st March, 2004.
Prepare trading and profit and loss account for the year ended 31sl March, 2004 and the balance sheet as on that date.
5. What procedure would you adopt to study the liquidity of a business firm?
Who are all the parties interested in knowing this accounting information?
What ratio or other financial statement analysis technique will you adopt for this.
6. From the following particulars, determine the bank balance as per pass book of Priya & Co. as on 28th February 2008.
a) Credit balance as per cash book on 28th February, 2008 was Rs. 15,000
b) Interest charged by the bank up to 28th February Rs. 500 was recorded in the pass book.
c) Bank charges made by the bank Rs. 125 were also recorded only in the pass book.
d) Out of the cheques of Rs. 25,000 paid into the bank, cheques of Rs. 18,750 were cleared and credited by the bankers.
e) Two cheques of Rs. 7,500 and Rs. 15,000 were issued but out of them only one cheque of Rs. 7,500 was presented for payment up to 28th February.
Dividends on shares Rs. 4,500 were collected by the bankers directly, for which Priya & Co. did not have any information.
7. A company manufactures a single product in its factory utilizing 600% of its capacity. The selling price and cost details are given below:
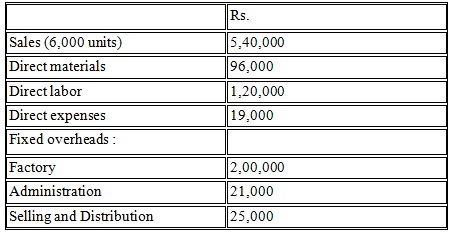
12.5% of factory overheads and 20% of selling and distribution overheads are variable with production and sales. Administrative overheads are wholly fixed. Since the existing product could not achieve budgeted level for two consecutive years, the Company decides to introduce a new product with marginal investment but largely using the existing plant and machinery.
The cost estimates of the new product are as follows:
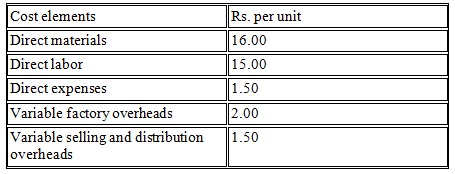
It is expected that 2,000 units of the new product can be sold at a price of Rs. 60 per unit. The fixed factory overheads are expected to increase by 10%, while fixed selling and distribution expenses will go up by Rs. 12,500 annually. Administrative overheads remain unchanged.
However, there will be an increase of working capital to the extent of Rs. 75,000, which would take the total cost of the project to Rs. 8.75 lakh.
The company considers that 20o/o pre-tax and interest return on investment.
You are required to:
(a) Decide whether the new product be introduced.
(b) Make any further observation/recommendations about profitability of the company on the basis of the above data, after making assumption that the present investment is Rs. 8 lakh.
8. (a) What is Master Budget? How it is different from Cash Budget?
(b) What are the various methods of inventory valuation? Explain the effect of inventory valuation methods on profit during inflation. What are the provisions of Accounting Standard 2 (AS-2) with regards to inventory valuation?