Distance Vector Routing Protocols
Question
1 What does RIP stand for?
2 What metric does RIP use for Path Selection?
3 If metric used by RIP exceeds this value for a route it is considered unreachable, effectively making this value appear to be infinity to RIP?
4 How often does RIP send updates by default (update timer)?
5 What are the major differences between RIPv1 and RIPv2?
6 What is convergence and why is it significant?
7 Is RIP considered to be a fast or slow converging protocol?
For the simple 3 router network (Figure below), fill in the information that will be in each router’s routing table once the network has converged
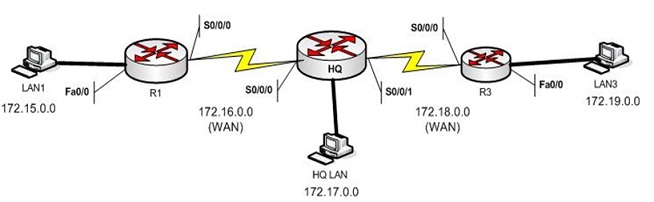
R1 HQ R3
Network Interface Hop Network Interface Hop Network Interface Hop
172.15.0.0 Fa0/0 0
Subnetting and Assigning Addresses
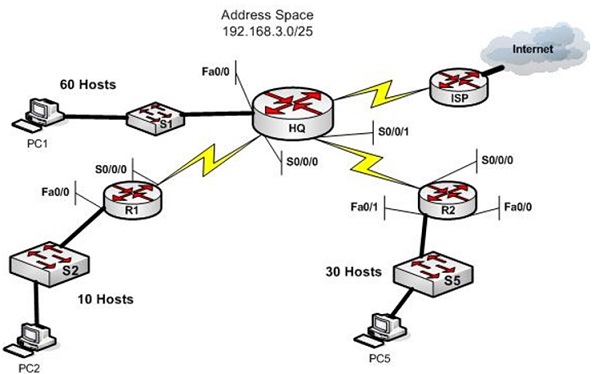
You are a network administration for the small network in above Figure. It consists of your headquarters location with a LAN with 60 hosts, remote office R1 with 10 hosts, and remote office R2 with 30 hosts. You have been assigned the address space 192.168.3.0/25. From this space you would require to create the subnets for each of the sites on your network and the two WAN links. Once you find the subnets assign addresses to the Routers interfaces and PCs using the following guidelines: Assign the first address from LAN subnets to the router interface connected to that LAN. Assign the second IP address in the LAN subnet to the PC on the LAN. Assign the first Address from WAN subnets to the HQ router end of the WAN link and the second address to the remote router interface. Use the steps below to help you work through it.
Create the subnets:
Address space: 192.168.3.0/25
Write it out in binary form identifying the host and network in table given below as a scratch pad to help you in subnetting as needed. Remember to be competent you generally want to start by creating the largest subnet you require first and then continue subnetting to determine the smaller subnets in succession.

Question
8 What is the HQ subnet (address/mask)?
9 What is the R1 subnet (address/mask)?
10 What is the R2 subnet (address/mask)?
11What is the subnet for the HQ to R1 WAN (address/mask)?
12 What is the subnet for the HQ to R2 WAN (address/mask)?
13 What subnets do you have left available for future use?
PC’s on a LAN require to have a default gateway configured that identifies the next hop IP address for packets leaving the network. This is the address of the router interface on the LAN. Based on this what address will be assigned as the default gateway on the following PCs.
14 PC1 =
15 PC2 =
16 PC5 =
Fill in the address and subnet mask for the device interfaces in the table below using the assignment rules described above.
Device Interface Address Mask
HQ Router Fa0/0
S0/0/0
S0/0/1
R1 Router Fa0/0
S0/0/0
R2 Router Fa0/1
S0/0/0
PC1 Ethernet
PC2 Ethernet
PC5 Ethernet