Assignment:
1) A long capillary tube (radius=0.0015 cm) with a semi-permeable membrane on the lower end is oriented vertically and placed in a dilute sodium chloride solution at T=20OC. If the height of rise of water in the tube is 20 cm,
a. What is the solute potential (in head units) of the solution? State assumptions.
b. Estimate the concentration of the sodium chloride solution.
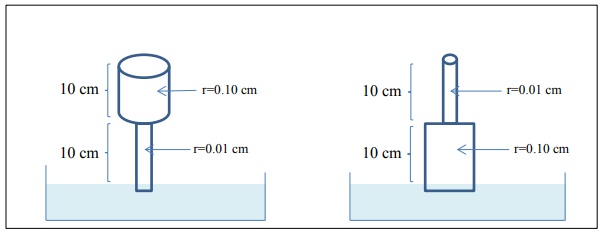
2) Consider the following cylindrical pores. Determine the height of rise in each configuration. You may assume a contact angle of zero and 20 oC.
3) Suppose you have a homogeneous soil sample with a volume of 400 cm3 and a known moisture retention function,
??(h) = 0.43 (-5/h)0.40
If the average matric potential of the sample is -1000 cm, how much water would you need to add to the soil sample (assuming the water is distributed uniformly in the soil) in order to increase the matric potential to -100 cm?
4) Suppose you have a homogeneous soil sample with a known moisture retention function;
??(h) = 0.48 for |h| ≤ 10cm
??(h) = 0.48 [10/|h|]0.20 for |h| > 10 cm
If you have a 100 cm3 sample that is water saturated, how many grams of water can you remove by applying a suction of 0.40 atm?
5) Two soil samples, A and B, are placed next to each other with good contact. Both soils are at θ=0.25. The soil water characteristic function for each soil is given below. Will soil water move from one soil to the other? If so, which sample will lose water? Briefly explain.
Soil A: ??(h) = 0.55 *[-18cm/h cm]1/3
Soil B: ??(h) = 0.48 *[-12cm/h cm]1/2
6) The horse-shoe shaped soil system below contains a homogeneous loam and is at equilibrium. Prior to setting the horse-shoe into water as shown below, the soil on the left was saturated with water while the right side was oven dry
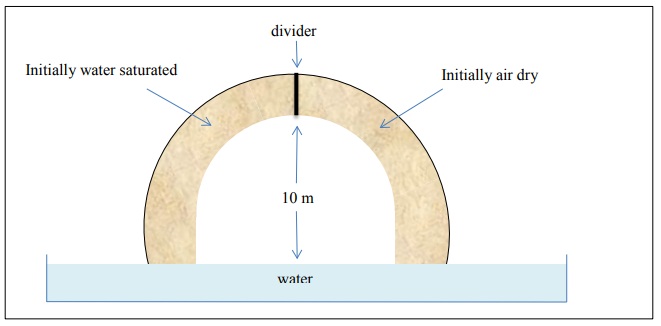
a. Provide a qualitative sketch of the water content vs. elevation above the water table for the two sides of the horse-shoe. Provide a brief explanation.
b. If the divider at the top of the horse-shoe is removed, will water move to the right? Explain.
c. If a hole is drilled in the sidewall of the arc holding the soil, will water drip out? Explain.
7) Consider the following soils separated by a no flow barrier. The soils are resting in water at equilibrium.

a. Provide a qualitative sketch of the soil water content distribution (that is, θ vs. distance) above the water-table in the two soils. Explain the similarities or differences in the sketches for the two soils.
b. Suppose that a portion of the no flow barrier at 3 m above the water is carefully removed allowing contact between the two soils. Will water move from the clay to the sand? From the sand to the clay? Explain.
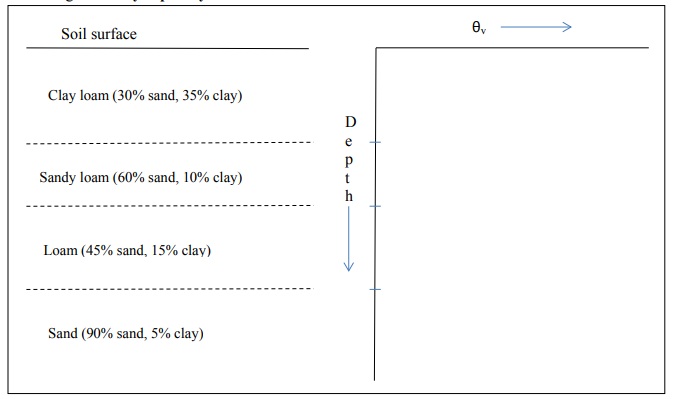
8) A freely draining field soil (soil profile shown below on left) has a uniform matric potential of -150cm several days after a rain-storm that had saturated the soil profile. Provide a qualitative diagram (no calculations needed) of the relative water content versus depth using the axes on the right. Briefly explain your rationale.
Equilibrium diagram problems- These examples cover the type problems that will appear on the exam but the actual exam problem may be altered.
