Q1. Answer the following in relation to medium access control.
a) Explain in detail with the help of diagrams the CSMA/CD media access control technique used in Ethernet.
b) Explain in detail with the help of diagrams the CSMA/CA media access control technique used in IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs.
c) Compare the techniques described in a) and b).
Q2. Following questions relate to WLAN security.
Part-I
Briefly describe the following techniques/standards used for WLAN security.
- MAC address filtering
- SSID hiding
- Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
- Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
- IEEE 802.11i (WPA2)
Part-II
Note: The war-walking activity (part a) can be done together by a group of 2-3 students. Give the full names and student Ids of team members. The report (part b) must be written individually.
a) Use the inSSIDer package installed on your laptop to perform a War-Walking activity at a shopping centre, state the centre. Visit the shopping centre with your laptop sniffing the details of available wireless networks. Record the wireless networks available in three different spots. Include the inSSIDer screenshots. Compile the gathered information in a table, listing the available access points with their technical characteristics like channel number, RSSI, 802.11 standard, security, supported data rate, etc.
b) Write a report on your observations analyzing the data collected in previous step. Your analysis can investigate into following aspects:
i. Channel occupancy - crowded and free channels.
ii. Interference from neighboring access points and its effects.
iii. Dual band WiFi and its advantages.
iv. The security situation of the discovered wireless networks.
v. How easy (or hard) is it to break into those networks.
vi. Any other aspect of your own choice.
Q3. Use Internet resources to search for the information of Australia's Academic and Research Network (AARNet) and answer the following questions:
a. Describe briefly the history and purposes of Australia's Academic and Research Network (AARNet).
b. Tabulate the data speed capacity between Australian capital cities (Adelaide,Canberra, Melbourne, Perth and Sydney). Note that the speed capacity between two points in a serial path is equal to the slowest speed segment. For example, the speed capacity between points A and C in the path from A to B to C will be the slower link between points A to B or points B to C.
c. Tabulate international links and speed capacity from AARNet PoPs to overseas.
Q4. Consider an example of a multi-switch Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) presented in the figure below.
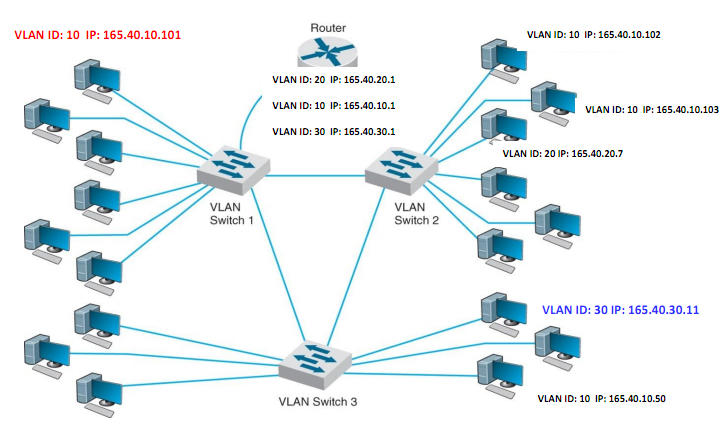
a. What is the Ethernet standard used in such a VLAN? List the fields in the VLAN Tag and describe their purpose. Describe in detail the VLAN-tagging system and how it is implemented in Ethernet frames.
b. Give a step by step explanation of the flow of packets when a computer with an IP address 165.40.10.101 (connected to switch 1) sends a packet to a computer with an IP address 165.40.30.11 (connected to switch 3).
Assume that all the devices have just been switched on, all PC were configured with static IP addresses.