1) Price elasticity of demand is a measure of
A. the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a changes in the price of the good.
B. the quantity demanded of a good at a given price.
C. the demand for a product holding prices constant.
D. the horizontal shift in the demand curve when the price of a good changes.
2) If the price of oil goes up by 50 percent and the quantity demanded goes down by 25 percent, the absolute value of the price elasticity of demand is
A. 0.25.
B. 0.50.
C. 0.75.
D. 1.00.
3) The greater is the absolute price elasticity of demand, the
A. larger is the responsiveness of quantity demanded to the price change.
B. smaller is the responsiveness to a price change.
C. larger is the income of the buyer.
D. higher is the change in demand to an income change.
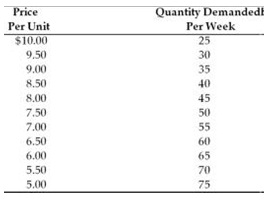
4) Refer to the table below. For which prices is demand elastic?
A. in a range of prices below $6.50
B. in a range of prices above $6.50
C. in a range of prices between $5 and $10
D. in a range of prices above $9.00
5) When total revenue and price are inversely related, demand is
A. unit-elastic.
B. inelastic.
C. elastic.
D. not related.
6) Moving downward on a downward-sloping linear demand curve, the absolute value of the price elasticity of demand
A. is constant.
B. increases continuously.
C. decreases continuously.
D. may either increase or decrease.
7) Use the figure below. When price increases from $2 to $10, total revenue
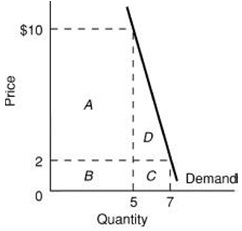
A. increases from areas A + B to areas B + C and demand is inelastic.
B. increases from areas B + C to areas A + B and demand is inelastic.
C. increases from areas B + C to areas A + D and demand is elastic.
D. increases from areas C + D to areas B + A and demand is elastic.
8) An elastic response in the quantity of a good demanded would be caused by
A. the availability of many substitutes.
B. a lack of substitutes.
C. a lack of sensitivity to the good's price.
D. the good representing a small portion of a person's budget.
9) When numerous but imperfect substitutes exist for a good, the demand for the good would tend to be
A. inelastic.
B. elastic.
C. unitary.
D. perfectly elastic.
10) When the consumer spends less than 3 percent of his income on a good, demand would be:
A. elastic.
B. unit-elastic.
C. inelastic.
D. elastic, unit-elastic, or inelastic depending upon supply.
11) Assume that number of units of good X consumed falls 6 percent when the price of good Y falls 4 percent. The cross price elasticity of demand between goods X and Y is
A. 0.66.
B. 1.75.
C. 2.0.
D. 1.5.
12) Refer to table below. Based on the information in the table, we could say that
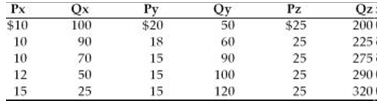
A. all three goods are substitutes for each other.
B. all three goods are complements.
C. X and Y are substitutes, Y and Z are complements, and X and Z are substitutes.
D. X and Y are complements, Y and Z are substitutes, and X and Z are complements.
13) Use the figure below. Which graph depicts complementary goods?
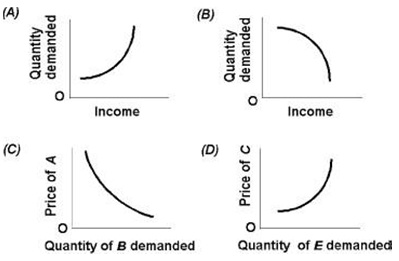
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
14) Income elasticity relates to
A. a movement down a demand curve.
B. a movement up a demand curve.
C. a horizontal shift in a demand curve.
D. the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in the price.
15) If demand for Rolls Royce automobiles rises in an area where incomes have increased, this tells us that Rolls Royce is
A. a normal good.
B. an inferior good.
C. a complementary good.
D. a substitute good.
16) The income elasticity of demand
A. is positive only.
B. is negative only.
C. must lie between -1 and +1.
D. can be positive, negative, or zero.
17) If price elasticity of supply of television sets is constant and equal to 3, a 10 percent increase in price would result in a change in quantity supplied equal to
A. 3 1/3 percent.
B. 30 percent.
C. 1/3 percent.
D. -30 percent.
18) If supply of a good is perfectly inelastic, the price elasticity of supply would equal
A. positive infinity.
B. one.
C. zero.
D. none of the above.
19) Supply curve for housing in the very short run is likely to be
A. very elastic.
B. very inelastic.
C. unit-elastic elastic.
D. perfectly elastic.
20) If price elasticity of supply is less than 1,
A. supply is elastic.
B. demand is elastic.
C. demand is inelastic.
D. supply is inelastic.