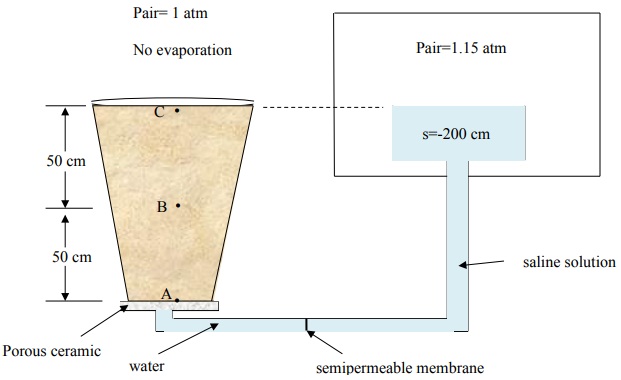
9) A sandy loam soil sample is placed on a saturated porous plate in contact with water as diagramed below. Determine the equilibrium matric potential or hydrostatic pressure (in your choice of unit systems) in the soil at point A. Would you expect this soil to be saturated? Why or why not.
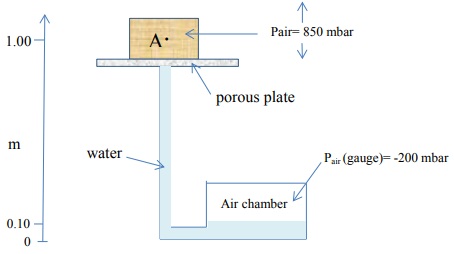
10) The following system is at equilibrium.
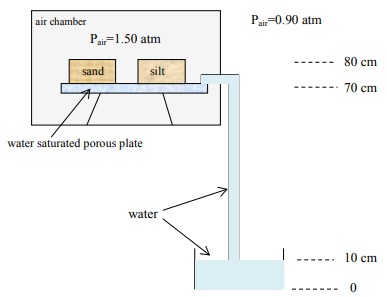
a. Find the matric potential (at the midpoint) in the sand and in the silt.
b. At equilibrium, how do you expect the water content to compare in the two soils (circle one):
θsand = θsilt
θsand < θsilt
θsand > θsilt
Explain your reasoning.
11) The following system is at equilibrium. Find the water pressure term (h or P) of the total soil water potential at point A and point B. You may express your response in either energy/volume or energy/weight of water
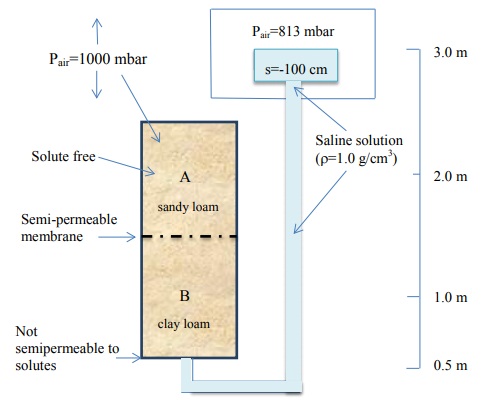
12) The following soil-water systems are at equilibrium (two separate problems). Find the requested information (indicated by the question mark) in each figure. You may express your response in either energy/weight or energy/volume of water.
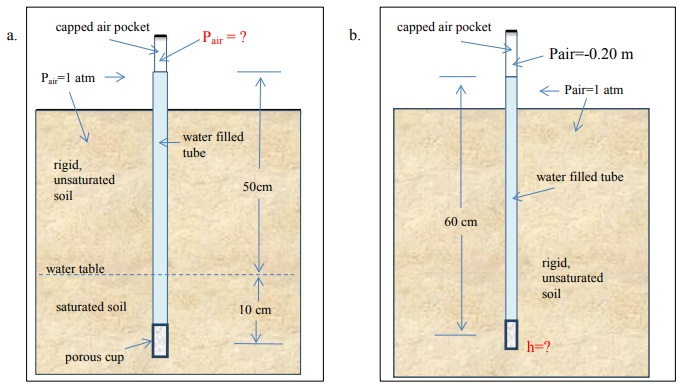
13) A soil sample is placed on a saturated porous plate and then subjected to a series of manipulations. Determine the equilibrium matric potential at the midpoint of the soil sample (in your choice of unit systems) at each step in the sequence.
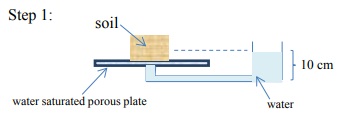
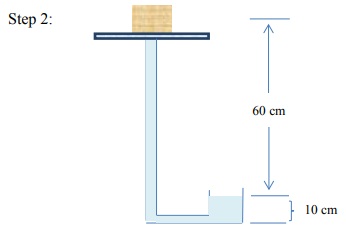
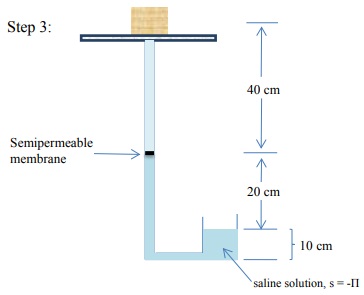
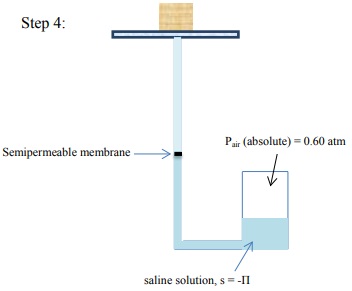
14) The following soil-water system is at equilibrium. Find all the components of the soil water potential head at locations A, B, and C.