Assignment:
Part I. Multiple Choice Question (pick up only one correct answer.)
1. The budget line ____.
A) identifies affordable bundles.
B) identifies preferred bundles.
C) identifies the maximum utility which can be achieved from consumption.
D) identifies the satisfaction received from consumption.
2. Ernie has an income of $40 which he plans to spend on cookies and milk. The price of milk is $1 per gallon, and the price of cookies is $2 per dozen. If Ernie buys 12 gallons of milk, how many dozens of cookies will he buy if he spends all of his income ____?
A) 28
B) 20
C) 14
D) 12
3. The level of utility a consumer can achieve is limited by ____?
A) prices only.
B) income only.
C) the consumer's preferences.
D) prices and income.
4. Tom has $50 to spend on pizza and movies. If movies are $5 each and a pizza is $10 then, assuming he spends all his money, he can buy ___?
A) 6 movies and 2 pizzas.
B) 8 movies and 4 pizzas.
C) 2 movies and 6 pizzas.
D) 6 movies and 4 pizzas.
5. Which of the following is NOT an assumption of marginal utility theory?
A) A consumer derives utility from the goods consumed.
B) Each additional unit of consumption yields additional utility.
C) Consumers maximize their total utility.
D) As more of a good is consumed, the decrease in the marginal utility from the good means that the total utility from the good decreases also.
6. If you calculated all of the benefit you enjoy from drinking coffee, this measure would be called
A) your marginal utility of coffee.
B) your marginal utility per dollar spent on coffee.
C) your total utility from coffee.
D) your total utility per dollar spent on coffee.
7. For Elvis, his utility function (U) for consuming a bundle of two goods, X (soda) and Y (Netflix drama) is U = X + Y2. Now suppose, soda gives Elvis a constant utility at 10. Y is the number of movies he watches. What is marginal utility of watching the 5th movie for him ____?
A. 5
B. 9
C. 15
D. 35.
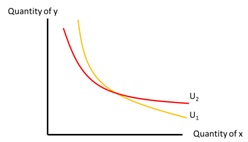
8. The following graph violates what property of Indifference Curves ____?
A. Indifferent curves are convex to the origin.
B. Indifferent curves have negative slopes.
C. Indifferent curves yield the higher utility, the further they go northeast.
D. Indifferent curves cannot intersect
9. The following table shows you production function of a chair manufacturer in using labor
|
Number of Workers
|
Number of Chairs
|
|
1
|
10
|
|
2
|
18
|
|
3
|
24
|
|
4
|
28
|
|
5
|
30
|
When using five workers, what is the average product (AP) per labor and the marginal product of the 5th labor (MP, L = 5)?
A. AP = 7 and MP = -2
B. AP = 6 and MP = -1;
C. AP = 6 and MP = 2
D. AP = 8 and MP = 4.
10. A printing firm uses one equipment (copy machine), various amount of materials (mainly ink and paper) plus various part-time labors. Suppose the cost of copy machine (renting) is $200 per day. In October 2018, there are five workers were employed by this firms at the cost of $60 per worker per day. Total output is the number of weekly ad for a local grocery store. The net material cost is $ 0.10 per ad. Now try to figure out the average fixed cost (AFC) and average total cost (ATC) per copy of ad when the total output is 10,000 copies per day ____.
A. AFC = $0.02 and ATC = $0.10
B. AFC = $0.02 and ATC = $0.15;
C. AFC = $0.12 and ATC = $0.15
D. AFC = $0.03 and ATC = $0.10.
Part II. Short-Answer Questions
1. If a 3% increase in the price of corn flakes causes a 6% decline in the quantity demanded, what is the elasticity of demand?
2. Suppose the demand curve for a product is given by Q = 10 - 2P + PS, where P is the price of the product and PS is the price of a substitute good. The price of the substitute good is $2.00. Suppose P = $1.00. What is the price elasticity of demand? What is the cross-price elasticity of demand?
3. Please explain why indifference curves are always not positively sloped?
4. Steve has a budget $200 for dining and entertainment this Saturday. If he has multiple choices of allocating his money. Use concepts of consumer behavior and utility theory to explain what is his optimal choice in equilibrium. You can present your answer intuitively (explain), graphically (draw of graph) or mathematically (use equations).
5. Why does production (after the initial increasing trend) eventually experience diminishing marginal returns to labor in the short run?
6. A firm pays its accountant an annual retainer of $10,000. Is this an economic cost?