I: Binary
Problem 1. The presence of structural unemployment in the economy means the economy is not in equilibrium.
a. True
b. False
Problem 2. The consumption function is the relationship between real consumption spending and real disposable income.
a. True
b. False
Problem 3. In the simple Keynesian model, consumption spending increases when the interest rate increases.
a. True
b. False
Problem 4. If the increase in exports equals the increase in imports, the aggregate expenditure function is unaffected.
a. True
b. False
Problem 5. In the simple Keynesian model, the expenditure multiplier is always equal to 1/(1-MPC), no matter the value of the MPC.
a. True
b. False
Problem 6. The Keynesian model is a more recent and better tool to analyze the behavior of the economy at the aggregate level.
a. True
b. False
Problem 7. The aggregate expenditure function and the consumption function have the same slope.
a. True
b. False
Problem 8. An increase in wealth results in a movement along the consumption function.
a. True
b. False
Problem 9. The tax multiplier is equal to the negative of the expenditure multiplier pre-multiplied by the marginal propensity to consume.
a. True
b. False
II. Multiple Choice Questions
Problem 10. Which of the following are true about the definition of the marginal propensity to consume?
a. It is the slope of the consumption function.
b. It is the change in consumption divided by the change in disposable income.
c. It is the amount by which consumption spending rises when disposable income rises by one dollar.
d. All the definitions above are correct.
Problem 11. We usually assume that the marginal propensity to consume is between zero and one because:
a. We are economists and we do whatever we want.
b. It is reasonable to assume that on average an extra unit of income is partly spent on extra consumption and partly saved.
c. Because it makes the mathematics simple.
d. None of the above.
Problem 12. An increase in wealth:
a. Results in a movement along the aggregate expenditure function.
b. Results in an upward-shift of the aggregate expenditure function.
c. Results in a downward-shift of the aggregate expenditure function.
d. Affects the consumption function but not the aggregate expenditure function.
Problem 13. Which of the following graphs best represents the equilibrium level of output in the short run macro model?
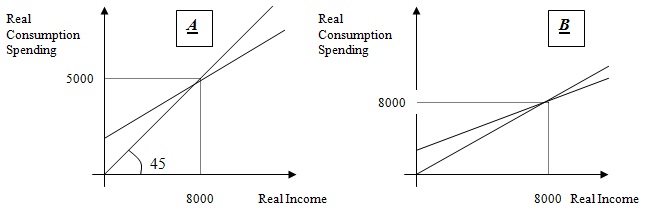
a. Both A and B.
b. None of the above.
c. Only A.
d. Only B.
Problem 14. The expenditure multiplier and the tax multiplier:
a. Are equivalent.
b. Are always different.
c. Coincide when the marginal propensity to consume is zero.
d. Get closer and closer as the marginal propensity to consume approaches one.
Problem 15. Which of the following is true? Automatic stabilizers:
a. Decrease the width of oscillations that characterize the business cycle.
b. Increase the MPC and the expenditure multiplier.
c. Increase the MPC and decrease the expenditure multiplier.
d. Increase the impact of changes in planned investment, government expenditure, autonomous consumption and net export.
III. Problems:
Consider an economy described by the following parameters:
G = 2000
X - M = 500
I = 1300
T = 1000
C = 1000+0.8(Y – T)
Where G is government expenditure, (X – M) is net exports, I is the level of planned investment, T are lump-sum taxes on income, C is household consumption and Y- T is disposable income.
Problem 16. The level of autonomous consumption and the MPC in this economy are, respectively:
a. 1000 and 0,8.
b. 800 and 0,8.
c. 1200 and 5.
d. 1000 and 5.
Problem 17. The equilibrium level of income is:
a. 22500.
b. 20000.
c. 16250.
d. 26250.
Problem 18. The expenditure multiplier and the tax expenditure multiplier are, respectively:
a. 0.8 and -0.64.
b. 0.2 and 0.2.
c. 5 and 4.
d. 5 and –4.
e. 5 and -6.4.
Problem 19. The perception of an increase in wealth (due, say, to the inflating of a speculative bubble in the stock market) results in an increase in autonomous consumption by 100. As a result equilibrium GDP:
a. Will not be affected since the increase in autonomous consumption concerns only the consumption function and not the aggregate expenditure function.
b. Will not be affected because autonomous consumption is the level of consumption when disposable income is zero.
c. Will increase the equilibrium level of GDP by 400.
d. Will increase the equilibrium level of GDP by 500.
Problem 20. Suppose the potential GDP is 30000 and it is reached when the level of employment in the economy equals 2000000. Suppose also the government wants to design a fiscal policy in order to attain full employment. The government asks you what should be the level of government spending in order to achieve this goal. Using a Keynesian model you answer:
a. 2000.
b. 2500.
c. 10000.
d. 5000.
Problem 21. Consider the original economy. What should the level of production be in order for inventories to increase by 100?
a. 20500.
b. 20550.
c. 20100.
d. 19500.